Hyundai Motor Strategy 2024: Insights for China's Auto Electrification, Intelligence, and Globalization
![]() 12/16 2024
12/16 2024
![]() 669
669
As mentioned in our previous article, "Defeated by Chinese Automakers - The Performance of Korean Brands (Hyundai and Kia) in 2023," Hyundai Motor Group ranked third globally in sales in 2023 and is projected to maintain its third-place position in 2024, trailing only Toyota and Volkswagen.
Hyundai Motor Group has excelled in both electrification and globalization.
In terms of electrification, the latest third-quarter data reveals that while pure electric vehicle sales accounted for 6% of total sales—lower than Volkswagen's 8%—when considering other new energy vehicles, Hyundai's electrified sales actually reached 20%.
Regarding overseas expansion, over 80% of Hyundai's sales are generated overseas, primarily in profitable developed markets in Europe and North America, which Chinese automakers can only envy.
Recently, Hyundai Motor unveiled its 2030 strategy in its 2024 investor report, aiming to achieve global sales of 5.55 million units by 2030 for the Hyundai and Genesis brands (which account for approximately 60% of Hyundai Motor Group's sales, with Kia accounting for the remaining 40%; Kia is excluded from the following content of this article).

This article organizes relevant information based on the report's content to share insights from Hyundai Motor's 2024 strategy for China's auto electrification, intelligence, and globalization, hoping to provide domestic automakers with information and inspiration on how to excel in electrification, intelligence, AI, and globalization.
Brief Content:
- Cooperative yet Differentiated Globalization Strategy: Adopting a win-win approach in different markets, building factories in various regions, and differentiating execution directions for different markets.
- Intelligent Strategy: Based on a standardized hardware platform + AI, where software defines the car, forming a closed data loop, applying AI, and standardizing autonomous driving vehicles on the platform to empower mobile travel.
- Diversified Energy-Driven Electrification Strategy: Integrating extended-range, gasoline, hybrid, pure electric, hydrogen, and other energy modes.
Cooperative yet Differentiated Globalization Strategy: Hyundai Motor has set three main directions for its strategic goals: leading and dominating the automotive industry. Firstly, it clarifies that the main business of Hyundai is still the automotive business. Therefore, in terms of the automotive business, Hyundai plans to collaborate with parts suppliers, platforms, and other automakers for joint development; adhering to deep cultivation and innovation in core manufacturing of the automotive business, such as factory innovation; facing automotive transformation, Hyundai explores the development of next-generation partners to ensure keeping up with or leading the transformation, as it is generally difficult for giants or traditional automakers to initiate innovation and transformation internally; since it is a global business, it mainly adheres to a unified global standard system and technology, otherwise, costs and management will be exceptionally difficult; strengthening supply chain management.
New Mobile Travel Businesses and Services: In terms of new energy, Hyundai Motor is laying out the hydrogen energy business, fuel cells, hydrogen energy production, and transportation, which is a way to diversify risks; transforming through alliances with digitalization and cloud services, as expenditures and technology on cloud infrastructure in the digital era are significant issues that cannot be ignored by automakers; a new mobile travel ecosystem, as cars are evolving into a third space and a multi-directional development tool for mobile travel, new travel ecosystem layout is a must; reinventing the customer journey, as the digitization and networking of life have changed the original offline customer journey, reinventing the customer journey is currently the core focus of the automotive market and sales service. Rethinking capital and finance, dealer partners, and vertically integrated ecosystems; globalization blueprint; cross-industry partners; and next-generation energy infrastructure. In general, how to integrate through innovative capital and financial methods to face change.

For the specific implementation and methods of the strategy:
- Upgrading and Expanding Dealerships: While direct online and offline sales were popular in China for a period, dealerships are crucial for foreign brands like Hyundai, so it is necessary to continue upgrading and expanding the dealership network. Similarly, for Chinese automakers going global, sharing profits with local dealerships is essential.
- Pricing and Subsidy Guidance: Unfortunately, this exceeds the scope of this article. Those with relevant knowledge are welcome to share their insights in the comments.
- New Financial and Accountability Models: Implementing innovative financial models to enhance accountability and transparency.
- Digitization of Customer Experience: Comprehensive digitization from car usage to purchase and after-sales, which Chinese brands have excelled at based on their internet experience.
- Localized Product Matrix and Design: Geopolitical changes are irreversible, and cultural and ideological factors will increasingly emphasize the localization of future products and designs.
- Innovation and Optimization of Marketing Advertisements: Particularly evident in China, where self-media platforms like Douyin and Xiaohongshu are currently the most effective, unlike airport and radio advertisements that may work abroad.
- Localized Production: Given the irreversibility of geopolitical changes, localization is a safe choice in all aspects.
