【In-depth Analysis of WRC 2025】Unveiling the Six Most Compelling Robot Investment Themes and Promising Ventures
![]() 08/14 2025
08/14 2025
![]() 672
672
Stepping into the north gate of the Yichuang International Convention and Exhibition Center, you're immediately engulfed by the hum of awe from the crowd—some capturing the swift arm movement of a boxing humanoid robot on their phones, while others are mesmerized by the precise dexterity of a robotic arm grasping scattered parts, unable to tear their eyes away.

This year's World Robot Conference (WRC) feels more like a 'delivery capability' exam. Over 500 companies worldwide brought industrial, service, special, and humanoid robots to the stage, unveiling over 100 new products, including 50 OEMs vying in the 'humanoid' race.
An investor whispered on the scene, 'Last year's buzzword was 'showing off skills,' this year it's 'getting the job done.' First Frontier Capital's prediction is even more forthright—global shipments of humanoid robots will surpass 10,000 units this year, with five or six manufacturers exceeding 1,000 units each.
As a leading consulting firm deeply rooted in Silicon Valley, we've not only identified the six most noteworthy robot investment themes for investors but also selected the most representative listed companies and high-potential Silicon Valley startups under each theme.
Next, let's follow the pulse of the exhibition and the steering wheel of global capital to see which names are transitioning from demo tables to production lines and which Silicon Valley startups are poised at the cusp of the next growth wave.

Six Themes of Robot Investment
Behind 'delivery' lies a vast and intricate industrial chain. Any robot capable of 'doing the job' cannot function without the synergy of its 'brain, nerves, joints, muscles, and eyes.' For secondary market investors, understanding these six themes is crucial to pinpoint core targets across different links.
Theme 1: Embodied AI and Software Platforms
Hardware sets the lower limit of a robot's capabilities, while AI software determines its upper limit. This distinction underscores the gap between 'getting the job done' and 'doing it intelligently,' and it's where future value growth will accelerate the most.
As large models transition from language (LLM) to behavior (LBM), robots can truly comprehend the physical world and execute complex tasks, forming a formidable moat for all OEMs.
Market Representatives:
