Chinese Automakers Embrace Embodied Intelligence Revolution
![]() 01/03 2025
01/03 2025
![]() 598
598

Author | Xiang Xin
Editor | Bai Xue
In December 2024, the field of embodied intelligence robots welcomed another formidable entrant: GAC Group.
Recently, GAC Group unveiled the third-generation embodied intelligence humanoid robot, GoMate, boasting 38 degrees of freedom throughout its body.
At the launch event, GoMate demonstrated precise movement control, accurate navigation and positioning, and agile autonomous decision-making capabilities.
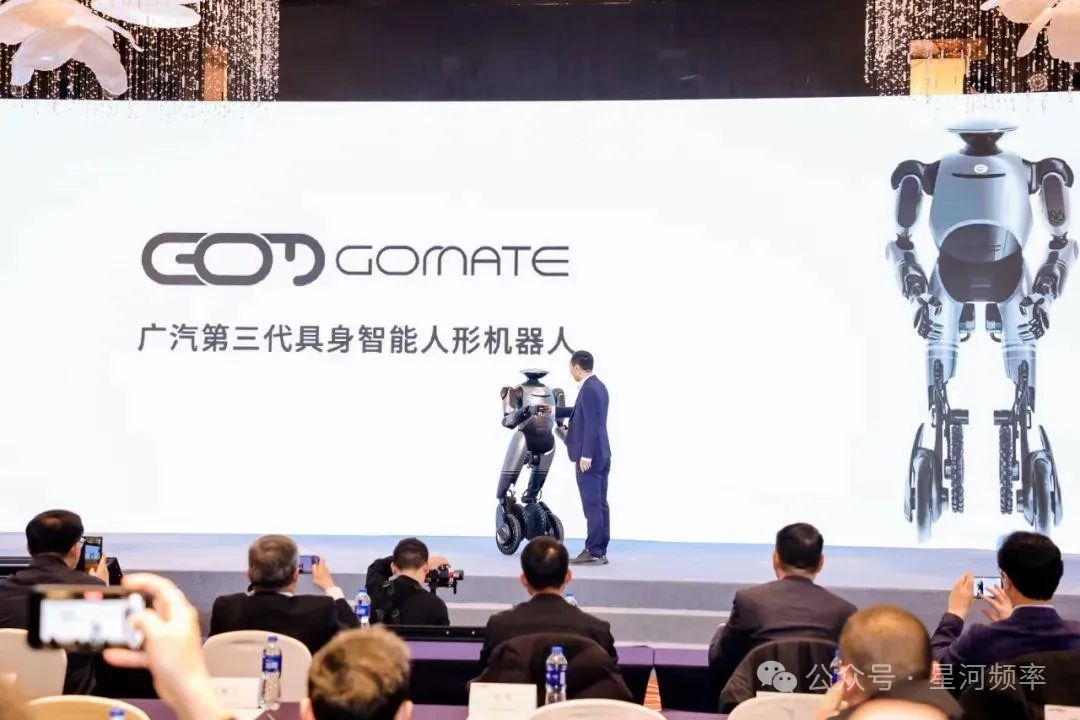

Listed on the Fortune Global 500 for 11 consecutive years, GAC Group has recorded annual revenues exceeding 100 billion yuan in the past two years. Its financial and technological prowess for developing robots should not be underestimated. Its entry has further ignited the already heated embodied intelligence robot industry.
Embodied intelligence integrates AI into physical entities such as robots, endowing them with the ability to perceive, learn, and dynamically interact with their environment. In essence, it's an AI brain coupled with a machine body, creating an intelligent robot entity.
Remarkably, the enthusiasm of Chinese automakers for embodied intelligence robots is unparalleled. All eight Chinese automakers listed in the Fortune Global 500 have ventured into this realm.
These eight top 500 automakers include SAIC Motor, FAW Group, BYD, GAC Group, Geely Holding Group, BAIC Group, Dongfeng Motor Group, and Chery Automobile.
Five of these automakers have entered the market through self-development, collaborative research and development, investment, and other means, while the remaining three (FAW Group, Geely Holding Group, Dongfeng Motor Group) are exploring the application of humanoid robots with Unitree.
If we broaden our focus beyond the Fortune Global 500, 13 automakers in China are exploring the field of embodied intelligence robots. In addition to traditional automakers, new forces such as XPeng Motors and Xiaomi have also joined the fray.
Embodied intelligence robots appear to be the next battleground for automakers. Each automaker aims to carve out new territories and secure a commanding position in this nascent technological frontier.