- Launch of New Models: Introducing new models to meet diverse market demands.
- Inventory Optimization: Ensuring efficient inventory management to reduce costs and improve profitability.
- Strategic Partners: Collaborating with strategic partners to enhance capabilities and expand market reach.

In the market segment, Hyundai Motor divides the market into primary and growth markets based on different characteristics, with varying focuses in each market:
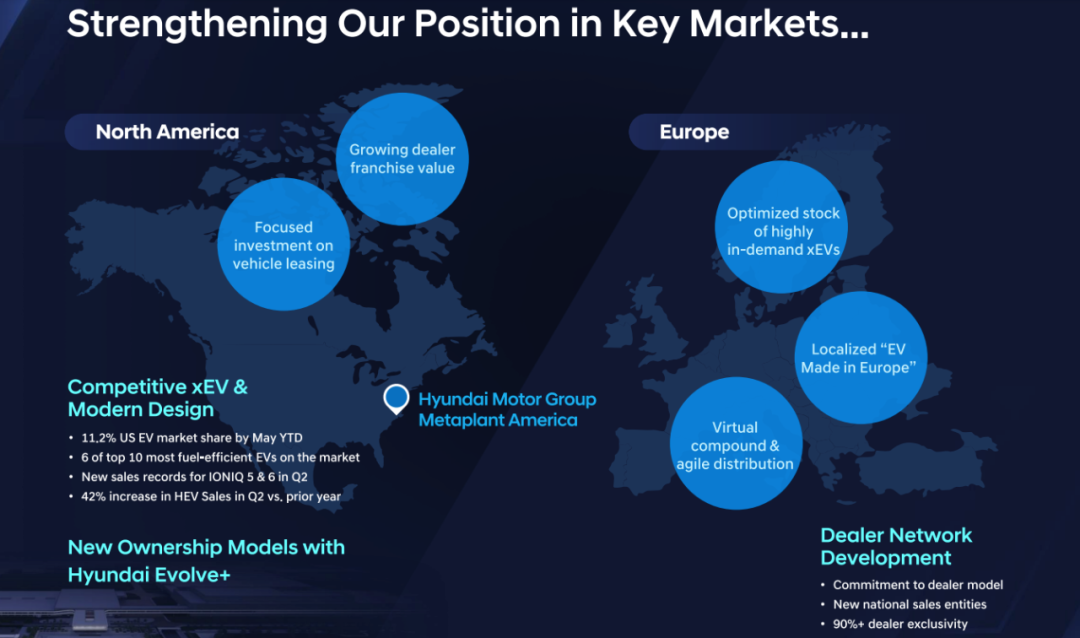
- Primary Markets: In North America, enhancing dealer franchise value and focusing on investments in vehicle leasing; in Europe, optimizing the inventory of high-demand new energy vehicles, manufacturing electric vehicles locally, and implementing virtual integration and agile launches.
- Growth Markets: In South America, focusing on a regionalized product matrix and customer management systems; in Asia, the Middle East, and the Pan-Pacific region, adopting a new Hyundai capital finance model, expanding vehicle insurance services, and building a talent pool in new regions. For example, in South America, unifying distribution and delivery, using a single dealer network to provide all model options, and building a harmonious IT system; in the Middle East, establishing a CKD parts assembly plant to produce vehicles like the Kona and IONIQ5 with an annual production capacity of 50,000 units; in Indonesia, establishing a 10GWh battery plant to ensure supply chain resilience, which can support the production of 150,000 electric vehicles annually; and seeking breakthroughs in the Japanese market.