NVIDIA: The undisputed ruler of underlying computing power. It not only provides GPUs but also offers 'operating system'-level support through the Project GR00T humanoid robot base model and Isaac Sim simulation platform, aiming to replicate its AI ecosystem advantage.
Microsoft: Deeply involved in enabling robots with large models through strategic investments in OpenAI. Its Azure cloud platform also provides massive computing power for model training to numerous robot companies.
High-potential Silicon Valley Startups:
Figure AI: The hottest star on the market. Its Figure 01 robot integrates OpenAI's large model and has secured investments from giants like Microsoft, NVIDIA, and Amazon founder Jeff Bezos, embodying the synergy of 'top AI' and 'top hardware'. 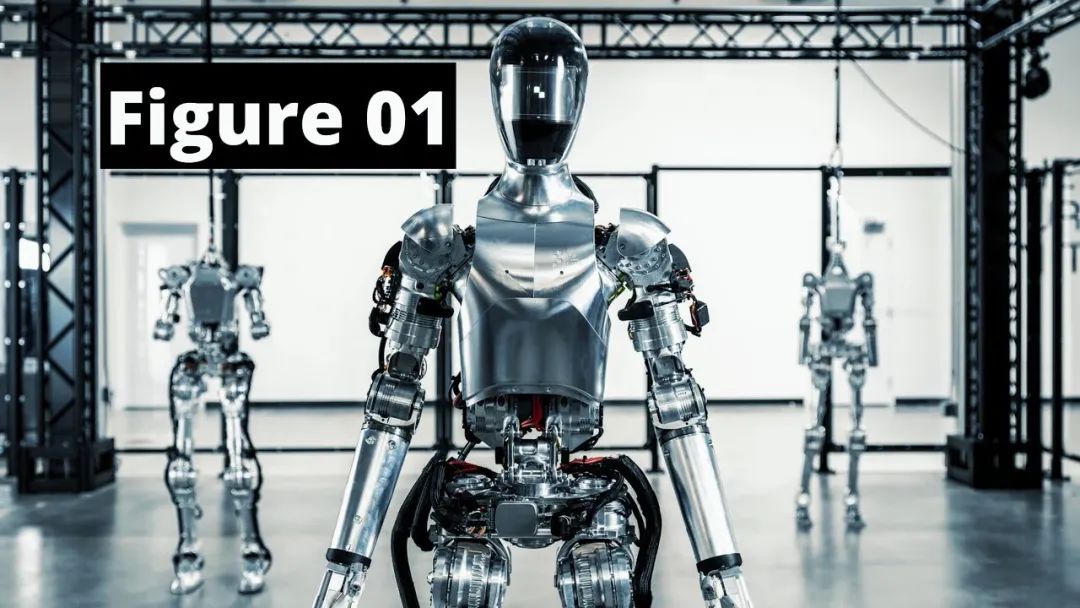
Sanctuary AI: Specializes in the general AI robot Phoenix™, equipped with its proprietary Carbon™ AI control system. Emphasizing 'thinking, learning, and acting like humans,' it's a strong contender in another 'full-stack self-developed' technology route.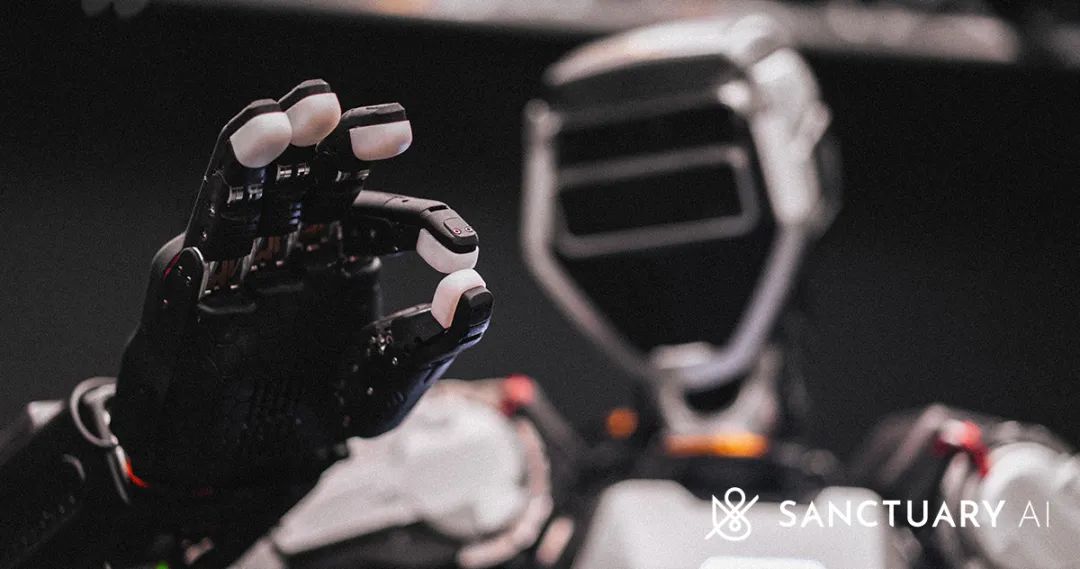 
Theme 2: Performance and Cost of Core Hardware
Every fluid and powerful robot movement is underpinned by the precise support of 'joints' (reducers), 'muscles' (servo systems), and 'touch' (force sensors).
Performance and cost in this domain directly dictate the speed and scale of robot commercialization. For cost-effective humanoid robots, 'cost reduction and efficiency enhancement' is the core proposition, presenting immense opportunities for local supply chains.
Market Representatives:
Reducers: Leadshine Technology, Double Transmission. As one of the highest cost-share hardware components in robots, the localization of harmonic reducers and RV reducers is the market's focal point.
Servo Systems: Inovance. A leader in industrial automation, with deep expertise in core components like robot servo systems and controllers, serving as the backbone of the domestic supply chain.
Sensors: Keli Sensor. Torque sensors endow robots with the ability to perform delicate operations, crucial for safe human-robot interaction. Market demand is surging as robot intelligence levels increase.
Theme 3: Multimodal Perception Systems
To operate in unstructured home, factory, and outdoor environments, robots must possess perception capabilities beyond traditional 2D cameras. Multimodal perception, integrating 3D vision (depth cameras), LiDAR, force sensing, and auditory sensing, is a rigid demand for robots to 'see' and 'understand' the complex world.