Fully Self-Developed Key Components
Autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance are the hallmarks of GoMate, embodying high performance and low cost.
In terms of hardware, GoMate adopts a unique "variable wheel-foot mobile structure," achieving full self-development of key components.
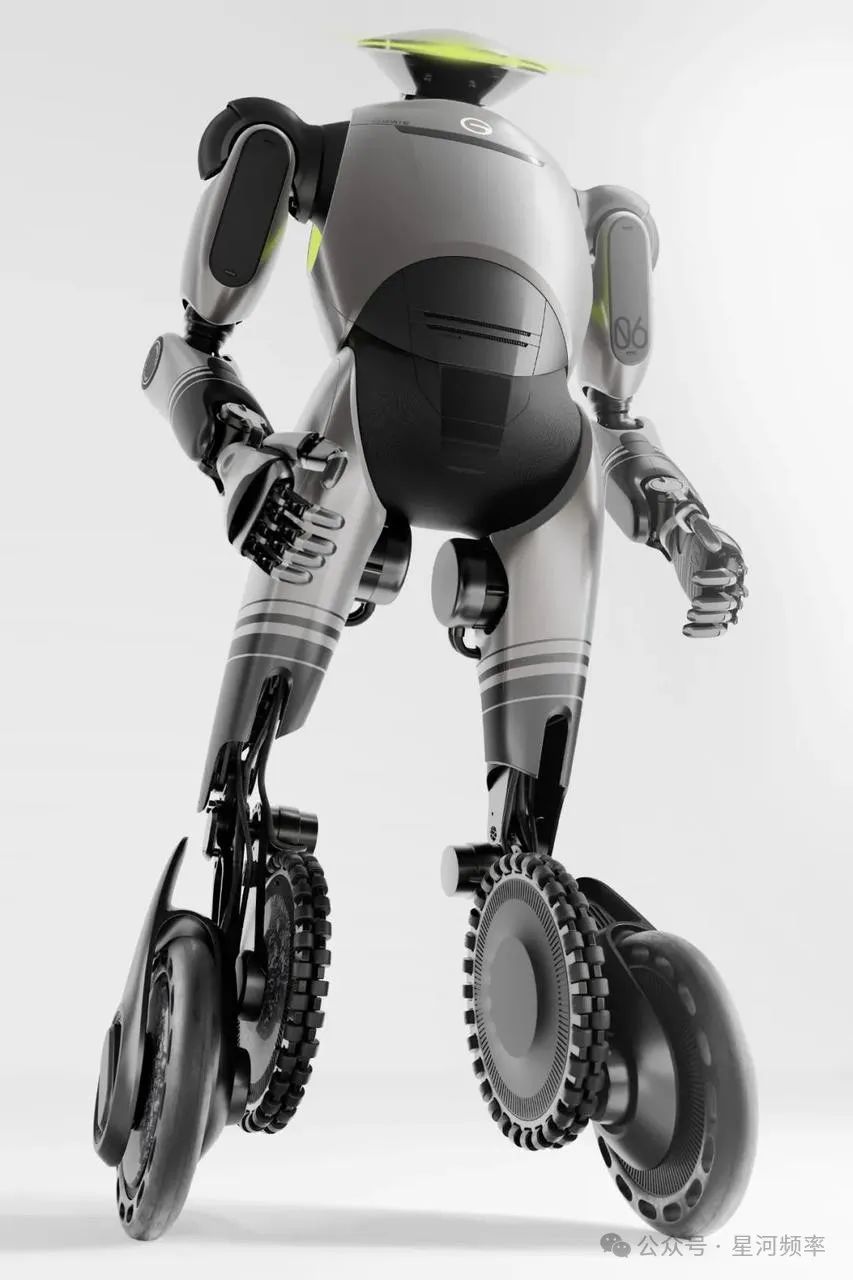
Within the robot industry, there is ongoing debate about whether to opt for efficient wheeled feet or bipedal feet that can adapt to various terrains. GAC Group's innovative solution: combining both.
The "variable wheel-foot mobile structure" integrates both four-wheeled and two-wheeled modes, harnessing the advantages of both. The robot can switch between wheel-foot structures based on different terrains.
In four-wheeled mode, GoMate stands approximately 1.4 meters tall and can navigate stairs, slopes, and single obstacles. In two-wheeled mode, it reaches a height of 1.75 meters, enabling efficient movement on flat ground with a maximum speed of up to 15 km/h.

This innovative structure significantly reduces the robot's energy consumption, saving up to 80% more energy compared to similar products.