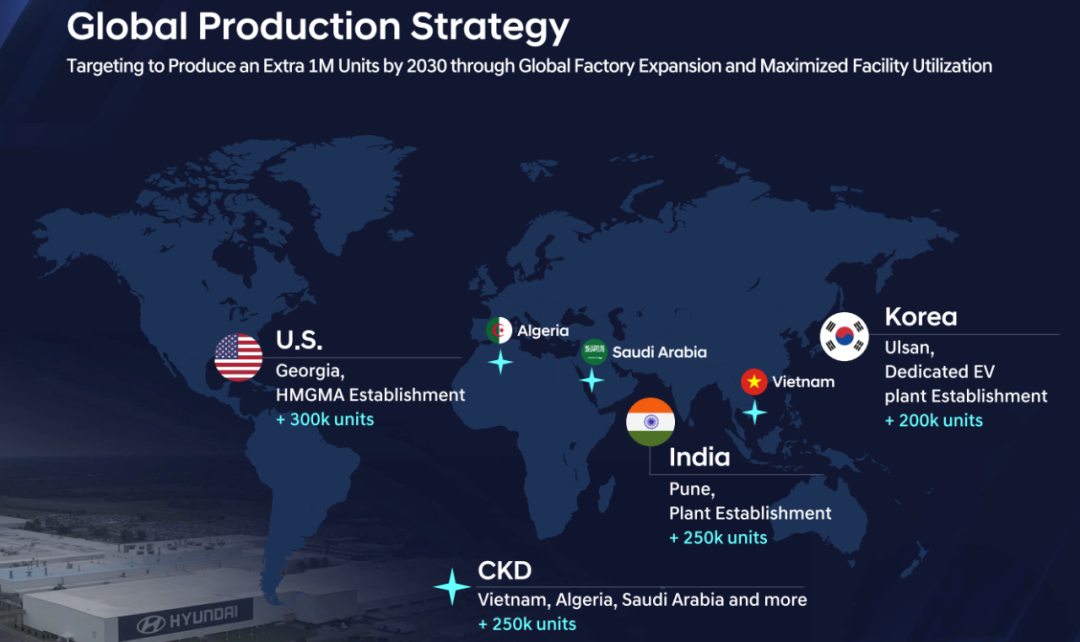
In terms of localized factories, Hyundai Motor is increasing its global factory plans by adding 300,000 units of production capacity in Georgia, USA, a dedicated electric vehicle factory with a capacity of 200,000 units in South Korea, a 250,000-unit capacity factory in Pune, India, and CKD factories with a total capacity of 250,000 units in Vietnam and Saudi Arabia.
Standardized Hardware Platform + AI Intelligence Strategy: The transformation of automobiles from traditional industrial products with four wheels and a seat to intelligent terminals with four wheels and a computer is a consensus in the automotive industry. Therefore, software-defined vehicles have become the current development direction for automobiles. Hyundai Motor's approach to software-defined vehicles (SDVs) is to use automotive hardware as the terminal, with services and data hosted in the cloud, forming a closed data loop between the terminal and the cloud. AI is used to mine data, thereby iterating software and services. The main applications include personalized intelligent connected autonomous driving for vehicles, third-space entertainment systems, and mobile travel services such as shared travel and fleet management systems, including L4 robotaxi, etc.
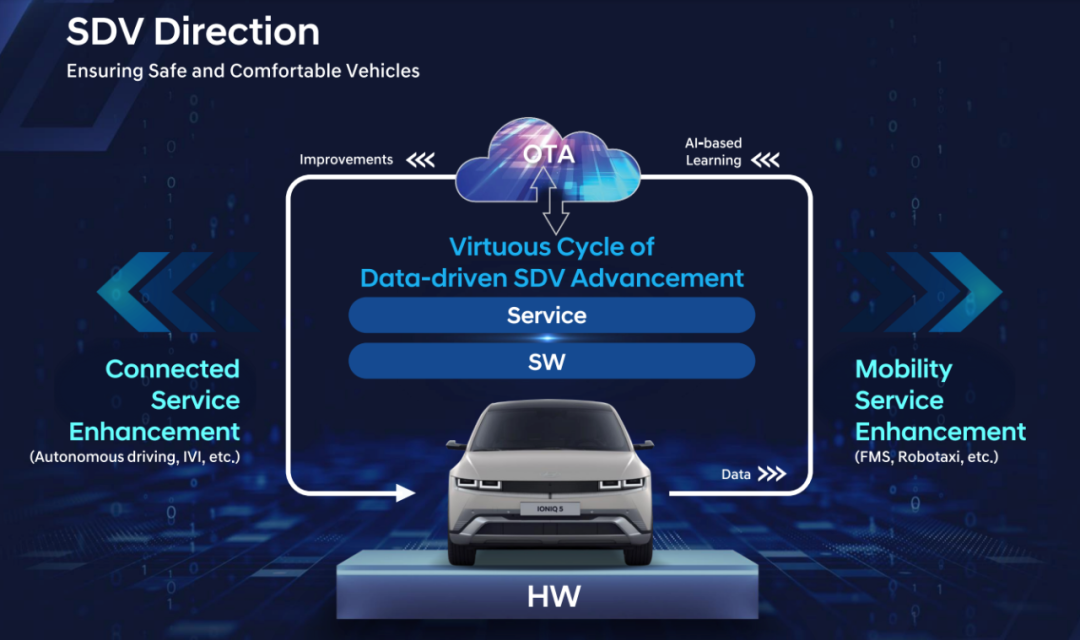
Hyundai Motor Group's autonomous driving technology division, 42dot Inc., serves as the leading department, absorbing the electronics, infotainment, and autonomous driving technology departments from the group's major research centers to drive the provision of connected and personalized services in the software-defined vehicle (SDV) era, such as cybersecurity, digital twins, autonomous driving, AI computing centers, vehicle data platforms, and supporting third-party app stores.

