Laying off 100,000 people! The European automobile industry suffers a severe blow, losing to China
![]() 12/09 2024
12/09 2024
![]() 469
469
For the European automobile industry, winter has arrived, and the chill has already affected many people. Recently, a wave of layoffs has swept through the European automobile industry, totaling approximately 100,000 layoffs.
Some believe that established European automakers have lost to emerging Chinese automakers. Is this really the case?

1. A total of about 100,000 layoffs
This year, the plight of the European automobile industry has become increasingly apparent. Especially towards the end of the year, the winter chill is particularly harsh for the European automobile industry.
According to incomplete statistics, more than 10 European multinational automotive giants have recently announced layoff plans.
Among automakers, Volkswagen has decided to close three factories in Germany and plans to lay off about 30,000 employees.
In response, the Volkswagen trade union strongly opposed and organized about 100,000 employees from nine factories to join the strike, leading to a complete suspension of Volkswagen's European production.
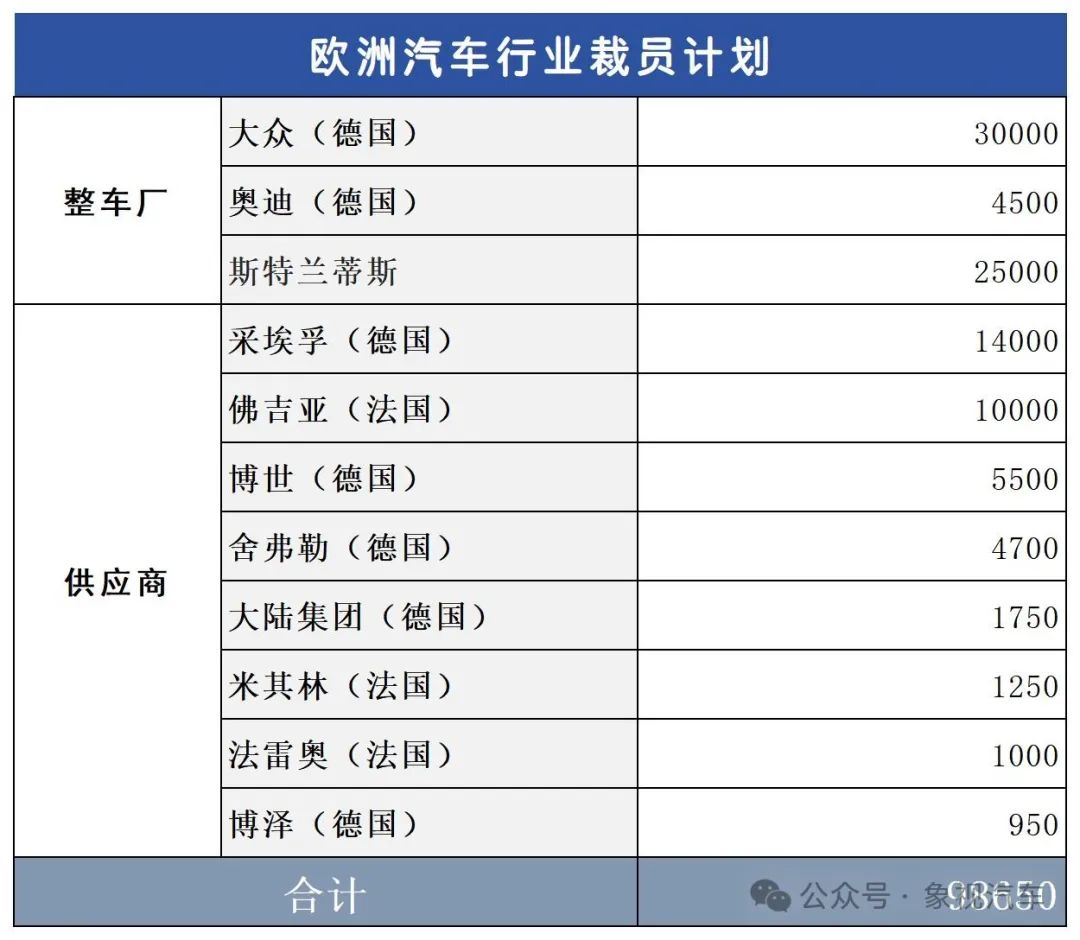
Additionally, Audi will lay off 4,500 indirect production positions, and Stellantis is also considering laying off up to 25,000 employees.
Furthermore, major European automotive component suppliers have also undergone significant layoffs: ZF will lay off 14,000 employees, Faurecia will lay off 10,000, and Bosch will lay off 5,500.
Other companies such as Schaeffler, Continental, Michelin, Valeo, and Brose will also lay off several thousand employees each.
The total number of layoffs mentioned above is close to 100,000, indicating that the European automobile industry is going through a difficult period.
2. The European automobile industry suffers a severe blow
Such a large-scale wave of layoffs is not just a reflection of individual corporate difficulties but a severe blow to the entire European automotive industry.
Behind the mass layoffs lies the enormous operational pressure on European automakers.
In the third quarter of this year, the main financial indicators of mainstream European automakers almost completely collapsed, with net profits of several leading automakers declining sharply.
Among them, Volkswagen's net profit in the third quarter was only 1.57 billion euros, a dramatic drop of 63.8% compared to the 4.34 billion euros in the same period last year; the operating profit margin fell from 6.2% to just 3.6%, the lowest level in over four years.