Zhang Aimin, head of GAC Group's robot research and development team, believes that mastering core technologies is key to enhancing the company's competitiveness in the embodied intelligence robot field.
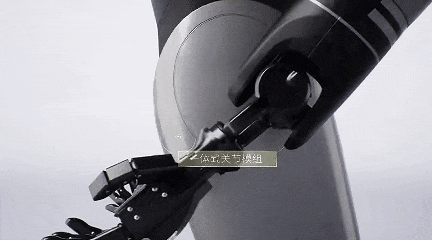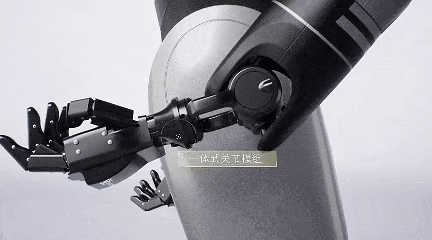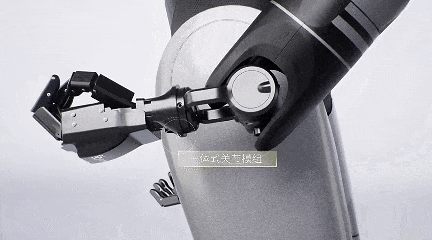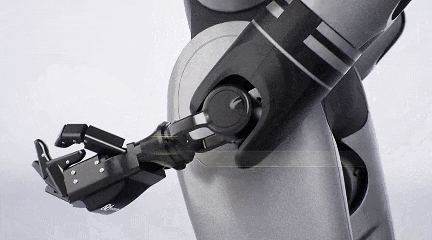
Therefore, GAC Group has self-developed core robot components such as dexterous hands, actuators, and motors.
GoMate's dexterous hand boasts high load capacity and flexibility, reducing manufacturing costs by 90%.
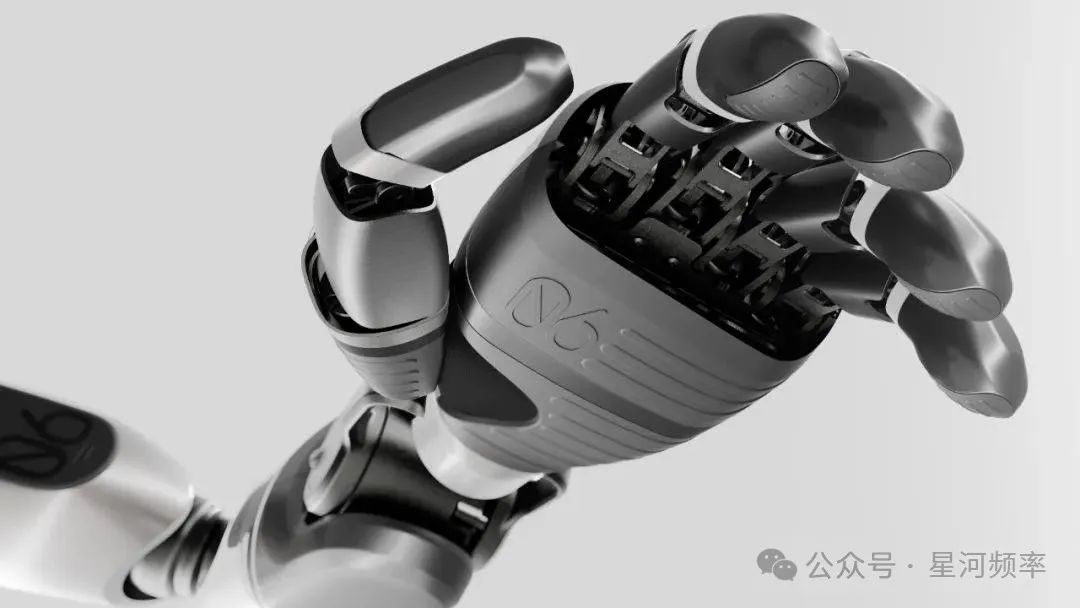

Weighing less than 500 grams, this dexterous hand can carry a load of up to 1.5 kilograms. It features a positive and negative flexible protection design, effectively preventing damage from accidental touch or overload, and supports over 20 interactive gestures.
Additionally, the dexterous hand is equipped with tactile and visual sensors, enabling it to automatically adjust gripping force and position to complete grasping tasks.
GAC Group's research and development of core components focus on lightweighting, such as for dexterous hands and joints, and miniaturization, such as for actuators and motors, all while maintaining high performance.