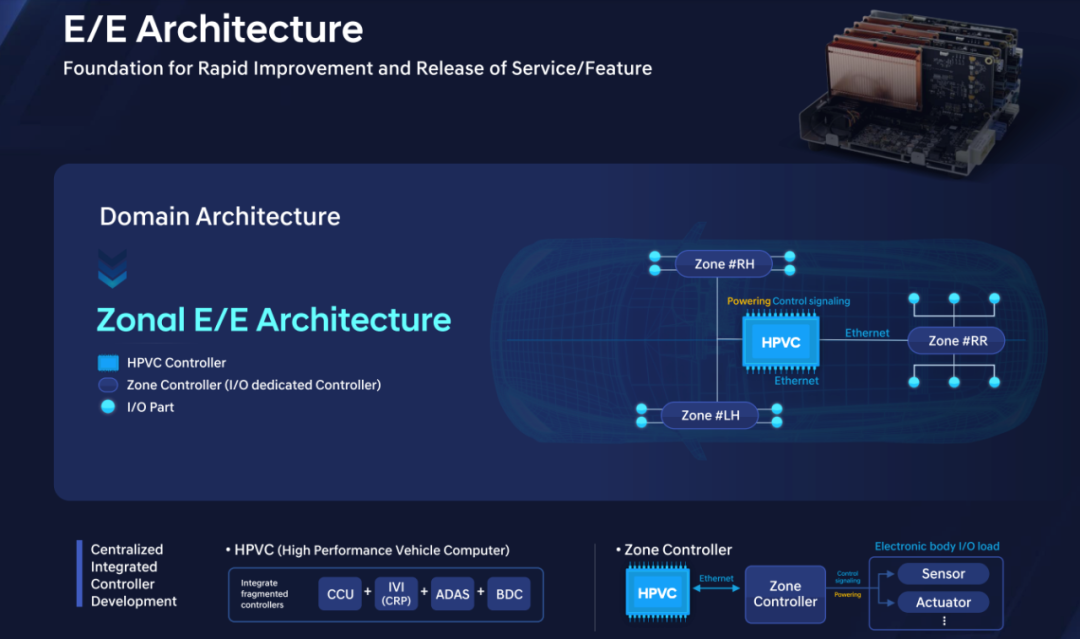
The foundation of software-defined vehicles is the electronic and electrical architecture. Hyundai Motor's electronic and electrical architecture is currently transitioning from domain to zonal. The terms 'domain' and 'zonal' may seem similar in English translation, but 'domain' can be understood as integrating more functions into larger functional modules, such as the ADAS domain or infotainment domain. In contrast, 'zonal' focuses more on the physical location within the vehicle. Therefore, we can see that Hyundai Motor's future zonal architecture will feature one zone controller on the left and right sides and at the rear, with a central integrated HPVC high-performance computing center. Electrical application terminals are responsible for sensing and execution, while zone controllers handle power supply and communication. Some functions are processed within the zone controllers, while others requiring shared resources and powerful computing power are transmitted and processed through Ethernet connections to the central computing center, such as visual AI.
The electronic and electrical architecture is the foundation of software-defined vehicles, providing the basis for rapid service and feature upgrades and releases.
Regarding interaction, Hyundai stated that it will adopt a next-generation UX/UI system. Although Chinese automakers, especially new forces, are already ahead in this area, they have largely become homogeneous. Hyundai will also adopt the Android system with UX/UI compatible with different screen sizes; an open ecosystem supporting the integration of Android OS and its ecosystem applications, AI assistants, and personalized services.

