GPT-5 Unveils Mixed Reviews: User Interaction with AI Still Trapped in the Past
![]() 08/21 2025
08/21 2025
![]() 478
478

Since its official launch on August 8th, GPT-5 has garnered a mixed bag of reviews, with complaints piling up.
Prior to its release, GPT-5 was touted as an AI product boasting doctoral-level intelligence.
The official team exuded confidence, swiftly discarding previous models and proclaiming that GPT-5 would "surpass all."
However, within days, negative user experiences forced them to hastily reinstate the old model.
Technically speaking, GPT-5's advantages are evident from testing and benchmarking.
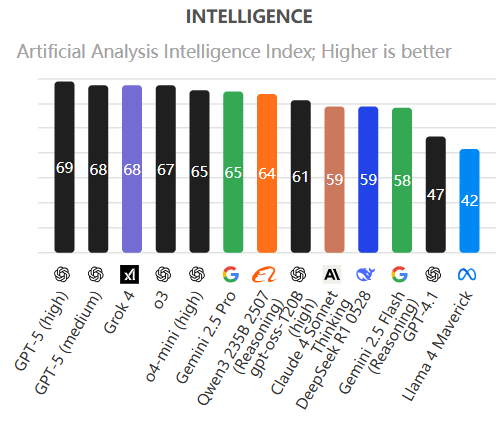
Moreover, official evaluations underscore GPT-5's superior prowess in mathematics, real-world coding, multimodal understanding, and healthcare.
Many reviewers describe the current GPT-5 as a pure "science and engineering student."
In scientific and technological domains, its performance is quite impressive, excelling at solving mathematical problems and writing complex code.
While GPT-5's intelligence ceiling has risen, it exhibits extreme "instability,"
sometimes even making errors on basic questions.
Furthermore, when tackling tasks involving human emotions, such as writing emails and reading comprehension, where it previously shone, it behaves like a robot.
No significant improvement in creativity has been observed, leading to widespread skepticism about GPT-5's practicality.
However, what users find most unacceptable is that its "emotional intelligence" has fallen short of expectations.
It is no longer the chatty online companion it once was but has transformed into a professional work and study assistant.
With heightened intelligence but diminished emotional intelligence, GPT-5 has actually become less user-friendly.
Consequently, within 72 hours of its release, OpenAI received a deluge of unsubscribe requests.
01
Overlooked Prompt Guide
In fact, the day before GPT-5's release, OpenAI published a GPT-5 prompt guide.
This guide offers usage tips that users might overlook and addresses external doubts by explaining some of its operating mechanisms.
More crucially, it elucidates an important fact:
It's not that GPT-5 has become less useful, but rather that users' interaction methods with AI are still entrenched in the past.
Do you recall the importance of prompt engineering we discussed earlier?
Many are accustomed to using AI products like GPT-5 as search engines or "tool persons," but GPT-5 has evolved into a "digital mind" capable of autonomous planning and deep thinking.
Thus, outdated communication methods naturally fail, and it's time for a "forced update."
First, let's examine GPT-5's changes.
According to the guide, its core evolution spans four aspects:
1. Agentic Task Performance:
It's no longer the "question-and-answer" human-machine interface.
Current GPT-5 resembles a project manager.
It can grasp more intricate goals, autonomously plan steps to achieve them, select suitable tools, and persist until the task is complete.
2. Coding
Previously, we published an article assessing the code-writing capabilities of domestic large AI models.
If previous AI models were akin to programmers, GPT-5 can be regarded as a full-stack engineer.
It can manage the refactoring of large codebases, fix complex bugs, and even build a fully functional application from scratch.
3. Raw Intelligence
Compared to older models, GPT-5 boasts stronger logical reasoning, common sense understanding, and creativity.
Of course, considering GPT-5's wave of negative reviews, this aspect still bears a question mark.
4. Steerability
This is the core focus.
GPT-5 is highly sensitive to subtle differences in instructions.
Therefore, users can precisely control its behavior, tone, and output style, akin to using scientific research instruments.
Additionally, the official team recommends a new tool called Responses API.
On May 21st of this year, OpenAI announced the expansion of Responses API to support remote connection to MCP servers, image generation, and other functions, aiding developers in creating smarter agent applications.
This tool's application is akin to giving GPT-5 an extra "short-term memory chip."
Previously, interacting with AI often necessitated repeating context backgrounds, thereby wasting numerous tokens and increasing costs.
Now, simply by passing a "previous_response_id," you can prompt AI to recall previous thinking processes and reasoning chains.
Official data reveals that GPT-5's score on the Tau-Bench test (retail scenario) has surged from 73.9% to 78.2%.
In simpler terms, it offers superior performance, lower latency, and cost savings.
For all complex, multi-step tasks, the Responses API will likely become indispensable.
02
Taming AI Agents
Evolving from a chatbot to an agent, GPT-5's double-edged sword effect has become more pronounced.
When utilized well, it attains doctoral-level intelligence; when used poorly, it reverts to "artificial stupidity."
OpenAI defines this double-edged sword effect as agentic eagerness.
Thus, the primary challenge users face when using GPT-5 is how to become an adept "trainer."
The guide provides the following application scenarios:
1. Pursuing Efficiency and Simplicity: How to "Hold the Reins"