Market Representatives:
Orbbec: One of the few companies globally that master core 3D vision perception technology. Its depth camera products are widely used in various service robots and consumer electronics.
KEYENCE: The absolute leader in the global industrial vision and sensor field. Its high-precision, high-stability products are the 'standard eyes' for robots in high-end manufacturing.
High-potential Silicon Valley Startups:
Strella Biotechnology: An exemplary 'perception application.' The company uses its sensing technology to monitor fruit ripeness, helping distributors reduce food spoilage. This showcases advanced perception technology's ability to create significant commercial value in specific vertical industries. 
Theme 4: Intelligent Upgrade of Industrial Robots
Don't overlook industrial robots. With the largest installed base and most mature applications, the industrial robot market is being profoundly reshaped by AI and collaborative robots (Cobots). The industry is shifting from 'machines' replacing simple, repetitive labor to 'intelligent partners' working alongside engineers and workers to handle complex tasks.
Market Representatives:
FANUC, ABB: Representatives of the 'Big Four' traditional industrial robots, they're actively embracing AI and launching smarter, easier-to-use product lines to consolidate their market positions.
Universal Robots: The pioneer and leader in global collaborative robots (parent company is Teradyne). Known for its safe and easy-to-program products, it's opening up new application scenarios.
High-potential Silicon Valley Startups:
Covariant.AI: Founded by a student of 'AI godfather' Yann LeCun, it provides a universal 'brain' for various industrial robots, enabling them to handle constantly changing items and tasks in warehouses. A typical representation of 'software-defined hardware.' 
Theme 5: Logistics and Special Application Scenarios
Before humanoid robots achieve generalization, wheeled, bipedal, or quadrupedal robots for specific scenarios are the fastest track to commercialization. Especially in fields like e-commerce warehousing, automated factories, security inspections, and post-disaster rescue, with clear demand and measurable value, they serve as excellent testing grounds for verifying technology and business models.
Market Representatives/Mature Companies:
Boston Dynamics: Its Spot quadrupedal robot dog has become a benchmark for special applications. After being acquired by Hyundai Motor, it's accelerating commercial deployment in industrial inspections, public safety, and other fields.
Geek+: A unicorn in the global warehouse logistics AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) market. Through solutions like 'goods-to-person,' it has achieved large-scale deployment in thousands of warehouses globally.
High-potential Silicon Valley Startups:
Agility Robotics: The star bipedal robot Digit has 'secured' a contract with Amazon for pilot work in warehouses. A crucial step for humanoid robots to move from laboratories to real commercial scenarios, its commercial progress warrants close attention.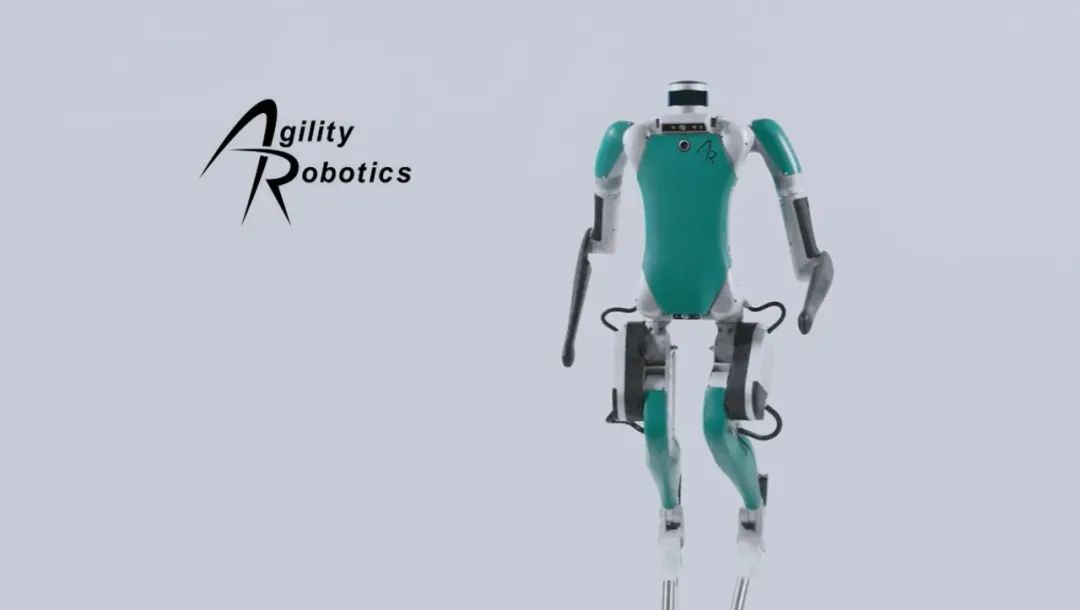 
Theme 6: Humanoid Robot OEM Competition
This is the 'star-studded' realm of technology and the ultimate narrative in the capital market. The smooth movements and task capabilities demonstrated by major manufacturers at WRC are underpinned by a comprehensive competition encompassing capital, technology, and supply chains. At this stage, the investment core is to identify who can lead in specific scenarios, turning unit economics positive and achieving the transition from 'burning money' to 'generating revenue'.