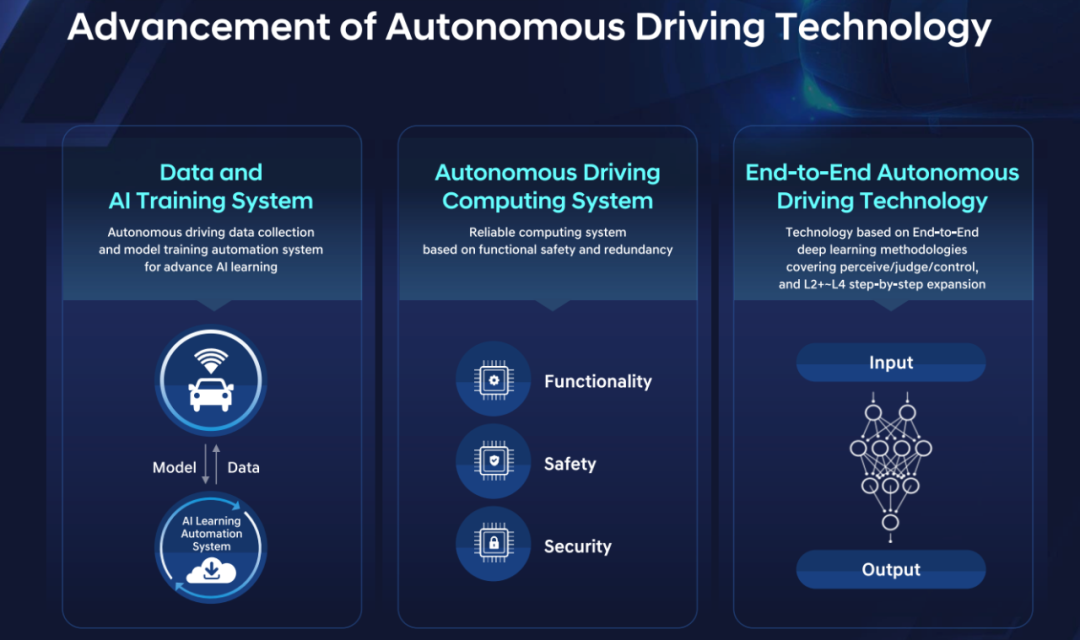
Regarding autonomous driving, Hyundai's autonomous driving system will be based on AI, utilizing end-to-end algorithms for perception, planning, and execution. In autonomous driving, the industry consensus is to gradually expand from L2+ to L4. Additionally, Hyundai emphasizes safety and redundancy in autonomous driving. The popularity of end-to-end technology in China has led General Motors to abandon its direct L4 Cruise project and integrate it into its autonomous driving division, as discussed in our previous article, "Insights into the Landing Route of Intelligent Driving from Volkswagen and Ford's Withdrawal from L4 Autonomous Driving Argo AI." Since then, there has been a consensus among automakers to gradually expand from L2+ to L4, supporting their driving assistance business while maintaining an L4 evolution path.
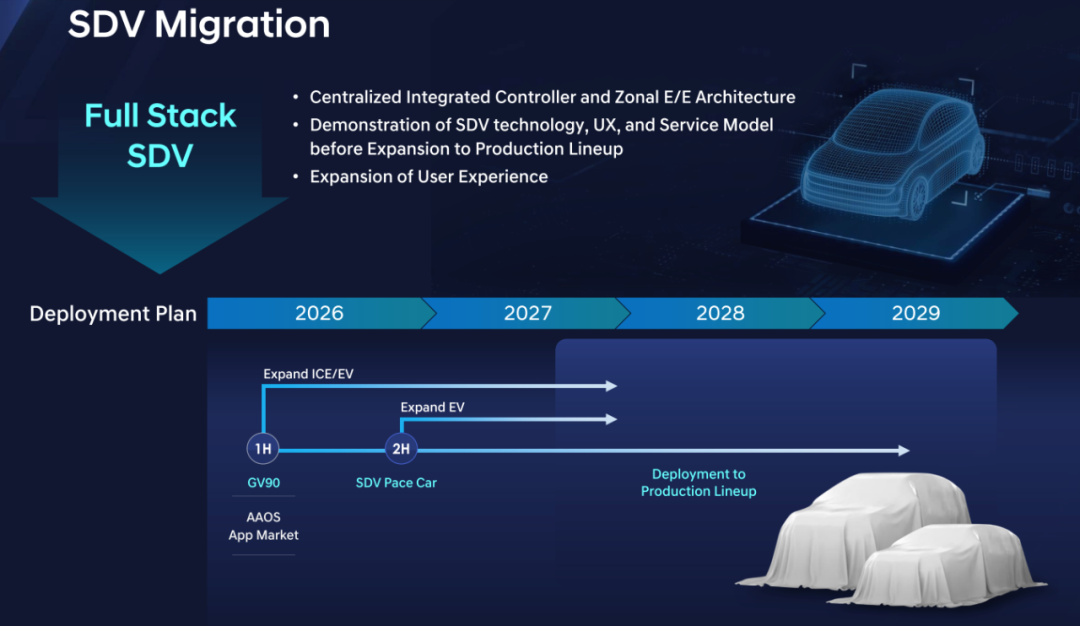
Regarding Hyundai Motor's software-defined vehicle expansion plan, Hyundai will deploy it on its premium Genesis GV90 model in the first half of 2026, utilizing the Android Automotive OS (AAOS) app store. In the second half of 2026, it will begin expanding to its electric vehicle lineup through SDV Pace Car. Ultimately, by the end of 2027, it will expand to all Hyundai Motor models.
In terms of autonomous driving business strategy, Hyundai Motor envisions utilizing the hardware and manufacturing advantages of the Hyundai Group to provide autonomous vehicles globally. Autonomous driving capabilities will be acquired through mergers and acquisitions, such as acquiring autonomous driving technology solution companies and Robotaxi service companies.
Platformization of Autonomous Vehicles: Standardizing the electronic and electrical architecture, redundancy solutions, safety and functional safety, software, and vehicle interfaces.
