In the Era of AI: Will the "Electronic Industrial Staple" Undergo a Cycle Reversal?
![]() 03/26 2025
03/26 2025
![]() 547
547
In the expansive industrial tapestry of electronics, there lies a crucial foundational component known as the "industrial staple" – Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs). These tiny, cost-effective passive elements are the bedrock supporting the stable operation of modern electronic devices, from smartphones to new energy vehicles, and from AI servers to industrial control systems. None of these technologies can function without them.
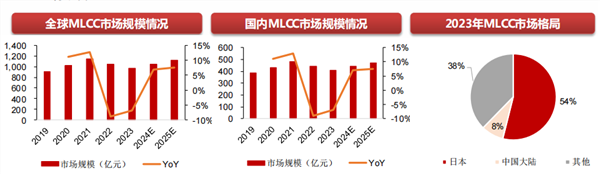
However, this industry has seen drastic cyclical fluctuations over the past three years. In 2021, the global MLCC market size peaked at 114.8 billion yuan, only to retract to 97.4 billion yuan in 2023 due to factors such as waning consumer electronics demand and inventory buildup. Now, with the advancement of the AI technology revolution, the surge of automotive intelligence, and structural adjustments in supply and demand, is the MLCC industry on the cusp of a cycle reversal?
01. Cycle Trough Emerges: Triple Signals of Inventory, Operating Rate, and Price
The MLCC industry is notably cyclical, with its prosperity typically dictated by inventory levels, capacity utilization rates (operating rates), and product prices. Since the third quarter of 2021, the industry has embarked on a downward trajectory, with overcapacity leading to a supply-demand imbalance and persistent price declines. Taking the consumer electronics sector as an example, the dwindling demand in the smartphone and PC markets directly pulled down MLCC manufacturer shipments. According to data from the China Electronic Components Industry Association, the global MLCC market size declined by 6.9% year-on-year in 2023, while the Chinese market size fell by 6.8%, plunging the entire industry into a downturn.
However, since the second half of 2023, multiple indicators suggest that the cycle’s nadir is forming.
Firstly, inventory levels are gradually returning to healthy ranges. After a two-year inventory destocking cycle, channel and end-customer inventories have fallen from peak levels to normal.
Secondly, capacity utilization rates have rebounded. Murata Manufacturing, a Japanese industry leader, exemplifies this trend, with its fiscal year 2024 (ending March 2025) operating profit expected to surge by 39% to 300 billion yen, accompanied by progressing capacity expansion plans.
Additionally, prices have stabilized. Leading companies such as Yageo and Murata have indicated that MLCC prices for certain specifications have shown month-on-month improvements, particularly for high-capacity automotive products, which remain firm due to tight supply and demand.
This inflection point is not solely the result of spontaneous supply-demand adjustments but is also closely tied to the explosion of emerging downstream demand.
02. AI and Automotive Electronics: Structural Changes on the Demand Side
Traditionally, the MLCC application market has been dominated by consumer electronics, with mobile phones accounting for 38% and PCs for 19%. However, in recent years, automotive electronics and AI hardware have emerged as new growth engines for the industry.
1. The "New Four Modernizations" of Automobiles Double MLCC Demand
Amid trends of electrification, intelligence, networking, and sharing, the amount of MLCCs used per vehicle has soared exponentially. According to Murata Manufacturing, hybrid vehicles require approximately 12,000 MLCCs, while the demand for pure electric vehicles has risen to 18,000, with high-end intelligent models utilizing up to 30,000. The rise of Tesla and domestic new-energy vehicle companies has further amplified this demand. ICwise Consulting predicts that by 2025, global demand for automotive MLCCs will reach 650 billion pieces, significantly increasing the market share from its current 16%.
2. The AI Hardware Revolution Reshapes the High-End MLCC Market Landscape
The proliferation of AI technology places heightened demands on hardware. Whether it's AI servers training large models or smartphones and wearable devices equipped with edge AI, they all necessitate more stable and compact MLCCs. For instance, a high-end smartphone model requires approximately 1,000 MLCCs, with devices supporting AI functions witnessing a surge in demand for high-capacity, high-temperature-resistant, and high-frequency response MLCCs. Murata Manufacturing has developed the world’s smallest (0.16mm) MLCC for AI hardware, planning mass production in 2025, five years ahead of Asian competitors in technology.
It's worth noting that the performance requirements for MLCCs in AI and automotive electronics are substantially higher than those in consumer electronics, directly driving an increase in the proportion of high-end products. Currently, the automotive and industrial-grade MLCC markets are still dominated by Japanese (Murata, TDK, Taiyo Yuden) and Korean (Samsung Electro-Mechanics) companies, but domestic manufacturers are accelerating their penetration into this domain.
03. Supply and Demand Game: Japanese Contraction and Opportunities for Domestic Substitution
On the supply side, the global MLCC market has long exhibited a "pyramid" structure: Japanese companies dominate the high-end market (with a 54% market share), Korean companies lead the mid-range, and Chinese mainland manufacturers focus on the low-end. However, this pattern is undergoing profound changes.
