Why Are Big Companies Racing to Develop AI Agents?
![]() 09/17 2025
09/17 2025
![]() 655
655
As we edge closer to the latter half of 2025, it's evident that over half of this year's tech trends have been dominated by large models and AI agents. Among these, AI agents have emerged as a hot topic of discussion among numerous major companies. Whether it's international tech behemoths like Microsoft, NVIDIA, Google, and OpenAI, or domestic leaders such as Alibaba, Tencent, ByteDance, and Baidu, all are fervently pushing forward the development of AI agent technologies.
Looking back at the past few years, AI technology has made remarkable strides. However, most applications still linger at the 'tool' level, performing specific tasks, answering straightforward questions, and executing standardized processes.
While these applications are undeniably useful, they have yet to fully harness AI's vast potential. Today, a more sophisticated form of AI is emerging—one capable of autonomous perception, decision-making, execution, and learning. This is the AI agent. As an intelligent system that interacts with its environment and exhibits a degree of autonomy, it may well represent the pinnacle of large-scale AI technology implementation.
So, what exactly is an AI agent? Why is it poised to dominate the future? And what transformations will it bring to the business landscape?
01. From Tools to Partners: Technological Breakthroughs in AI Agents
The term 'AI agent,' or AI Agent, is derived from 'Agent,' meaning 'representative.' This sets agents apart from conversational AI: they are not confined to question-and-answer interactions but are intelligent applications capable of deep thinking, autonomous planning, decision-making, and execution. The fundamental difference between AI agents and traditional AI applications lies in their autonomy and interactivity.
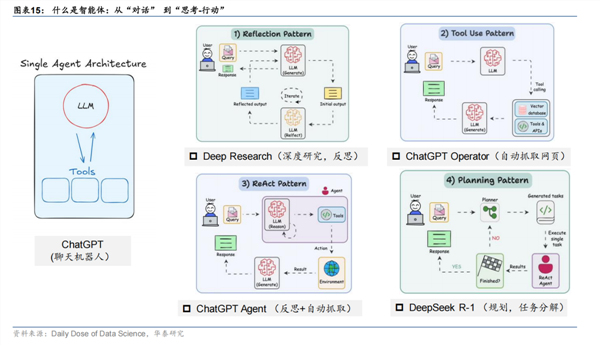
Traditional AI systems rely heavily on explicit human instructions to function, whereas AI agents can make decisions by perceiving their environment. This capability is underpinned by breakthroughs in multiple technologies. Large language models endow agents with the ability to understand natural language and reason, reinforcement learning enables them to continuously optimize strategies through trial and error, and multimodal technology allows them to process various inputs such as visual and auditory information. The integration of these technologies has given rise to intelligent systems capable of truly 'understanding' human intentions and taking proactive actions.
Technological advancements have not only made AI agents more intelligent but have also significantly lowered the barriers to their development and application. Previously, creating an autonomous AI system required substantial expertise and resources. Now, leveraging pre-trained models and open-source frameworks, developers can build powerful agents at relatively low costs. This trend towards technological democratization lays the foundation for widespread AI agent adoption, enabling both startups and large enterprises to leverage this technology to solve practical problems.
02. Competitive Advantages: Why Agents Will Triumph
Due to lowered barriers and technological progress, AI agents exhibit unique advantages in the competitive landscape of AI applications.
Compared to traditional AI systems, agents can handle more complex and dynamic environments and tasks. Traditional automation systems excel in structured settings but falter when faced with unexpected situations. AI agents, with their learning capabilities and adaptability, can navigate unstructured environments and unknown challenges—a flexibility that is highly valuable in real-world applications.
Another key advantage of agents is their reduced reliance on human intervention. In many scenarios, human supervision and intervention constitute a major portion of AI system operational costs. Agents, through autonomous decision-making and execution, can significantly lower these costs. Take customer service as an example: traditional chatbots can only handle a limited range of standard questions, whereas AI agents can deeply understand customer needs, access multiple systems for information, and genuinely resolve issues, greatly reducing the need for escalation to human agents.
Furthermore, agents create entirely new value propositions. They are not just efficiency tools but capability extenders. Through AI agents, individuals and businesses can achieve what was previously unattainable: individuals can have around-the-clock digital avatars handling multiple tasks simultaneously, while small and medium-sized enterprises can access expert-level services previously affordable only to large corporations. This democratization of capabilities will generate immense market demand for agents.
03. Business Model Innovation: From Products to Ecosystems
AI agents not only bring technological innovation but also foster entirely new business models. The most apparent shift is from one-time sales to ongoing services. Since agents require continuous learning and improvement, suppliers naturally lean toward subscription-based or usage-based pricing models, creating more predictable revenue streams and higher customer lifetime value.