GoMate's micro low-voltage servo actuator is less than 30mm in height, roughly the size of a coin. Compared to traditional actuators, it reduces space by 80% but boasts a driving capacity of up to 20A, with a maximum continuous current of up to 50A.
GoMate's axial flux motor module is 15% shorter than competitors of the same specification, offering a maximum output torque of 1000N·m, a torque density of 200N·m/kg, and an overload capacity of over 5 times.
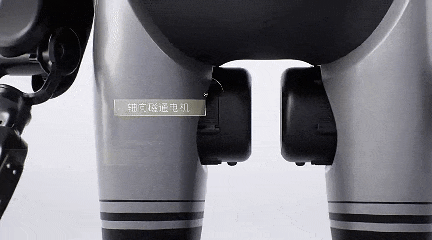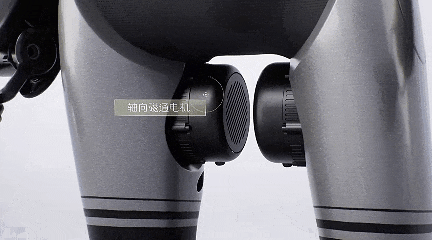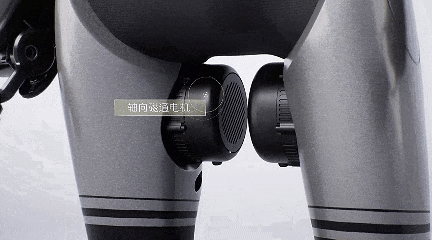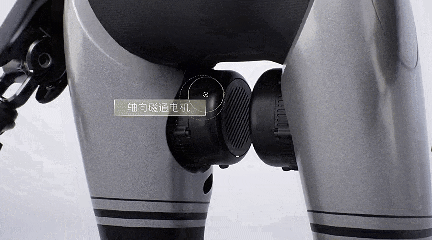
The robot's joint module is also highly integrated, maintaining excellent heat dissipation performance with a weight of only 300 grams and an output torque of 10N·m, keeping the temperature rise below 55°C.
GoMate's low cost is largely attributed to the reuse of GAC's intelligent driving software and hardware in the robot.
In addition to cost control through self-developed components, GoMate also utilizes GAC Group's solid-state batteries, providing a range of up to 6 hours.
On the software side, GoMate incorporates GAC's self-developed pure vision autonomous driving algorithm, enabling autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance. It can perceive changes in obstacles within 100 meters and achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy.
In terms of comprehension ability, the application of a cloud-based multimodal large model allows the robot to respond rapidly to complex human voice commands within milliseconds.
When faced with complex tasks beyond its capabilities, GoMate can seamlessly switch between AI autonomous control and remote control through GAC Group's force feedback handle system, completing tasks under human remote operation.
While performance appears robust, GAC Group's humanoid robot has yet to demonstrate strong task execution capabilities, and the robot demonstration videos are rendered composites.
However, GAC Group's commercial application of embodied intelligence robots is already underway.
GAC Group's mission is clear: to create the industry's first commercially applied humanoid robot. They have identified four application scenarios for GoMate: security, industrial manufacturing, smart living, and automotive aftermarket services.
Security and industrial manufacturing are expected to be the fastest areas for application.
GAC Group is collaborating with leading enterprises in the Guangzhou security industry to upgrade passive security systems to active security defense systems.

Furthermore, GAC Group plans to establish the world's first demonstration application zone in Guangzhou in 2025, leading the way in demonstration applications of the entire machine in production lines and industrial parks of GAC Motor, AION, and other OEMs.
Regarding mass production plans, GAC Group aims to achieve mass production of self-developed components by 2025, small-scale production of the entire machine by 2026, and gradually expand to large-scale production.
The robot research and development took two years, and GAC's strategy aligns with that of XPeng Motors.
In early 2022, GAC Research Institute embarked on the research and development of embodied intelligence robots, two years after automotive industry bellwether Tesla announced its humanoid robot.
Two years of research and development have yielded two generations of results. Half a month before unveiling the third-generation embodied intelligence humanoid robot, GAC Group announced the second-generation embodied intelligence robot.
The primary difference between the two generations lies in their form. The second-generation robot lacks a humanoid appearance and resembles a mini-car equipped with two dexterous hands.
