Qualcomm's Innovations in Robot Solutions
![]() 01/08 2026
01/08 2026
![]() 543
543
Produced by Zhineng Technology
At this year's Consumer Electronics Show (CES), Qualcomm placed 'robots' at the forefront, unveiling a more systematic approach. The company officially launched a comprehensive technology suite tailored for robots, with a particular focus on humanoid robots and advanced autonomous mobile robots (AMRs).
Through a systematic display that encompasses everything from the underlying System on Chip (SoC) to system architecture, software stacks, and ecological partnerships, Qualcomm addressed the curiosity of all partners regarding how it achieves the transition of physical AI from the laboratory to widespread deployment.

The challenges facing robots have evolved from mere entertainment, such as dancing and fighting, to enhancing productivity. The goal now is to solve the critical issue of enabling robots to operate in a long-term, stable, safe, and cost-effective manner.
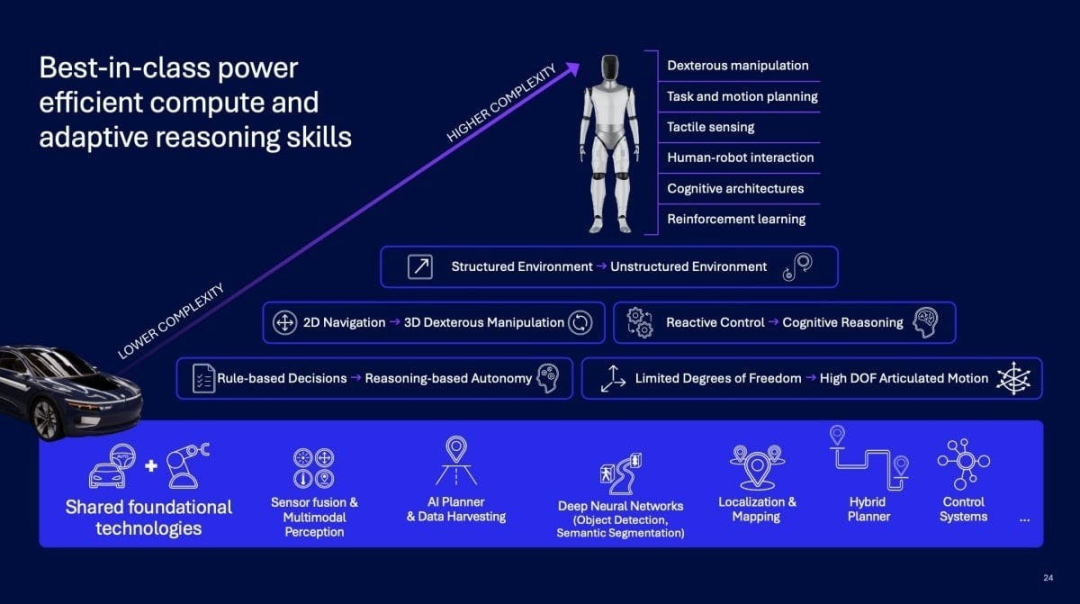
Leveraging its long-standing strengths in high-performance, low-power SoCs, and edge AI, Qualcomm has proposed a versatile robot architecture. This architecture spans a broad spectrum, from household service robots and industrial AMRs to full-size humanoid robots endowed with reasoning, adaptation, and decision-making capabilities.
Qualcomm's robot architecture prioritizes energy efficiency, scalability, and functional safety, with a clear objective: to facilitate the deployment of robots as seamlessly as conventional products.
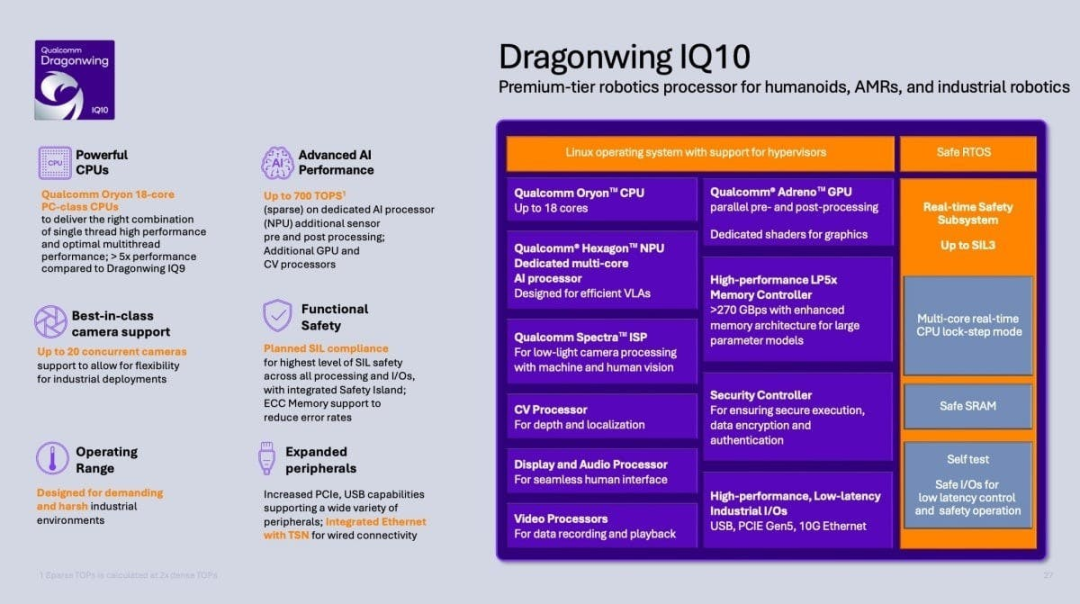
The Dragonwing IQ10 represents Qualcomm's high-end robot SoC, designed specifically for humanoid robots and industrial-grade AMRs. Its overall design emphasizes the parallel advancement of high computing power, low latency, and functional safety.