The agent economy also promotes the formation of platforms and ecosystems. Major tech companies are building agent platforms that allow third-party developers to create and distribute agent applications. These platforms provide core AI capabilities, development tools, and distribution channels, akin to mobile app stores. This ecosystem strategy rapidly expands the scope and diversity of agent applications, creating powerful network effects.
More intriguingly, agents may usher in a new 'digital labor' market. In the future, we might see specialized agents offering services for specific tasks in open markets, with businesses able to 'hire' these digital workers as needed. This model will greatly enhance resource allocation efficiency, allowing companies to flexibly scale their AI capabilities without substantial upfront investments. Against this backdrop, the application potential of AI agents is virtually limitless.
On a personal level, we might have true personal assistants that not only execute commands but also anticipate our needs and proactively offer help. Such assistants will integrate our digital lives, managing schedules, communications, information filtering, and decision support, truly becoming our 'digital extensions.'
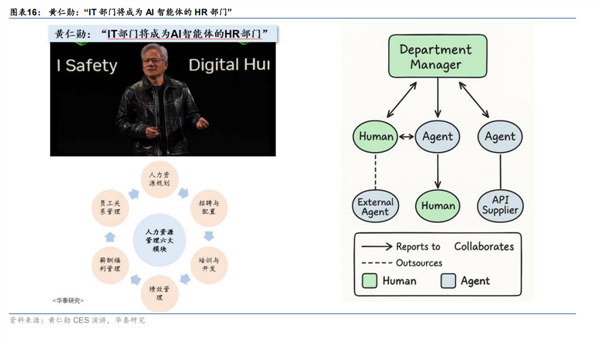
In the corporate realm, agents will reshape business processes. Unlike current automation tools, agents can handle end-to-end complex processes, operate across systems, and adapt to anomalies. From supply chain management to customer relationship maintenance, from financial analysis to human resources, agents will serve as the digital backbone of enterprises, significantly boosting operational efficiency and decision quality.
Huatai Securities argues that the grand vision of the agent economy rests on a fundamental physical reality: every AI thought, reasoning, and action consumes tangible electricity and computational resources. As agents transition from experimental to large-scale deployment, their demand for energy and semiconductors is growing rapidly, elevating these physical resources from ordinary operational costs to strategic, bottleneck resources that determine the pace and scale of AI development. Consequently, the software industry is shifting from fixed SaaS subscription models to token-based pricing, converting corporate operational expenses (OPEX) directly into sustained demand for computational infrastructure, creating a robust business model flywheel that drives persistent, non-cyclical growth in hardware sales.
04. Challenges and Reflections: Obstacles on the Path to Agent Proliferation
Despite their promising future, the large-scale adoption of AI agents faces significant challenges. On the technological front, ensuring the reliability, security, and transparency of agents remains an unsolved issue. How can we trace the causes when agents make incorrect decisions? How can we prevent agents from being maliciously exploited? These technological challenges require ongoing research and innovation.
Ethical and societal considerations are equally important. As agents assume more responsibilities, how should accountability be allocated? How can we prevent biases and discrimination from appearing in agent decision-making? The impact of agents on the job market also needs careful management to ensure technological progress benefits society as a whole rather than exacerbating inequality.
Regulatory and legal frameworks must also adapt to the age of agents. Existing legal systems, largely designed for human actors, face open questions in accommodating autonomous AI systems. Data privacy, intellectual property, and liability determination all require new legal thinking and regulatory approaches.
05. Conclusion: Toward an Agent-Driven Future
Despite the challenges, AI agents represent the inevitable direction of AI development—from passive tools to active partners, from single functions to comprehensive capabilities, from human guidance to autonomous operation. This transformation is not only technologically significant but will also fundamentally alter how we interact with technology, reshaping personal lives, business operations, and societal structures.
While challenges lie ahead, agent technology has demonstrated game-changing potential. Its unique technological advantages, improving economics, and broad application prospects make it the most likely candidate for large-scale AI implementation. As the technology matures and ecosystems form, we can expect agents to permeate every corner, becoming a core component of future digital infrastructure, much like the internet and mobile technologies.
The AI era of the future may well be a world where agents are ubiquitous. In this world, humans are not replaced by technology but enhanced by it, enabling us to focus on more creative and strategic work while letting agents handle routine decision-making and operational tasks. This collaborative model will create unprecedented value for society, truly fulfilling the promise of AI technology—enhancing human capabilities, improving quality of life, and solving complex challenges.
- End -