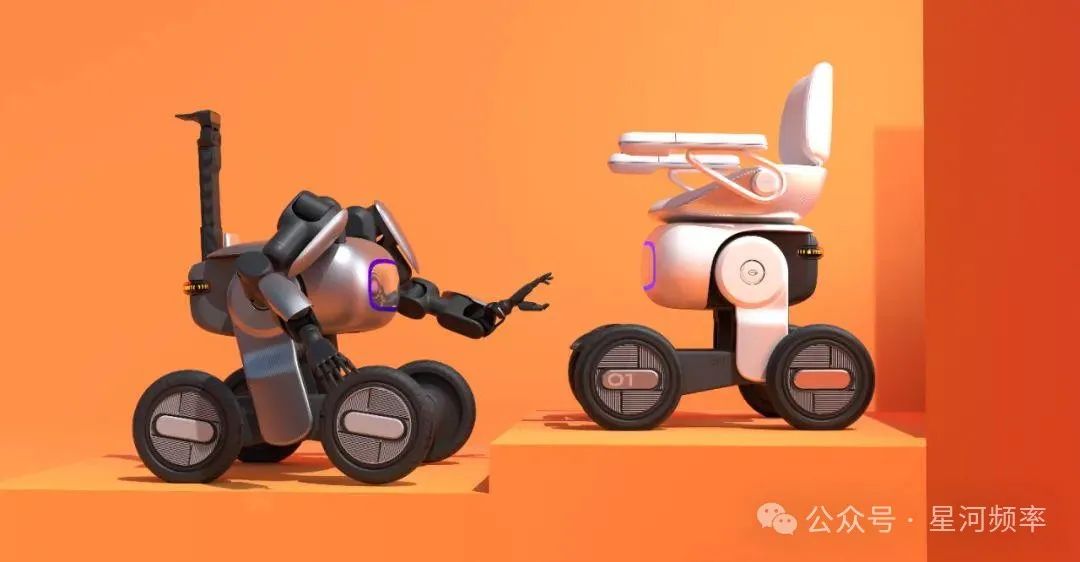

The second-generation embodied intelligence robot shares the same variable wheel-foot structure, dexterous hand functions and structure, and endurance as the third-generation model. It also achieves low-cost development by sharing components such as automotive chips and LiDAR, spreading research and development costs.
Zhang Aimin, head of GAC Group's robot research and development team, believes that based on the current development level of artificial intelligence technology, purely AI-controlled embodied intelligence robots will take a relatively long time to be truly applied. Therefore, GAC Group has opted for the "remote control + AI end autonomy" model, facilitating faster application of embodied intelligence robots.
GAC Group did not release a first-generation embodied intelligence robot. Prior to introducing the latest two generations, GAC Research Institute's robots were known as AI robots.
In earlier promotions, GAC Group's AI robots also featured a variable wheel-foot design, were powered by pure electricity, offered an endurance of over 20 kilometers, and were expected to be applied in households, initially providing services through remote control.
Responsible for AI robot research and development is the Foresight Technology Department of GAC Research Institute, established in 2021 on the foundation of GAC Group's former Guidance Technology Department.
Within GAC Research Institute, the Foresight Technology Department is primarily responsible for forward-looking technological innovation, including artificial intelligence, flying cars, and other fields, serving as the central system for innovative projects throughout the institute.
In addition to technological innovation, the Foresight Technology Department also plays a role akin to an "angel investor." When identifying promising innovation projects, it forms a team and coordinates multiple departments to support the project. When the timing is right, it considers establishing a company for independent operation.
GAC AION and GAC Motor are previous examples. As GAC's embodied intelligence robot project matures, there is a high likelihood that it will also be spun off to operate as a separate company.

GAC Research Institute's technology research and development adhere to the "91" principle, allocating 90% of funds, manpower, and material resources to the most mainstream products in the market; the remaining 10% focuses on more forward-looking technological innovations.
Currently, GAC Research Institute has invested a cumulative total of over 30 billion yuan in research and development and employs over 5,000 R&D talents.
Backed by GAC Group, GAC Research Institute's embodied intelligence robot project boasts deep financial and talent reserves. Compared to startups, GAC Group possesses a relatively mature R&D system, supply chain management, and market sales experience. These advantages enable GAC Group to accelerate the development of intelligent robots while reducing production costs.
Extensive automotive sales market channels also provide favorable conditions for GAC Group to tap into the user base for embodied intelligence robots.
Thus, GAC Group's ambition to create the industry's first commercially applied humanoid robot is not mere rhetoric but well-founded.
GAC Group's robot project is a crucial part of its intelligent layout. In terms of products, GAC has deployed a full-chain scenario of "three-dimensional transportation - ground mobility - indoor and outdoor mobility," with corresponding products being flying cars, conventional cars, and robots for each scenario.
GAC has unveiled two flying car models, GOVE and GOVY AirJet, and launched the flying car brand GOVY GaoYu.