In terms of general computing, the IQ10 incorporates an up to 18-core Oryon CPU architecture, striking a balance between single-thread real-time control and multi-thread complex task scheduling. This makes it well-suited for the parallel computing demands of robots during perception, planning, and execution stages.
For AI computing, the IQ10 integrates Qualcomm's new-generation Hexagon NPU, delivering up to 700 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second) of AI computing power under sparse computing conditions. It is primarily designed for visual language models (VLMs) and visual language action models (VLAs), supporting real-time fusion of multi-sensor data, target recognition, scene understanding, and action generation.
The chip can simultaneously connect up to 20 cameras, catering to the panoramic perception and precise operation needs of humanoid and industrial robots.
To cater to industrial and human-robot collaboration scenarios, the IQ10 incorporates a built-in real-time safety subsystem. This subsystem supports mixed-criticality system architectures and achieves SIL3 (Safety Integrity Level 3) functional safety levels, ensuring safe operation under abnormal or fault conditions.
Overall, the Dragonwing IQ10 is not merely about amassing computing power; it's about constructing a deployable robot computing platform for physical AI through heterogeneous computing and safety design.
Qualcomm Yuelong™ IQ10, the latest generation of high-end robot processors, is tailored for industrial-grade AMRs and full-size humanoid robots.
Unlike previous processors that focused solely on computing power, the IQ10 emphasizes system-level capabilities. It provides high-performance heterogeneous computing while meeting functional safety level requirements and balancing power consumption control.
This is crucial for robots—insufficient computing power limits intelligence, while unchecked power consumption leads to bottlenecks in battery life, heat dissipation, and reliability. The IQ10 serves as the 'robot brain'.
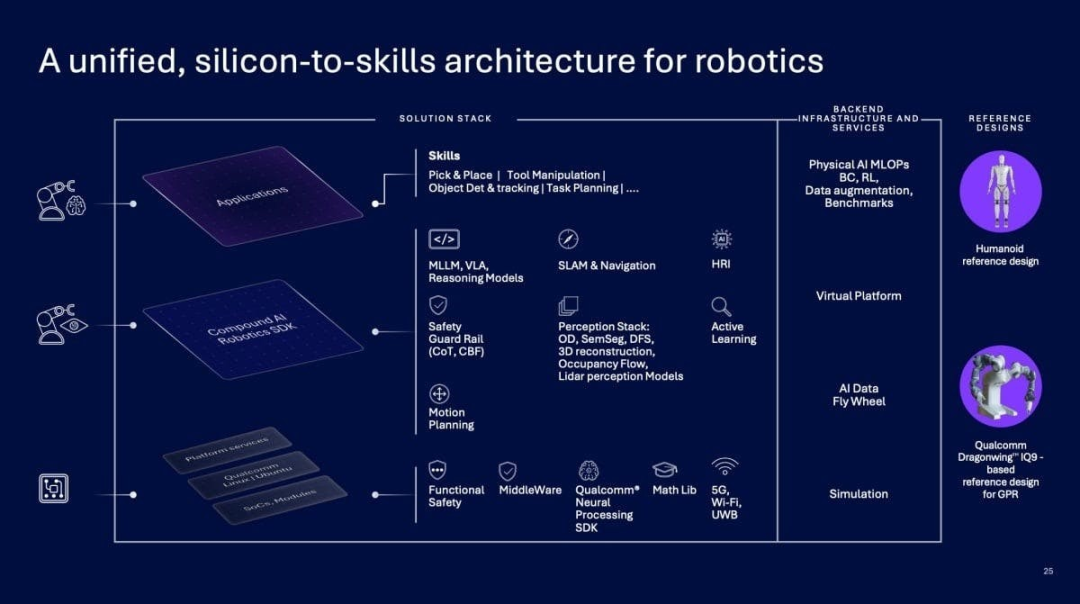
Qualcomm does not view the IQ10 as an isolated chip product but positions it within an end-to-end architecture.
From perception and decision-making to execution, this architecture supports the deployment of end-to-end AI models, such as VLMs and VLAs, on the edge. This enables robots to complete generalized operations and human-robot interactions in real-world environments.
