Tesla's Q1 2025 Global Market: Navigating Sales Divergence with Strategic Resilience
![]() 04/24 2025
04/24 2025
![]() 581
581
In the first quarter of 2025, Tesla's global market performance exhibited notable regional disparities. Vehicle deliveries declined by 13% year-on-year to 336,700 units, and automotive revenue dropped by 20%. Conversely, revenues from energy, storage, and services segments witnessed substantial growth.
Global Sales: Heightened Structural Divergence
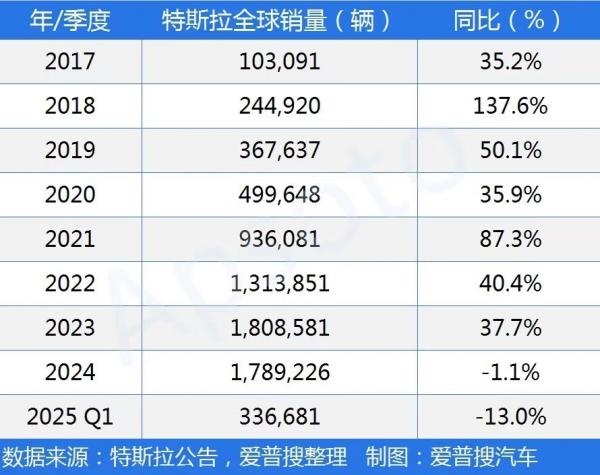
Overall Sales Under Pressure, China Factory Dominates with 51% Share
Global deliveries decreased by 13% year-on-year, from 386,800 units in Q1 2024 to 336,700 units in Q1 2025. This decline was primarily attributed to production line transitions for the Model Y, coupled with waning demand in European and American markets. Tesla's China factory accounted for 51.3% of global deliveries, achieving wholesale sales of 172,700 units despite a 21.8% year-on-year decline. Notably, the Shanghai Gigafactory surpassed 21,000 units delivered in a single week in March, marking a new high since 2022.
European and American Markets Experience Significant Slowdown
In the US, deliveries fell by 13% year-on-year, influenced by aging product lines (Model 3/Y comprising 96% of sales) and consumer backlash against Musk's political comments. Despite this, the overall US auto market witnessed a "buying frenzy" fueled by tariff expectations, leading to a 4.8% year-on-year sales increase in Q1. Europe, specifically Germany and the Netherlands, saw sales plummet by over 50%, with the energy crisis and brand image doubts exacerbating demand contraction.
Table 1: Tesla's Global Sales
Automotive Business Contracts, Energy/Services Rise as New Growth Engines
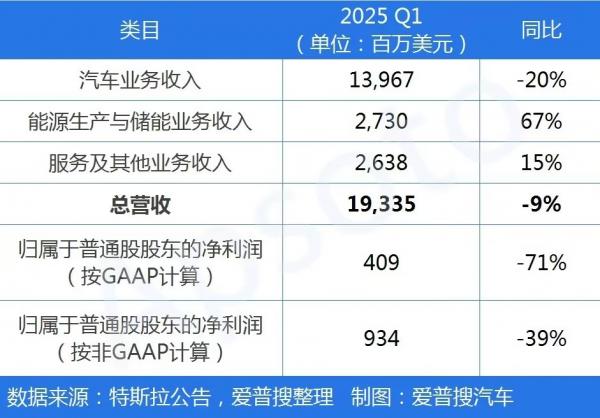
Revenue and Profit Decline, Automotive Business Faces Pressure
Revenue structure shifted, with total revenue decreasing by 9% year-on-year to $19.335 billion. Automotive revenue specifically dropped by 20% to $13.967 billion, accompanied by a gross margin reduction from 17.4% to 16.3%. GAAP net profit plummeted by 71% year-on-year to $409 million, primarily due to production line transitions and promotional price cuts.
Energy and Service Businesses Thrive
The storage business experienced explosive growth, with energy revenue increasing by 67% year-on-year to $2.73 billion. Energy storage installed capacity surged by 154%, and Powerwall deployments exceeded 1 GWh in a single quarter for the first time. The service network expanded, with the number of Superchargers rising by 17% year-on-year. Non-Tesla users' charging proportion increased to 26%, and service revenue grew by 15% to $2.638 billion.