Stellantis Group reported a net revenue of 3.3 billion euros in the third quarter, a year-on-year decrease of 27%. Due to irreconcilable differences between CEO Carlos Tavares and the board, Tavares had to resign, leading to management turmoil.
German luxury carmakers BMW, Benz, and Audi have been hit particularly hard by declining profits.
In the third quarter of this year, Mercedes-Benz's net profit was 1.719 billion euros, a year-on-year decrease of 53.8%; BMW's net profit was 476 million euros, a year-on-year decrease of 83.8%; and Audi's operating profit was only 106 million euros, a year-on-year decrease of 91%.
These alarming figures expose the difficult situation of the European automobile industry.

3. Lost to Chinese automakers?
As everyone knows, Germany is the birthplace of the automobile. For more than a hundred years, automobiles have been a strong suit for Europeans.
However, with the advent of the new energy vehicle era, traditional fuel vehicles will eventually be phased out.
As vested interests in traditional fuel vehicles, European automakers and component suppliers have been slow to adopt electrification and intelligence, lagging far behind China and the United States in core technologies and market share.
In particular, Chinese brands like BYD, Huawei, and CATL have intensified competition in the European automotive industry through industry-leading technology and the low-cost advantage of mass production.

The wave of layoffs in the European automotive industry is a manifestation of the "growing pains" of the global automotive industry's transformation.
The dual pressures of electrification and intelligence force European automakers and component manufacturers to undergo structural adjustments, with layoffs being a direct means of reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
The transition from traditional fuel vehicles to new energy vehicles is an unstoppable trend. The global automotive industry is facing a major reshuffle. The European automotive industry is encountering new challenges.
Amidst significant changes in the automotive industry, many traditional production models, supply chains, and jobs are at risk of being eliminated. If European automakers and component suppliers do not respond appropriately, they risk being squeezed out.

The automotive industry is too important to Europe.
Data shows that the market size of the European automotive industry exceeds 1 trillion euros, accounting for about 7% of its overall GDP, far exceeding Japan's 3%.
Across Europe, approximately 13 million people are directly or indirectly employed in the automotive industry. Therefore, the automotive industry is one of the pillar industries of the European economy.
Nowadays, European automakers are being caught up by Chinese automakers and may even be significantly surpassed, signifying a significant change in the global automotive industry's competitive landscape.
The days of easy profits for the European automotive industry are gone, and Chinese automakers are ushering in their own era.