GOVE underwent flight verification over Guangzhou's CBD in March this year, while GOVY AirJet was released in December, boasting a maximum flight speed of up to 250 km/h.
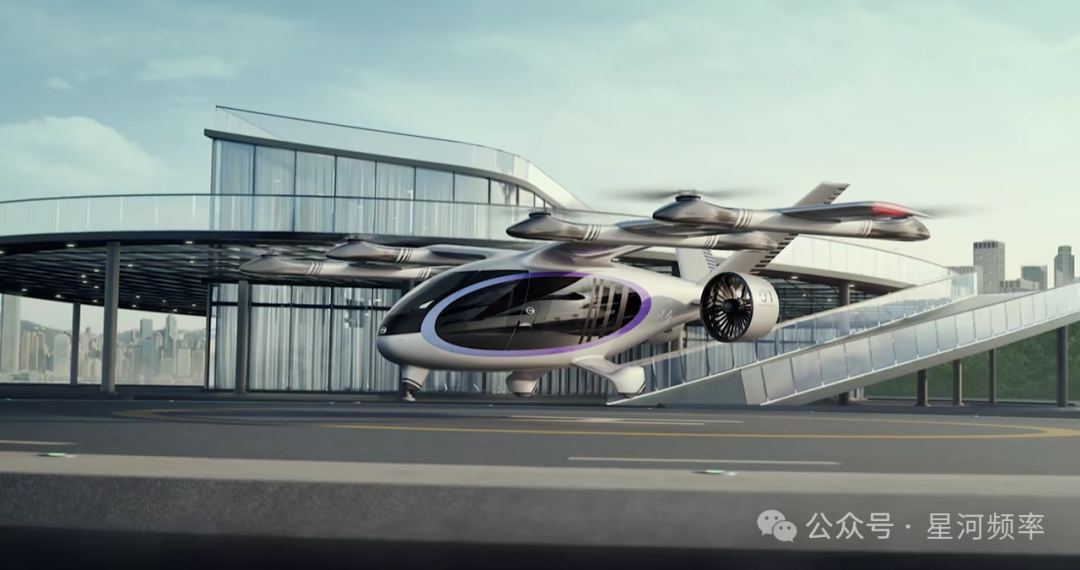

With its focus on developing flying cars, conventional cars, and robots, GAC Group's product research and development strategy aligns with that of XPeng Motors.
Technologically, GAC Group aims to gradually establish an intelligent industrial ecosystem encompassing autonomous driving, artificial intelligence, big data platforms, intelligent robots, and other technological fields.
Under a comprehensive intelligent layout, GAC Group's development strategy is clear: it is not just an automotive enterprise but also a technology enterprise.
Eighteen automakers worldwide are competing in the realm of embodied intelligence.
Amid the wave of artificial intelligence, automakers are scrambling to transform into AI companies.
Tesla leads the pack. Elon Musk has repeatedly emphasized that Tesla is not just an automotive or new energy company but an AI + robot company.
Firms such as XPeng and Li Auto are at the forefront. XPeng Motors aspires to become a global leader in AI automotive technology, while Li Auto envisions itself as a pioneering global AI enterprise.
This surge is fueled not only by technological advancements but also by the ambition of various automakers to stay ahead of the times.
Embodied intelligent robots have emerged as the gateway for automakers to transform into AI companies.
Currently, domestic and international automakers are entering the embodied intelligent robot arena through four primary pathways: in-house R&D, collaborative R&D, investment, and joint exploration of practical applications. According to incomplete statistics,
18 automakers worldwide have already embarked on this journey.
