Power Triopoly: The Trillion-Dollar Chess Game Among NVIDIA, Oracle, and OpenAI
![]() 09/23 2025
09/23 2025
![]() 607
607
When NVIDIA declared its intention to invest a staggering $100 billion in OpenAI in Silicon Valley, the entire tech community was abuzz, eager to decipher the rationale behind such astronomical figures. This funding, equivalent to the annual R&D investment of the entire global chip industry, is poised to reshape the AI power landscape and ignite a multitrillion-dollar infrastructure arms race. In this high-stakes contest, NVIDIA, Oracle, and OpenAI have formed a 'computing power triopoly' characterized by cooperation and checks-and-balances, with each strategic move redefining the future boundaries of AI. What stories lie beneath the surface of this monumental funding?
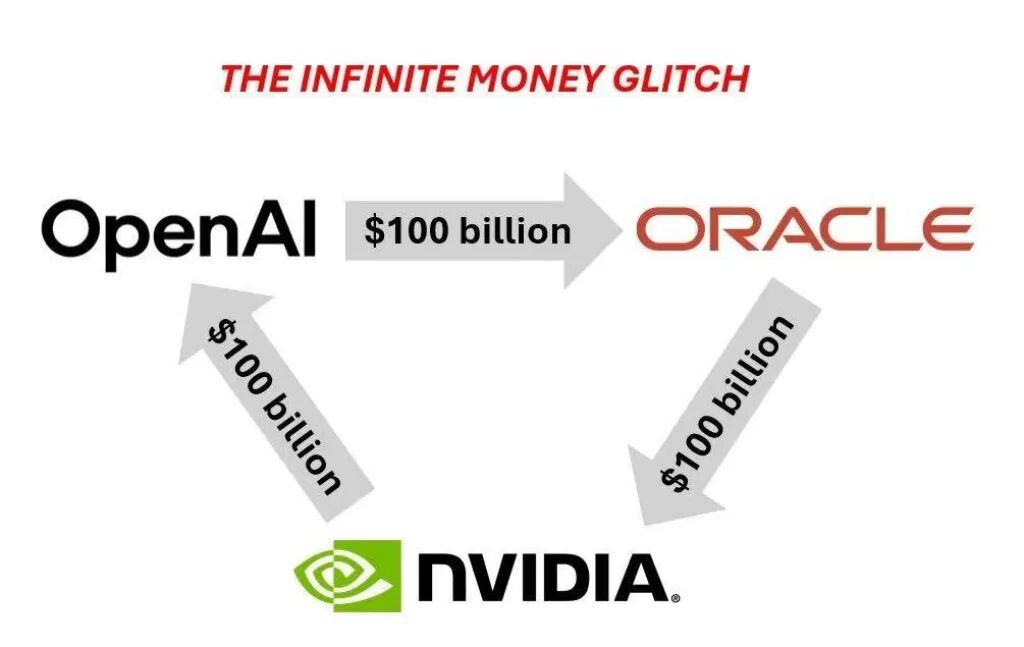
NVIDIA's Closed-Loop Empire: A $100 Billion 'Self-Investment' Maneuver
'NVIDIA invests $100 billion in OpenAI, which then channels the funds back to NVIDIA'—this succinct remark by Bryn Talkington, partner at Requisite Capital Management, cuts to the heart of the matter. This seemingly paradoxical capital maneuver is, in fact, a masterstroke by Jensen Huang to construct a computing power empire. Under their agreement, the investment will be phased in, with each gigawatt of computing capacity built triggering a corresponding financial infusion, representing the deployment of approximately 400,000–500,000 GPUs. According to NVIDIA CEO Huang, this volume matches the company's entire annual chip shipment, doubling last year's figure.
This 'you-in-me' cooperation model creates a seamless business closed loop: NVIDIA secures long-term orders from its largest customer, OpenAI, while OpenAI gains vital funding and technical support for its next-gen AI infrastructure. More profoundly, the two entities will collaborate to optimize hardware-software roadmaps, ensuring that future OpenAI large models are deeply integrated with NVIDIA's chip architectures, thereby erecting a technical moat that competitors will find difficult to breach.