This means that robots no longer rely solely on preset rules but possess the ability to continuously learn and adapt in complex scenarios, providing a higher ceiling for automation in retail, logistics, manufacturing, and other sectors.
At the industrial cooperation level, Qualcomm's strategy is equally clear: without an ecosystem, there is no scale.
Currently, Qualcomm is building a collaborative network around its robot platform, encompassing OEMs, system integrators, and software companies. Partners announced at CES include Advantech, Agxion, Autocore, Accelerated Evolution, Figure, KUKA Robotics, Robotec.ai, VinMotion, and others.
These companies span multiple directions, including industrial robots, humanoid robots, AMRs, and development platforms, with a shared goal of promoting the implementation of 'ready-to-use, scalable' robot solutions.
The collaboration with Figure is particularly noteworthy.
Figure is advancing the large-scale development of its universal humanoid robot platform, while Qualcomm is jointly defining the next-generation computing architecture with it. Brett Adcock, Founder and CEO of Figure, explicitly stated that the balance between computing power and energy efficiency on Qualcomm's platform is a crucial foundation for achieving his vision.
This collaboration also sends a signal: as humanoid robots transition from 'demonstrating capabilities' to 'entering factories and real-world work scenarios,' the underlying computing platform is becoming a key competitive factor.
'From concept to deployment' is a keyword repeatedly emphasized by Qualcomm.
In fact, Qualcomm's Yuelong industrial processor roadmap already supports various robot forms and is advancing implementation in multiple global projects.
By integrating heterogeneous edge computing, mixed-criticality systems, software platforms, machine learning operations and maintenance, and AI data flywheels, Qualcomm aims to address the long-standing 'last mile' issue in the robot industry—complex system integration, lengthy debugging cycles, and difficulty in replication.
This end-to-end approach essentially lowers the threshold for robots to transition from prototypes to mass production.
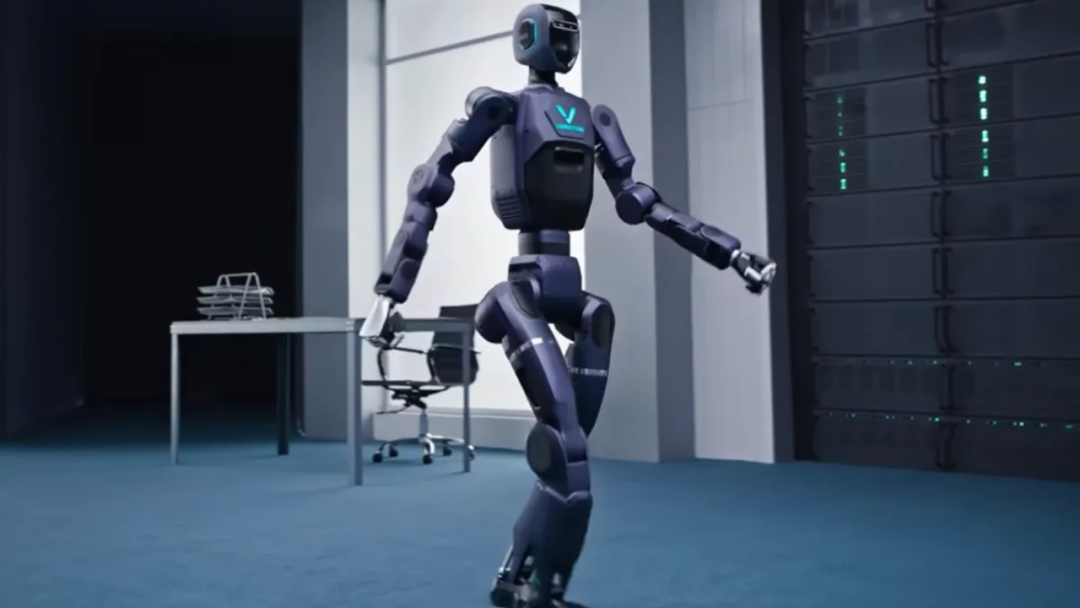

Qualcomm also showcased physical demonstrations, including the VinMotion Motion 2 humanoid robot equipped with Qualcomm's Yuelong™ IQ9 series and the Booster K1 Geek Edition robot from Accelerated Evolution. These demonstrations visually presented the capabilities of Qualcomm's edge AI platform in motion control, perception, and interaction. Advantech's commercially available robot development kit was also on display at Qualcomm's booth, highlighting the practical value of 'rapid development and rapid deployment.'
The AI data flywheel demonstration, focusing on remote operation, data collection, model training, and deployment, further completed the toolchain required for the continuous evolution of robots.
Summary
At CES, Qualcomm showcased a set of capabilities more oriented towards infrastructure. As robots truly move towards large-scale deployment and enter the real world, what should the underlying computing platform look like? This natural extension of Qualcomm's edge AI technology capabilities signifies a major undertaking!