Applicable Scenario: Clear tasks requiring prompt answers without unnecessary elaboration from AI.
When using various AI products, we've all encountered instances where we desire a simple, comprehensible answer from AI, but AI takes its time and presents a lengthy response we neither want nor need to read.
OpenAI offers two solutions:
The first is to reduce reasoning_effort.
This is an API parameter users can set to low or medium.
It's akin to telling an employee, "Don't overthink it; just follow the process and give me the results swiftly."
The second is to implement "traffic lights" in the prompt.
First, clarify the goal and method, informing AI that "speed" is paramount;
Second, set early stopping criteria, such as "stop searching as soon as you find XX," to interrupt its complex thinking process;
Third, set a tool invocation budget, specifying that AI "can only invoke online searches twice at most;"
Finally, provide an "escape hatch" by adding a sentence like "even if the answer may not be completely correct," to prevent AI from overthinking and exploring in pursuit of 100% accuracy.
After reading this section, I feel like OpenAI has once again "forcefully refreshed" my worldview on AI.
Previously, when using AI, I might add a sentence at the prompt's end saying, "Just tell me XX, don't add extra content."
But beyond modifying API parameters, I never considered speeding up AI by limiting search times or even not requiring absolutely accurate answers.
2. Encouraging Autonomy and Exploration: How to "Let Go and Take a Chance"

Applicable Scenario: Complex tasks with vague goals requiring in-depth research and autonomous decision-making by AI
Another common scenario when using AI is when we only have an initial goal or general direction and need AI to provide a comprehensive set of ideas and frameworks, but AI only offers a "half-baked" solution.
Corresponding to the previous point, OpenAI also presents two methods:
The first is to increase reasoning_effort.
That is, set the API parameter to high, informing the employee, "You have full authorization to use all resources to thoroughly examine the problem."
The second is to infuse a "sense of belief" into the prompt.

The content in this guide section might seem abstract when translated directly, but the core idea is straightforward:
Clearly instruct AI on what to do when encountering difficulties instead of halting to seek user assistance.
3. Making Good Use of Tool-led Prompts: Let AI "Report Work"
When tackling complex tasks with heavy workloads, to avoid AI becoming a "black box" that merely works blindly, you can require AI to report regularly.
The operation is simple; just append reporting style and frequency requirements to the prompt.

Users can then view a structured report akin to a table (i.e., in JSON format), encompassing AI's thinking summary, the current task being executed, and the next step's plan.
In complex agents, this monitoring and control process, akin to a print() function, is paramount.
03
Full-process Optimization from Planning to Execution
Beyond systematic explanations, this guide also shares "valuable experience" from frontline customers.
We'll illustrate with some application scenarios:
1. Making AI the "Architect"
Applicable Scenario: Building a new application from scratch
Currently, AI products aim for "low barriers to entry."
Users from diverse backgrounds frequently utilize AI, but most cannot simultaneously possess expertise in multiple domains.
Hence, it's common to have product managers without programmers.
The guide suggests using the "self-reflection" prompt method.
Instead of immediately asking AI to write code, first guide it to think.

This approach aligns with engineering thinking, essentially allowing AI to conduct requirements analysis and architecture design first.
Users then need to assess whether the AI-generated solution aligns with their expectations and make fine-tunings or modifications accordingly.
Although it might seem cumbersome to first produce a high-quality design document and then strictly implement it, based on actual usage, the quality and structure of the final code have significantly improved.
2. Giving AI a "Programmer Training Manual"
Applicable Scenario: Adding features or refactoring existing projects
This feature is also frequently used.
In real-world work, not only programmers' code but also many projects require repeated modifications and improvements.
When necessary, they may even need to be "deleted and rewritten."
However, work handovers entail risks, as new and old programmers may have differing coding styles, and new and old employees may have different working methods.
Therefore, providing AI with a set of specific and detailed rules can ensure the AI-generated content seamlessly integrates into the project, averting style conflicts and low-level errors.