Table 2: Tesla's Q1 2025 Financial Performance
Five-Year Interest-Free Policy: A Double-Edged Sword for the Chinese Market
Short-Term Sales Boost
Tesla China's five-year interest-free loan policy (e.g., Model 3 monthly payments as low as RMB 2,594) is expected to stimulate demand and propel subsequent sales growth. The refreshed Model Y, with completed production line transitions and rapid capacity ramp-up, supports enhanced delivery efficiency.
Long-Term Risks Surface
Profit margins face pressure as subsidy policies may erode per-vehicle profits, with the automotive business gross margin declining by 1.1 percentage points year-on-year in Q1 2025. Competition intensifies as local brands like NIO and XPeng follow suit with subsidies, risking market trust exhaustion through a "no interest-free, no participation" cycle.
Global Production Layout: Localized Strategy to Mitigate Risks
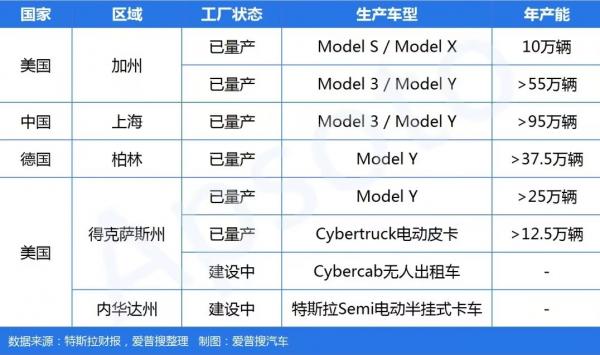
Capacity Distribution and Efficiency
China Dominates: The Shanghai factory boasts an annual capacity exceeding 950,000 units, accounting for 40% of Tesla's global total capacity, with 72% of Q1 deliveries originating from this facility.
US Diversification: The Texas factory has increased Cybertruck production capacity to 125,000 units, and a Semi truck production line is under construction in Nevada, though new models contribute minimally at present.
Geopolitical Responses
Tesla mitigates tariff risks through localized supply chains (e.g., the Shanghai Megapack factory's 40 GWh energy storage capacity). The European Berlin factory plans to expand into the Middle East to circumvent trade barriers.
Table 3: Tesla's Global Production Base Layout
Reasons for Sales Decline: Intertwined Multi-Dimensional Challenges
Internal Factors
Single Product Line: Model 3/Y accounted for 96% of deliveries, with new models like the Cybertruck experiencing slow commercialization, failing to effectively redirect demand.
Production Line Switching Costs: The Model Y refresh led to simultaneous shutdowns of four factories worldwide for several weeks, resulting in a capacity loss of approximately 80,000 units.
External Shocks
Trade Policy Uncertainty: Anticipated tariff adjustments in the US deter consumer decision-making, while European markets grow increasingly resistant to "politicized brands."
Intensifying Market Competition: Rivals such as BYD have launched new models, eroding Tesla's share of the global new energy vehicle market by 2.3 percentage points in Q1 2025.
Future Development: Technology Investment and Ecosystem Closure
Autonomous Driving and Robotaxi
FSD (Full Self-Driving) launched in China, enabling unmanned operations from production lines to logistics. Robotaxi pilot programs are set to commence mid-year. The Texas Cybercab factory is expected to commence mass production in 2026, targeting the shared mobility market.
Energy Storage and AI Synergy
Megapack capacity expands to 40 GWh, and AI computing demand elevates energy storage to a crucial role in grid stability, potentially contributing over 30% of revenue in the long term.
Short-Term Pain and Long-Term Game
Tesla's Q1 2025 performance underscores the dilemmas faced by global automakers: supply chain resilience, policy sensitivity, and product iteration challenges. Despite short-term pressures on the automotive business, the rapid growth of energy and service businesses, robust cash reserves (reaching $37 billion), and sustained technology investment pave the way for Tesla's transformation. Moving forward, Tesla must balance short-term profitability with long-term competitiveness in the "price war" and "technology war," fortifying its position in a volatile market.







