Google, Meta, and Microsoft Release Latest Financial Reports, Highlighting AI Internal Cycle as a New Growth Engine
![]() 08/14 2025
08/14 2025
![]() 625
625
Preface: As Microsoft's market capitalization briefly surpassed $4 trillion, Meta's share price surged 12% in a single quarter, and Google Cloud's business growth hit a new high, the global tech industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by AI. Beyond mere numbers, the AI concept has shifted from being a "money-burning black hole" to a "profit engine," with the emergence of a new growth logic centered around the "AI internal cycle," reshaping the industry landscape.
Author | Fang Wensan
Image Source | Network
Financial Reports Shine: AI Drives Revenue and Profit Growth
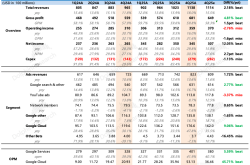
The three tech giants continue to break new ground in revenue. Alphabet, Google's parent company, leads with $96.43 billion in revenue, marking a 14% year-on-year increase, the highest growth rate in nearly three quarters.
Microsoft's revenue reached $76.44 billion, a 18% year-on-year increase, setting a new record for the fastest growth rate since 2024.
Meta's performance was particularly eye-catching, with revenue of $47.52 billion, a 22% year-on-year increase, setting a new high for the past four quarters.
Profit growth was even more impressive. Google's net profit stood at $28.19 billion, a 19% year-on-year increase, while Microsoft's net profit was $27.23 billion, a 24% year-on-year increase.
Meta's net profit surged 36% year-on-year to $18.34 billion, with an operating profit margin climbing to 43%.
Amidst a backdrop of slowing global economic growth, such performance can be described as "countercyclical growth."
The advertising business remains the cornerstone for Meta and Google. Meta's advertising revenue amounted to $46.56 billion, accounting for 98% of total revenue, with a 21% year-on-year increase.
Within this, the average unit price of advertisements increased by 9%, and impressions grew by 11%, underpinned by the robust empowerment of AI.
CEO Mark Zuckerberg candidly stated that AI-driven advertising recommendation models have enhanced Instagram's conversion rate by 5% and Facebook's by 3%.
Google's advertising business also benefited from AI optimization, with search advertising revenue reaching $54.2 billion (+12%) and YouTube advertising $9.8 billion (+13%).
New features such as AI Overviews and AI Mode have driven over 100 million monthly users in the US and India, significantly boosting advertisement click-through and conversion rates.
Cloud services have emerged as a new growth engine. Microsoft's Intelligent Cloud business revenue was $29.88 billion, a 26% year-on-year increase, with Azure cloud services growing at a rate of 39%, the highest since the end of 2022.
More notably, Microsoft's annualized revenue from AI-related businesses has reached $13 billion, a 175% year-on-year surge.
Google Cloud's revenue was $13.6 billion, a 32% year-on-year increase, with a backlog of orders reaching $106 billion and a significant increase in the proportion of large AI contracts.
To support the expansion of AI businesses, the capital expenditures of the three giants have soared simultaneously.
Microsoft's capital expenditures in the second quarter were $24.2 billion, a 27% year-on-year increase, with plans to invest $80 billion in AI smart computing centers throughout the year, and expected capital expenditures exceeding $30 billion in the next quarter.
Google increased its full-year capital expenditures from $75 billion to $85 billion, with second-quarter capital expenditures of $22.4 billion, a 70% year-on-year surge.
Meta raised its capital expenditure range to $66-72 billion, planning to invest hundreds of billions of dollars in the future to build ultra-large-scale data centers, with capital expenditures expected to exceed $100 billion in 2026.
These investments are not blind expansions. Microsoft Azure is already experiencing capacity constraints due to high demand for AI services and is accelerating the expansion of data centers and power supply.
Google Cloud's backlog of $100 billion in orders urgently requires computing power support.
Meta has stated that "infrastructure and talent are top priorities," selling non-core assets worth $2 billion for AI computing power.
AI Internal Cycle: Underlying Reconstruction of Growth Logic
In the traditional Internet era, the growth logic of tech giants revolved around a cycle of "capital expenditure attracting users - selling advertising to retail - reinvesting to expand user scale."
However, a more efficient "AI internal cycle" is now taking shape: AI applications drive growth in advertising and cloud revenue, and capital expenditures feed back into computing power infrastructure, further supporting the implementation of more AI applications, forming a positive feedback mechanism.
① Closed loop of AI applications → advertising revenue → computing power investment: Meta's AI advertising tools have attracted nearly 2 million advertisers, directly driving daily active users to 3.48 billion, with Facebook and Instagram user engagement increasing by 5% and 6%, respectively.
The growth in advertising revenue, in turn, supports investment in AI infrastructure, forming a virtuous cycle of "improved advertising effectiveness - revenue growth - increased computing power."
Google optimizes its core search business through AI. The Gemini large model has 450 million monthly active users, with the number of tokens processed each month in June doubling from 480 trillion in May to 980 trillion, a 100-fold increase from the same period last year.
The AIMaxinSearch tool significantly improves ad conversion rates, revitalizing the search advertising "cash cow" business.
② Symbiotic relationship between cloud services and AI models: The explosion of Microsoft Azure confirms the deep integration of cloud and AI.
Enterprise customers do not need to build AI infrastructure from scratch and can securely use GPT series models through the Azure platform via API calls, greatly reducing the threshold for AI application.
Currently, Microsoft's Copilot series products have 100 million monthly active users, and the popularity of M365Copilot has also increased the revenue per user for Office commercial cloud products, forming a cycle of "model services - cloud resource consumption - revenue growth."
Google Cloud rents out its self-developed TPU chip resources to companies like OpenAI, both reducing customer dependence on a single supplier and expanding infrastructure utilization.