Commercialization of Autonomous Vehicles: With autonomous vehicles based on the Hyundai platform, Hyundai plans to flexibly provide vehicles to different Robotaxi operators for profit.
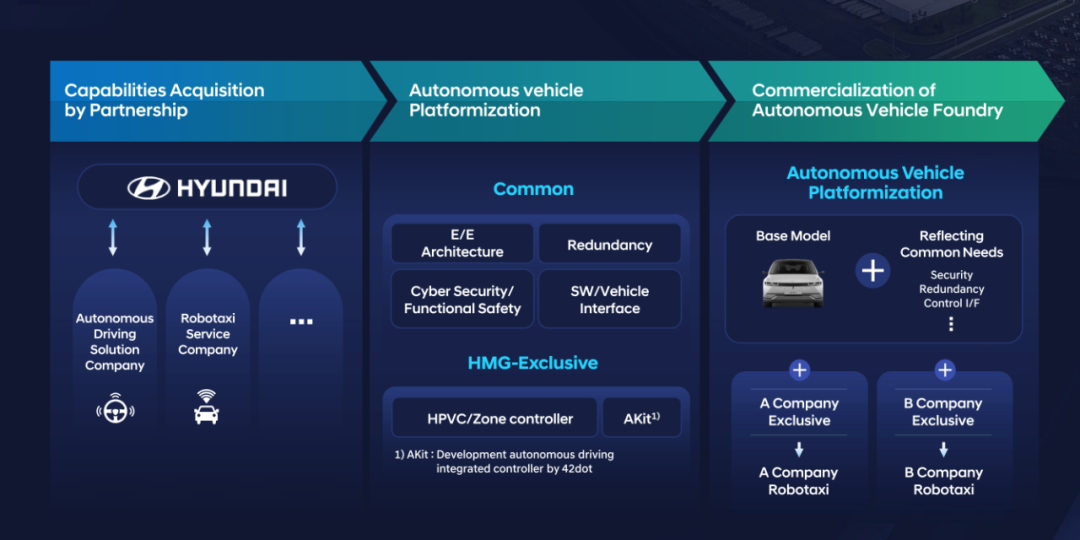
Automated Driving Expansion Strategy: Hyundai Motor's strategic focus on automated driving encompasses a comprehensive approach, from technology development to commercialization, aiming to position itself as a leader in the autonomous vehicle space.
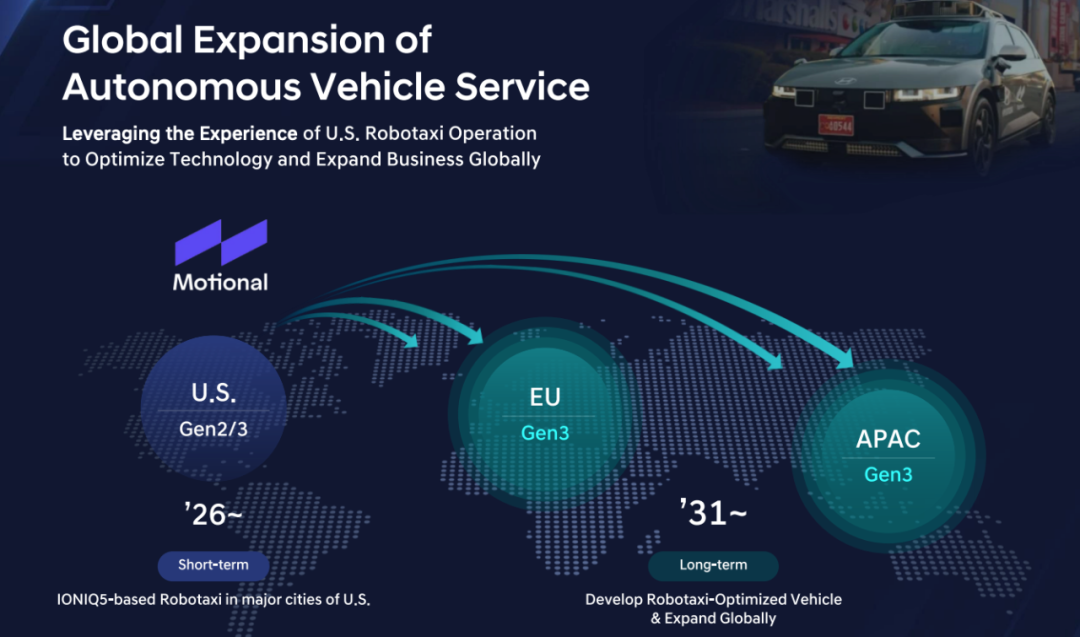
Leveraging the development and operations of Robotaxi in the United States, Hyundai aims to optimize its technology and expand its global business. Readers familiar with our previous article, "Exploring Autonomous Driving Road Tests in California, USA: Fierce Competition, Diligent Exploration, and Technological Challenges," will recall that Hyundai relies on Motional for its autonomous driving research and development operations in North America. Hyundai plans to deploy its second and third generations of autonomous driving technology in major US cities for Robotaxi operations around 2026, with aspirations to extend its third-generation technology to Europe and the Asia-Pacific region for application and operation by 2031.