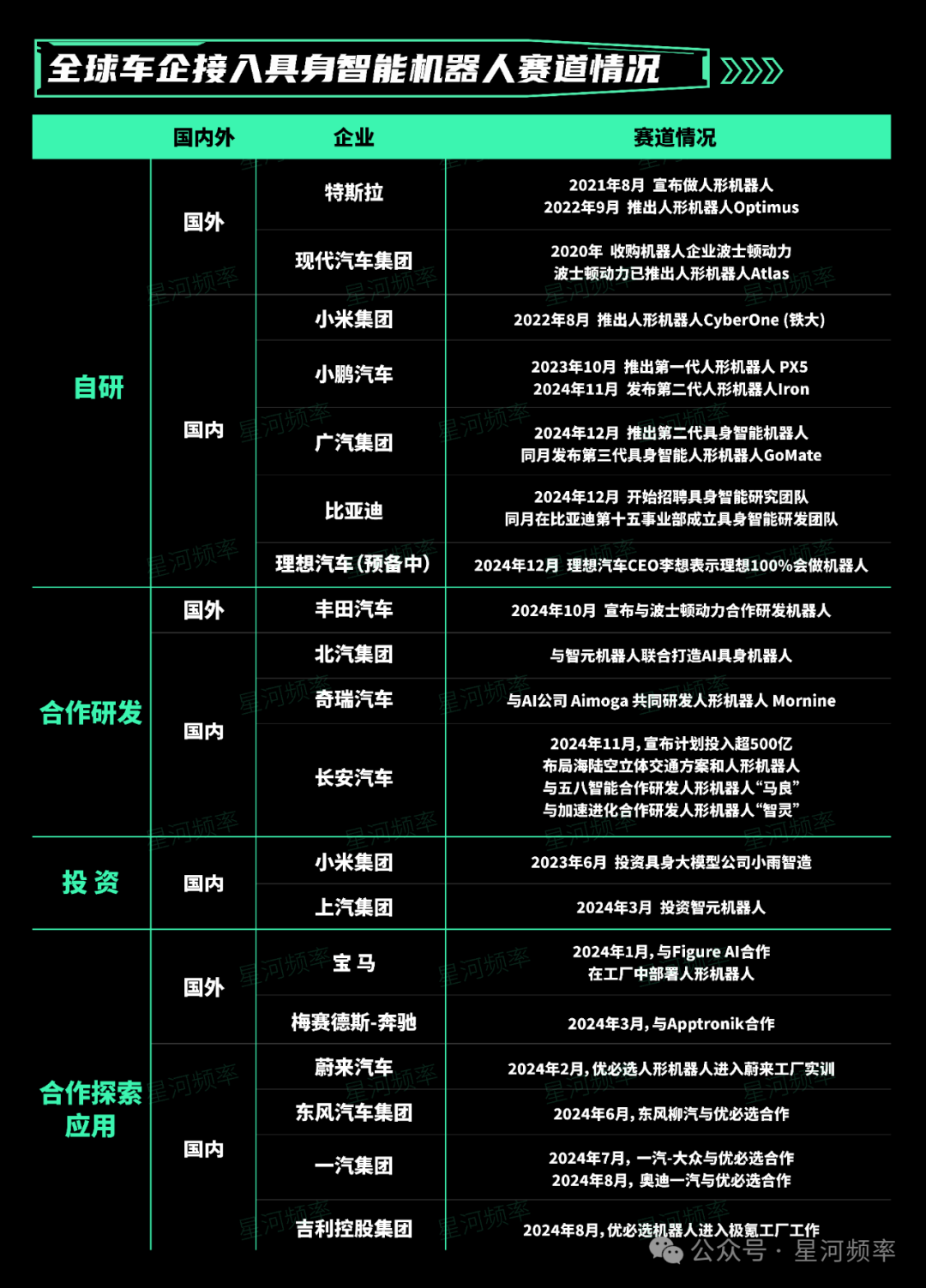
The table clearly indicates that domestic automakers demonstrate a stronger enthusiasm for embodied intelligent robots compared to their foreign counterparts.
There are three compelling reasons why automakers are flocking towards embodied intelligent robots.
Firstly, automakers possess inherent advantages in both hardware and software when developing embodied intelligent robots. They also enjoy a comprehensive supply chain, management expertise, and a substantial user base with abundant customer resources.
As both traditional and new-energy automakers strive to innovate in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technologies, automotive batteries, motors, cameras, and sensors can be repurposed for embodied intelligent robots in terms of hardware.
In software, autonomous driving algorithms, large models, end-to-end neural networks, and motion planning can be transferred to help embodied intelligent robots learn new tasks, navigate autonomously, and avoid obstacles.
Liu Shaoshan, Director of the Embodied Intelligence Center at the Shenzhen Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, noted that the embodied intelligence industry chain comprises upstream providers of core components, midstream entities responsible for system integration technology and complete machine manufacturing, and downstream entities with diverse application scenarios.
He believes that companies poised to dominate the embodied intelligence market in the future are either those that have already established upstream advantages and are moving towards midstream integration, or those progressing from downstream scenarios to midstream. A purely technology-driven approach faces challenges due to the competitive landscape and market complexity, which underscore the uniqueness of this industry.
Automakers uniquely occupy both upstream and downstream positions. They not only possess in-house R&D capabilities for embodied intelligent robot components, enabling them to build a component supply chain, but also maintain a vast user base.
Compared to startups, they also enjoy substantial capital and robust risk resilience.
Secondly, automakers aim to enhance productivity in their factories.