NVIDIA's confidence in this bet stems from its upcoming Vera Rubin platform. Dubbed by Huang as 'another leap in AI computing frontiers,' this system delivers a staggering 8 exaFLOPS of AI computing power per rack—7.5 times that of the previous generation. Its new Rubin CPX GPU, designed for long-context reasoning, supports the processing of millions of tokens simultaneously, a core capability for training next-gen Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). When the first Vera Rubin-based systems deploy in late 2026, they will serve as the powerhouse for OpenAI's model evolution.
But NVIDIA's ambitions extend even further. A week prior to announcing the OpenAI investment, the chip giant also invested $5 billion in Intel to co-develop data center and PC products. This 'both-sides' strategy aims to forge a more complete ecosystem—by integrating Intel's x86 CPU strengths, NVIDIA addresses its general-computing gaps, offering OpenAI and others a chip-to-system one-stop solution. Facing dual challenges from AMD and cloud vendors' custom chips, NVIDIA employs capital and technology to cement its dominance in AI computing.
Oracle's Comeback: The Cloud Infrastructure Ambitions Behind a $300 Billion Contract
When Larry Ellison briefly ascended to the position of the world's richest man amid Oracle's stock surge, few realized that this legacy software giant had quietly secured a pivotal position in the AI infrastructure race. Oracle's five-year, $300 billion cloud services contract with OpenAI, commencing in 2027, not only catapulted its remaining performance obligations (RPO) to $455 billion but also established it as a formidable force in AI infrastructure.
Oracle's resurgence is no mere coincidence. After OpenAI's exclusive partnership with Microsoft began to loosen, this database and enterprise software specialist seized the opportunity. The initial $3 billion cloud deal served as a trial run; the subsequent $300 billion mega-order cemented its role as OpenAI's core partner. Unlike NVIDIA's chip-centric focus, Oracle provides full-stack services, ranging from data center construction to cloud platform operations, complementing rather than competing with NVIDIA.
More notably, Oracle plays a pivotal role in the 'Stargate' project. Backed by the Trump administration and envisioned as a $500 billion AI infrastructure initiative, this project was seen as America's strategic move to counter global AI competition. Although progress lagged—initial $100 billion pledges dwindled to just one data center by late 2025—Oracle's eight data centers in Abilene, Texas, remain on track for completion in 2026. These facilities will synergize with OpenAI's other projects, forming key nodes in its computing network.
However, Oracle's gamble carries inherent risks. With free cash flow at negative $394 million in FY2025, the company has vowed to boost cloud infrastructure revenue from $18 billion to $144 billion in the coming years. This aggressive forecast hinges heavily on OpenAI's expansion; any downturn in the AI industry would exert significant pressure on Oracle's performance. But for Ellison, this is a must-win bet—having missed the cloud era, Oracle aims to leapfrog into prominence via AI infrastructure.
OpenAI's Balancing Act: Building Computing Autonomy Amidst Giants
'We must excel at three things: outstanding AI research, products that people need, and solving unprecedented infrastructure challenges.' Sam Altman's words encapsulate OpenAI's core strategy. With 70 million weekly active users demanding computing power and a long road to AGI, this AI pioneer is weaving a computing network amidst giants to secure support without relinquishing technical autonomy.
OpenAI's strategy revolves around 'multi-vendor checks-and-balances.' From relying solely on Microsoft Azure to now partnering deeply with NVIDIA, Oracle, and Microsoft, it prioritizes computing security. The $100 billion NVIDIA deal ensures a steady chip supply; Oracle's $300 billion contract provides cloud infrastructure; while the non-binding Microsoft MoU maintains strategic flexibility. This 'don't-put-all-eggs-in-one-basket' approach grants OpenAI significant bargaining power.