However, as evident from the image, this technique has a certain technical threshold.
Writing such prompts might require technical guidance from experienced "veteran employees."
3. Some Additional Practical Experience
Some users have found that GPT-5 can sometimes be verbose in conversations, while other times its content is overly concise.
It seems contradictory, doesn't it?
The solution is surprisingly simple: set the global API parameter verbosity to low to make it less talkative.
Then, clearly state in the prompt: "Please provide detailed and readable comments" to prevent it from omitting key information.
Another notable change is that mandatory prompts that were effective for GPT-4, such as "Please be sure to thoroughly and comprehensively analyze the context," may backfire with GPT-5.
GPT-5 naturally enjoys thinking and exploring, and excessive emphasis may cause it to overcomplicate simple tasks.
To avoid wasting time and resources, prompts need to be softer and more guiding.
04
General Control Techniques
The following techniques apply to all types of tasks.
1. New Controllers: verbosity and reasoning_effort
We've mentioned these terms before, and they are crucial yet somewhat confusing:
Reasoning Effort (reasoning_effort): Determines how deeply and thoroughly AI thinks.
Verbosity: Determines how lengthy and detailed AI's final answer is.
2. GPT-5's "Achilles' Heel": Instruction Conflict
Compared to previous models, GPT-5 exhibits a new trait: meticulousness.
As a rigorous and reliable AI assistant, it strictly adheres to every instruction input by users.
This poses an issue: poorly-constructed prompts can easily "trigger critical hits" on it.
For average users, they seldom scrutinize their prompts for issues after writing them.
However, problems arise when prompts inadvertently contain contradictory or ambiguous instructions.
GPT-5 won't arbitrarily select one to execute like older models; instead, it will attempt to reconcile these contradictions.
This process entails significant resource consumption (time and tokens).
The ultimate outcome might well be degraded performance, logical confusion, or even task failure.
OpenAI provides an example in the context of a medical assistant:
Instruction A: Never schedule an appointment without explicit consent from the patient.
Instruction B: Automatically assign the earliest available time slot of the day for high-risk cases to reduce risk.
From our perspective, Instruction B might have higher priority; but for GPT-5, this is a deadlock with no clear resolution.
OpenAI presents three solutions to address this issue:
Firstly, review the prompts to identify any logical inconsistencies.
Secondly, establish a clear hierarchy of instructions, highlighting the precedence of various rules in specific contexts.
Thirdly, utilize official tools; the prompt optimizer mentioned in the guide can assist in automatically detecting such issues.
The first two solutions necessitate user involvement, which contradicts the desire for "automation".
The third solution, however, would remain unknown to users unless they consult this guide or receive external guidance.
05
Advanced Enhancement Strategies
Finally, the guide divulges some "unique insights".
1. Turbo Mode: Minimized Inference
Designed exclusively for low-latency scenarios, this mode maximizes the model's speed while maintaining its inferential capabilities. However, it compromises on planning abilities. Therefore, the quality of prompts becomes paramount, requiring users to proactively instruct GPT-5 to plan the task from the outset. Users' instructions must also be unambiguous and free from contradictions.
Additionally, users should reinforce "persistent reminders", repeatedly instructing the AI to "complete the entire task" or specifying other detailed requirements.
2. Metaprompting
An unconventional yet effective way to interact with GPT-5 is to have it teach users how to craft better prompts. When initial prompts yield unsatisfactory results, instead of struggling to refine them, users can send them back to GPT-5:

Using its own strength against itself. Alternatively, tools like PromptPilot or other large models can facilitate this prompt optimization process, as mentioned earlier.
06
Final Reflections
After delving into this often-overlooked official guide, I gained a deeper understanding of some of the negative feedback surrounding GPT-5. Its significant changes from previous models make it challenging for most AI users to adapt swiftly.
Without this "official sneak peek" from OpenAI, many experienced AI users may find themselves at a loss. This experience highlights how our understanding of AI, much like humanity's grasp of the universe, is often flawed.

It underscores that our intuitions can be misleading. We assume that providing detailed instructions will yield better results, but this can lead GPT-5, with its tendency to overthink, down a path of inefficiency and confusion. There are numerous "switches" we cannot see, such as dedicated buttons (reasoning_effort and verbosity) that control the depth of AI's thinking and the length of its responses within the web version of GPT-5.
Our greatest adversary is our own "assumptions". We presume that clear instructions are sufficient for AI to complete tasks, unaware that we might inadvertently set numerous logical traps.
This guide, to a certain extent, unveils the underlying logic of collaborating with advanced AI. With the advent of GPT-5, major vendors will inevitably introduce newer, more intelligent models.
When confronted with such a "new species" far surpassing past capabilities, the primary obstacle is not the upper limit of AI's intelligence but the constraints of our own cognition and interaction habits.
Hence, the mindset of "human and tool" may need to evolve into a "human and mind" collaboration paradigm. This wave of negative feedback towards GPT-5 is merely a preview of countless cognitive shifts to come.