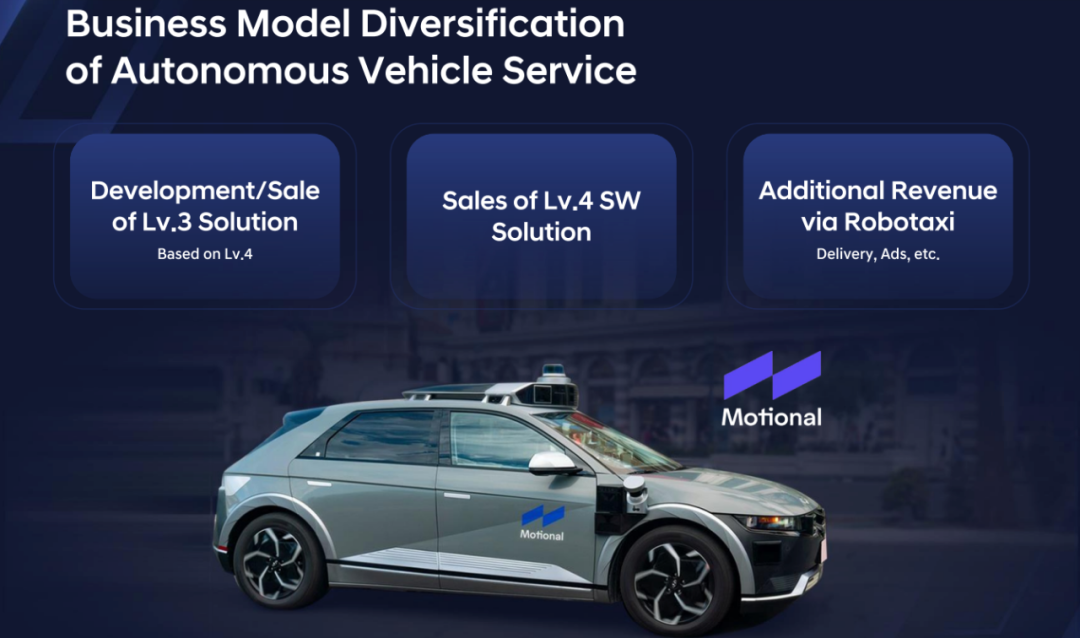
Diversification of Autonomous Driving Services
Hyundai is developing L4 technology and scaling L3, L4 software to generate additional profits from L4 Robotaxi services, such as through deliveries and advertising.
Diversified Energy-Driven Electrification Strategy
For any global company, placing heavy bets on a single electrification approach carries significant risks due to uneven global development and geopolitical factors. Diversification is therefore imperative.
Currently, Hyundai offers gasoline, hybrid, and electric vehicle models. In the future, it will introduce extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs) to form a diversified electrification strategy.
Hyundai's adopted EREV technology differs from traditional systems, which typically utilize a range extender (engine + generator) alongside two drive motors, one for each axle. Hyundai's innovative EREV integrates an engine and a drive motor, with the drive motor used for power generation or front-wheel drive, while another drive motor handles rear-wheel drive. This integration saves space, weight, and cost, representing a significant improvement and optimization.

The success of EREVs in the Chinese market underscores their benefits. New players adopting EREV technology have become highly profitable, avoided bankruptcy, and ranked among the top 10 new energy vehicle manufacturers. The key reasons for their success include long driving range, elimination of range anxiety, fast response, intelligence support, and lower costs compared to pure electric vehicles.

Hyundai plans to launch its EREVs in the US and China around 2026: in North America, for large SUVs with annual sales exceeding 80,000 units; and in China, for mid-to-large vehicles with annual sales expected to surpass 30,000 units, focusing on the US and Chinese markets.

Battery technology remains crucial due to its high value in the electrification process. Hyundai employs differentiated battery technologies tailored to its diverse range of powertrain options:
- Gasoline vehicles utilize 12V and 48V batteries. - Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles use 270V and 360V batteries. - Pure electric vehicles employ 400V and 800V batteries, available in prismatic and pouch cell formats. - Fuel cell vehicles, such as hydrogen-powered ones, use fuel cell stacks combined with batteries. - Commercial vehicles adopt 800V systems.