This "computing power rental + model service" model allows Google Cloud to quickly capture market share in the AI era.
③ Flywheel effect of user data and technological iteration: User scale and data accumulation are the key fuels for the AI internal cycle.
Meta has 3.48 billion daily active users, generating massive amounts of content related to social relationships and interests every day, providing high-quality training data for AI advertising models.
The more users, the richer the data, and the higher the accuracy of AI recommendations; more precise content and advertisements can attract more users, forming a flywheel of "user growth - data accumulation - model optimization."
Google also benefits from its data advantage. Its products such as search, maps, and email cover billions of users worldwide, with over 2 billion monthly active users for AI overview tools, and user interaction data continuously feeding back into model iteration, enhancing the practicality and user stickiness of AI functions.
Computing Power Competition: The 'Core Battlefield' of the AI Era
The operation of the AI internal cycle cannot be separated from the support of computing power infrastructure. Currently, the competition for computing power among tech giants has entered a white-hot stage, and this competition concerns not only the current market share but also determines the industry's discourse power for the next decade.
The combined capital expenditures of the three companies are expected to reach $260 billion in 2025, an increase of about 45% from 2024.
These investments mainly flow into three areas: AI server procurement, ultra-large-scale data center construction, and network equipment upgrades.
Microsoft allocates 70% of its capital expenditures to AI servers and data centers, with Azure already supporting liquid cooling technology across all regions.
Of Google's $85 billion budget, 60% is invested in TPU chips and supercomputing clusters.
Meta focuses on deploying GPU clusters, planning to increase AI training computing power by an order of magnitude by 2026.
In terms of chip architecture, the giants have taken differentiated paths. Microsoft cooperates deeply with NVIDIA to customize Azure Maia AI chips.
Google adheres to the self-developed TPU route, with the TPUv5e chip supporting the low-latency response of AI Mode.
Meta adopts a "GPU + TPU hybrid architecture" to reduce dependence on a single supplier.
Cooling and energy technologies have also become a focus of competition. Liquid cooling has become standard for AI data centers, with Microsoft Azure's single cabinet power reaching megawatt levels, utilizing high-voltage direct current transmission technology to reduce energy loss.
Google's data centers control power usage effectiveness (PUE) below 1.1 through advanced cooling systems, far below the industry average.
China-US Differences: Divergence in AI Commercialization Paths
While US giants achieve explosive profit growth through the AI internal cycle, the development paths of the AI markets in China and the US exhibit significant differences. These differences stem not from technological gaps but rather from differences in business environments and market demands.
The US market drives rapid AI monetization through "high willingness to pay + complete ecosystem."
Enterprise customers have a strong willingness to pay for AI tools, with Microsoft Copilot being popular among 90% of the Fortune 100 companies globally.
C-end users are also willing to pay for high-quality AI services, with monthly pricing for AI education products reaching $200 and AI companion app paid rates exceeding 40%.
This paying capacity supports the prosperity of AI applications, thereby driving the growth of giants' advertising and cloud businesses.
The Chinese market, on the other hand, prioritizes "scenario landing." AI is more empowering the real economy, such as optimizing the efficiency of takeout delivery algorithms, enhancing user stickiness through short video recommendations, and promoting the upgrading of the automotive industry through intelligent driving.
However, the size of the 2B enterprise services market is only one-tenth that of the US, and enterprises' willingness to pay is relatively low, leading to a longer AI commercialization cycle.
As insiders point out, Chinese AI applications need to "return to the physical world to earn real money," seeking breakthroughs in areas such as hardware and supply chains.
As Microsoft, Meta, and Google use their financial reports to prove that AI has transformed from a cost center to a profit center, the value hierarchy of the tech industry is being restructured.
Computing power infrastructure has become the new "oil drilling rights," AI models have become the "oil refining technology," and application scenarios are the "finished oil market."
In this restructuring, upstream enterprises such as liquid cooling technology suppliers, high-voltage direct current transmission equipment providers, and optical module manufacturers have already enjoyed the dividends of AI infrastructure.
Companies that possess unique data scenarios will receive premiums, such as AI applications in vertical fields like healthcare and industry.
Latecomers like independent AI companies need to rely on giant cloud platforms to survive, with models like OpenAI relying on Microsoft Azure and Anthropic relying on Google Cloud becoming the norm.
While US giants form a growth closed loop through the "AI internal cycle," Chinese enterprises may need to explore paths suitable for the local market.
This is not about simply replicating the US model but finding the value anchors of AI in real-economy scenarios such as manufacturing upgrades and smart cities.
Conclusion:
The formation of the "AI internal cycle" marks a complete transformation in the growth logic of the tech industry.
Instead of relying on the expansion of a single business, sustained growth is achieved through the positive feedback of "applications - revenue - infrastructure - technology."
In this transformation, giants with a large user base, data assets, and computing power reserves will continue to lead, and industry chain links such as computing power infrastructure, AI chips, and cloud services will also benefit simultaneously.
Reference Materials:
Global Trend: 'Microsoft Breaks $4 Trillion, Meta Surges 12%, and the Key Behind It Is Users and Data'
An Independent House: 'It's Officially Erupted'
ETF Evolution Theory: '$4 Trillion! This Race is Exploding'
Fang Wei's Decade View: 'Google, Microsoft, and Meta's Financial Reports are One More Explosive Than the Other. Why Can We Only Compete in Takeout Delivery in the Short Term?'
Sci-Tech Innovation Board Daily: 'The US Tech 'Big Three' Have Made a Fortune This Time!'
Silk Research Institute: 'After Reading Google and Meta's Latest Financial Reports, I Finally Understand Why They Are Going All In on AI'