Market Representatives:
Tesla: Leveraging its AI, vision algorithms, and supply chain advantages, its Optimus robot is considered one of the players with the greatest potential. Every technological iteration stirs up market nerves.
High-potential Silicon Valley Startups:
Apptronik: A team emerged from NASA's 'Apollo Program.' Its humanoid robot Apollo is designed to work alongside humans in factories and warehouses, with a clear commercialization goal. 
1X Technologies: Another Norwegian company invested in by OpenAI. Its wheeled robot EVE has been deployed on a large scale, and it's advancing the commercialization of its humanoid robot NEO, adopting a pragmatic 'wheeled to legged' approach.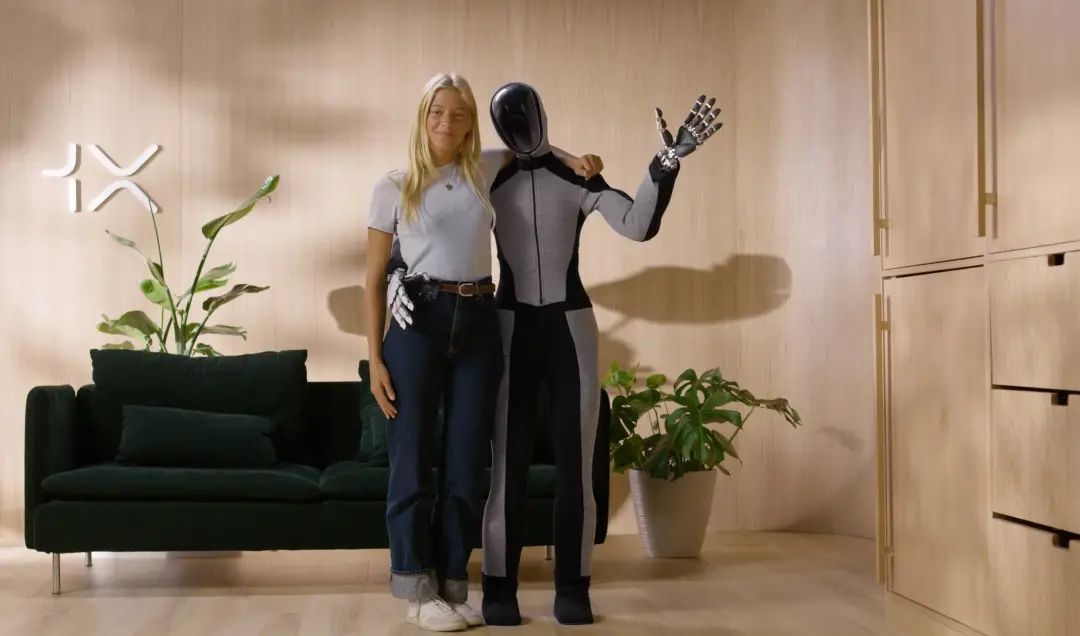 

This expansive industrial ecosystem map clearly outlines where opportunities lie but also poses more complex questions:
Among dozens of reducer companies, how do we ascertain which technology truly has long-term competitiveness?
When all humanoid robots claim to be driven by large models, how do we assess their genuine level of 'intelligence'?
Behind the dazzling demonstrations of a Silicon Valley startup, what are the real challenges of its supply chain and cost control?