1. Strategic Adjustment of Japanese Manufacturers: Abandoning Low-End and Focusing on High-End
Faced with price competition from Asian manufacturers, Japanese leaders have chosen to withdraw from the low-end market. In Murata's medium-term plan released in 2024, the operating profit margin target for fiscal year 2027 was lowered from 20% to 18%, clearly stating that "market share takes priority." Its president, Nakashima Norio, bluntly said, "We will firmly respond to the demand for sales growth and temporarily downplay the profit margin target." Behind this strategic adjustment lies the determination of Japanese companies to concentrate resources on capturing the high-end market for automotive and AI hardware MLCCs. For instance, Murata plans to increase its global share of MLCCs from 40% to 43% by 2030 and invest in the development of a new generation of miniaturized products.
2. Accelerated Domestic Substitution: Breakthrough from Low-End to High-End Layout
Under the imperative of supply chain security, domestic substitution has become an irreversible trend. Currently, Chinese mainland MLCC manufacturers (such as Fenghua Advanced Technology Materials, Sanhuan Group, Yuyang Technology, etc.) hold only an 8% global market share but exhibit strong competitiveness in the low-end market. Taking Fenghua Advanced Technology Materials as an example, its industrial-grade MLCC capacity continues to expand, and its automotive-grade products have passed certifications from multiple automotive companies in 2023.
What's more noteworthy is the leap made by domestic manufacturers towards the high-end market. Although technological barriers still exist in ceramic powder formulation, thin-layer technology, and co-firing processes, domestic enterprises are narrowing the gap through mergers and acquisitions, research and development cooperation, etc. TrendForce data shows that global MLCC demand is expected to recover to 4.33 trillion pieces in 2024, with domestic market demand accounting for "more than half of the pie," providing a vast testing ground for local enterprises.
Moreover, on the demand side, the current MLCC market is experiencing a mismatch in supply and demand, characterized by "low-end surplus and high-end shortage." In the consumer electronics sector, the pressure of overcapacity in low-end MLCCs has not fully abated; however, in the automotive and AI sectors, high-capacity and high-reliability products are in short supply. The widening of this price scissors gap has become the core driver for the industry cycle reversal.
1. Global Capacity Expansion Focuses on the High-End Market
In response to structural demand changes, leading manufacturers are adjusting their capacity layouts. Murata plans to increase sales to over 2 trillion yen by fiscal year 2027 and build a new factory specializing in automotive MLCCs; Samsung Electro-Mechanics will double the capacity of automotive-grade MLCCs at its Vietnamese factory; and Yageo will complement its high-end technology shortcomings through the acquisition of KEMET.
2. Price Differentiation Heralds Improved Profitability
Market differentiation has led to varying price trends for MLCCs: consumer-grade product prices remain under pressure, whereas automotive-grade and high-end industrial-grade product prices have continued to rise since 2023. Yageo's Chief Operating Officer Wang Danru pointed out that the MLCC order-to-shipment ratio has rebounded to above 1, and the industry's "downturn cycle is nearing its end." If AI hardware and new energy vehicle shipments exceed expectations in 2024, MLCC prices are anticipated to enter a comprehensive upward trajectory.
04. Future Outlook: 2025 May Become a Key Node for Recovery
By integrating changes on both the supply and demand sides, the outline of the MLCC industry cycle reversal gradually becomes clear. In the short term, 2024 will serve as a transitional year for marginal improvements; by 2025, with the volume release of AI terminals and the automotive intelligence penetration rate surpassing the critical point, the industry is expected to embark on a new growth cycle.
1. Technological Innovation Determines Long-Term Competitiveness
The trend towards miniaturization and high capacity of MLCCs is irreversible. Murata's mass production of 0.16mm products will create a technological generation gap. If domestic manufacturers can achieve breakthroughs in material science and process technology, they may replicate the domestic substitution path observed in the semiconductor field.
2. Geopolitics Accelerates the Reconstruction of the Industrial Chain
Amidst domestic substitution efforts, MLCCs, as strategic materials in the electronics industry, urgently require localized supply chains. Domestic terminal manufacturers (such as Huawei, BYD) have begun shifting orders to local suppliers like Fenghua Advanced Technology Materials, a trend that will be further strengthened in the next three years.
The cyclical fluctuations in the MLCC industry are essentially the outcome of the resonance between technological progress and market demand. Driven by AI and automotive electronics, the once "industrial staple" is transforming into "electronic gold." For Chinese enterprises, whether they can seize the opportunity of this cycle reversal hinges not only on the speed of capacity expansion but also on their ability to achieve breakthroughs in "choking points" such as ceramic powders and high-end processes.
If strategies are aptly implemented, by 2030, the global MLCC market may present a new landscape where "Japan and South Korea defend the high-end, China snatches the mid-range, and all parties compete for incremental growth." The rise and fall of this sub-sector will also serve as an excellent window for observing changes in the global electronics industry.
- End -