This balance is most evident in OpenAI's AGI control. Reports highlight its 'AGI clause' negotiations with Microsoft—whether Microsoft shares profits when superhuman AI emerges. Through its unique nonprofit parent structure, OpenAI ensures that all safety decisions align with 'benefiting humanity,' maintaining core tech control despite heavy investments.
Yet, infrastructure costs burden OpenAI. It is projected to burn through $115 billion in cash by 2029, with server leasing alone costing $100 billion in 2030. This 'burn rate' demands a delicate balance between technical breakthroughs and commercialization. Fortunately, its growing user base supports monetization, while diversified computing layouts reduce the risk of single-partner overpricing.
The Infrastructure Boom's Energy Crisis and Industry Shakeout
When Jensen Huang predicted that global AI infrastructure spending would hit $3–4 trillion by the end of the decade, he revealed not just market opportunities but severe industry challenges. This unprecedented boom faces energy supply constraints, environmental costs, and geopolitical tensions—reefs that may determine the outcome of the AI race.
Energy consumption is the most pressing bottleneck. IEA data shows that global data centers consumed 415 TWh in 2024 (1.5% of global electricity), soaring to 945 TWh by 2030—exceeding Japan's current annual use. A typical AI data center consumes as much electricity as 100,000 households; OpenAI's 10 GW project alone could power millions of homes. This demand is reshaping global energy—BloombergNEF predicts that renewable power generation will surge by 84% in five years.
Firms are adopting divergent energy strategies. Meta's Hyperion data center in Louisiana partners with nuclear plants for 5 GW capacity; meanwhile, Musk's xAI in Tennessee became the largest local polluter using gas turbines, allegedly violating the Clean Air Act. This contrast highlights the environmental dilemma of AI infrastructure: balancing growth with sustainability remains an unresolved challenge.
Geopolitics also shapes infrastructure layouts. The U.S. accounts for 45% of global data center electricity use, with its data center demand driving nearly 50% of national electricity growth, making AI infrastructure a national security issue. 'Stargate's political backing and NVIDIA's Intel investment reflect efforts to maintain U.S. dominance in AI chips and data centers. Globally, data centers are emerging as new battlegrounds for tech sovereignty, potentially fragmenting supply chains.
An industry shakeout is inevitable. With infrastructure thresholds soaring, smaller AI firms will struggle to afford model training and deployment, concentrating resources among OpenAI, Meta, and other giants. Traditional tech firms' fates are also being rewritten—Oracle leverages AI infrastructure for a comeback; Intel seeks revival via NVIDIA; while laggards face elimination. This computing arms race is reshaping the tech power map.
Computing Power as the New Civilization Pact
Examining the intricate ties among NVIDIA, Oracle, and OpenAI—and the global AI infrastructure boom—reveals not just commercial rivalries but a refactoring (reconstruction) of the foundations of future civilization. From Huang's 'computing power as new oil' to Altman's 'infrastructure as the future economic bedrock,' tech leaders agree: whoever controls AI infrastructure holds the key to tomorrow.
This multitrillion-dollar gamble essentially lays the physical groundwork for the AI era. Every data center completion, chip breakthrough, and giant partnership agreement shapes the basic rules of AI with humanity. Like railways and power grids in the Industrial Revolution, today's AI infrastructure will define decades of tech paths and economic landscapes.
Yet, amidst the tech frenzy, rationality is essential. When data center electricity use surpasses that of the steel and cement industries combined, sustainable models become imperative. As a few tech giants concentrate computing resources, ensuring tech inclusivity—rather than exacerbating inequality—is vital. When AI infrastructure becomes a geopolitical tool, international collaboration and regulation grow increasingly urgent.
NVIDIA, Oracle, and OpenAI's 'computing power triopoly' continues, with each move crafting a new civilization pact. The ultimate winners will need not just capital and tech but wisdom to balance commercial interests, social values, and environmental sustainability. After all, the true AI revolution requires not just computing might but human-centric development—a principle all participants should remember.