For consumers, automotive batteries are primarily judged by energy density, price, and safety. To maintain competitiveness in electrification, Hyundai focuses on and optimizes these three aspects:
- Continuously increasing energy density through three material approaches: low-cost lithium iron phosphate (LFP), cost-effective nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM) with balanced performance, and high-performance NCM. All three aim to significantly boost energy density post-2025. - Developing an entry-level NCM battery that substantially reduces nickel usage and increases manganese usage in high-demand batteries (70-100 kWh) to lower material costs and ensure cost competitiveness. - Adopting the Cell-to-Vehicle (CTV) integration architecture, which differs from CTC/CTB by mounting battery modules directly onto the vehicle structure. Hyundai claims this can reduce cost and weight by 10% and improve heat transfer efficiency by 45%.
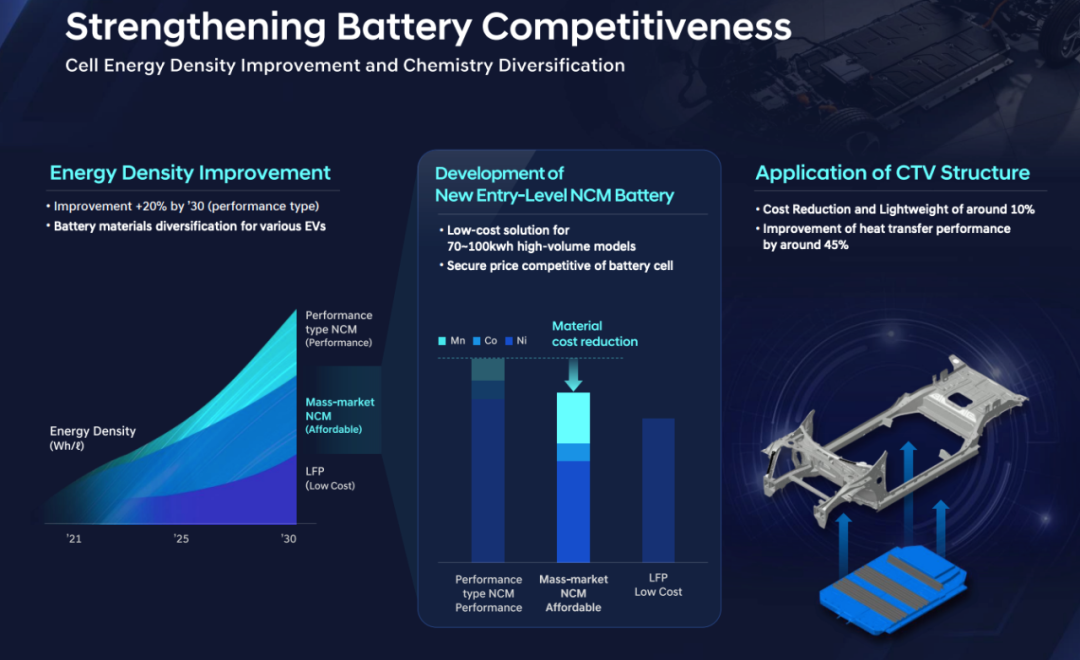
Battery Safety:
- Proactive battery management system for real-time cloud-based monitoring and diagnosis during parking and charging to ensure safety. - System safety design includes safety vents for thermal runaway, fire-resistant materials to control thermal conduction, thermal conduction impedance structures, and high-voltage relays to prevent thermal propagation in case of battery issues.

Beyond batteries, Hyundai has a comprehensive hydrogen energy strategy, encompassing production, transportation, refueling, and end-use across the entire supply chain.

Currently, in addition to Hyundai, global automakers like Toyota and BMW maintain an interest in hydrogen energy. China is also promoting this industry, though a turning point has yet to materialize.
Final Thoughts: Although China appears to be leading in electrification and intelligent application, European, American, Japanese, and Korean automakers have not given up. Electrification and intelligence are irreversible trends in the automotive industry, with Hyundai aiming to achieve annual global EV sales of 40% by 2030. The automotive industry is a marathon, and as discussed in my previous article, "Reflections on China's Auto Exports to Southeast Asia, Specifically Indonesia," China's automotive industry must remain humble, learning from the history and success of motorcycle exports. Additionally, Japan and Korea serve as exemplary models for China to learn from in terms of auto exports, both in terms of history and sales volume. Therefore, the electrification, intelligence, and globalization strategies outlined in Hyundai's 2024 strategy are worth studying and emulating. Feel free to leave comments for further discussion if you have deeper insights or thoughts.
*Reproduction and excerpting are strictly prohibited without permission - Reference Materials:
Hyundai Motor Company 2024 Investor Presentation - Hyundai Motor Company
Hyundai Motor Company Q3 2024 Financial Report - Hyundai Motor Company