Both humans and embodied intelligent robots are forms of labor. While human work efficiency, duration, and capacity are limited, embodied intelligent robots are essentially machines capable of continuous production. Theoretically, their numbers, efficiency, and operating hours can surpass those of humans.
Furthermore, it is envisioned that embodied intelligent robots will adapt to harsh and extreme environments intolerable to humans, performing tedious, repetitive, and labor-intensive tasks that humans prefer to avoid. For enterprises, robots offer greater stability than humans.
According to media reports, an investor in contact with the Tesla team revealed that Musk insists on manufacturing humanoid robots to replace workers on Tesla's production lines, thereby alleviating production capacity constraints.
If prices can be reduced, embodied intelligent robots will become ideal "workers," significantly boosting corporate productivity. The third reason lies in the enormous market potential of embodied intelligent robots. The concept of embodied intelligence implies that robots will possess a smarter brain and greater versatility in task execution.
While automobiles serve merely as a means of transportation for humans, embodied intelligent robots have the potential to fully integrate into human daily life and work, becoming indispensable assistants.
Humanoid robots represent the hottest segment within embodied intelligent robots.
Goldman Sachs predicts that the global market size for humanoid robots could reach $154 billion by 2035, equivalent to approximately RMB 1,103.73 billion.
Beyond humanoid forms, embodied intelligent robots come in various shapes and sizes, indicating vast market potential. Additionally, no company has yet achieved a commercial closed loop to capture a significant market share.
Summarizing these three reasons, there are essentially two facets: internally, automakers possess the capability and demand to develop embodied intelligent robots; externally, the vast market for embodied intelligent robots could be the next crucial growth area for automakers.
The potential of embodied intelligent robots has also garnered state support and recognition.
In November 2023, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the "Guidance on the Innovative Development of Humanoid Robots," stating that by 2025, China's humanoid robot innovation system will be preliminarily established, enabling mass production. By 2027, the technological innovation capabilities of humanoid robots will be significantly enhanced, with related products deeply integrated into the real economy, becoming a vital new engine for economic growth.
Before entering the pivotal year of 2025, in December 2024, various players in the embodied intelligent robot sector began their final push.
Giants have entered the fray. Apple has developed the ARMOR robot perception system to aid robots in comprehensively perceiving their surroundings; Google has partnered with the American humanoid robot company Apptronik; OpenAI is preparing to re-enter the humanoid robot competition.
Companies specializing in embodied intelligent robots have unveiled new products or announced new advancements. In December alone, eight brand-new embodied intelligent robots were launched domestically and internationally, including Brog Robotics' Brog 01, Pudu Robotics' first full-size bipedal humanoid robot PUDU D9, Zhongqing Robotics' PM01, and Youlike UniX AI's humanoid robot Wanda 2.0.
Robots are accelerating their evolution: Tesla's Optimus demonstrated its outdoor walking capabilities, Boston Dynamics' electrically powered Atlas learned to do backflips, and ZhuJi Dynamics' robots evolved to stand up from a flat surface...
A cohort of promising embodied intelligent companies with star potential has emerged.
Yu Yinan, former Vice President of Horizon Robotics, joined forces with Zhao Zhelun, former Director of Intelligent Driving Products at Li Auto, and Song Wei, former Chief Architect of the software platform at Horizon Robotics, to establish Vita Power, an embodied intelligence startup. Li Zhenyu, former Senior Vice President of Baidu, collaborated with Chen Yilun, former Chief Scientist of Huawei's Intelligent Automotive Solutions BU, and Ding Wenchao, former Huawei genius, to found Tashi Zhihang, an embodied intelligence company.
A number of promising embodied intelligent companies have completed funding rounds.
Titan Robotics announced the completion of two consecutive funding rounds, totaling over RMB 100 million. Magic Atom and Bridge Number Physics also announced the completion of angel funding rounds of RMB 150 million and tens of millions of RMB, respectively.
There are also companies advancing the commercialization of robots.
Figure AI announced the commencement of revenue generation, and Zhiyuan Robotics announced the mass production of nearly 1,000 units. NAVIAI, the leading humanoid robot from the Zhejiang Humanoid Robot Innovation Center, entered Lenovo's factory to produce AI computing equipment, while Magic Atom's MagicBot team integrated into factories to work.
December was a remarkable month for embodied intelligent robots, marked by a concentration of company activities, product launches, progress announcements, and funding rounds.
The year 2025, mentioned in national government documents and aiming for mass production of humanoid robots, will also witness robust development in the embodied intelligent robot industry.