Brand Attraction·Reconstructing Growth|Comprehensive Insight into the Growth Potential of Chinese Brands' Globalization by 2025
![]() 07/03 2025
07/03 2025
![]() 722
722


(I) Chinese Brands Embark on the "Global Growth" Stage

Over the past two decades, Chinese enterprises have undergone significant transformations. Initially, they ventured into foreign trade, achieving exports through OEM processing, marking the first step of globalization. Subsequently, they entered the era of product globalization, establishing overseas product presence, opening branches, and engaging in cross-border e-commerce to tap into online channels tailored to international markets. In the third stage, many Chinese enterprises operating overseas have gained brand awareness, prioritizing market localization and adopting an international perspective focused on global consumers, thereby imbuing Chinese products with universal values.
In this new phase, with evolving overseas market conditions, the issue of growth has taken center stage, with brand value emerging as the core driver of this growth.
(II) Chinese Brands' "Global Growth": A Synergy of Internal and External Factors
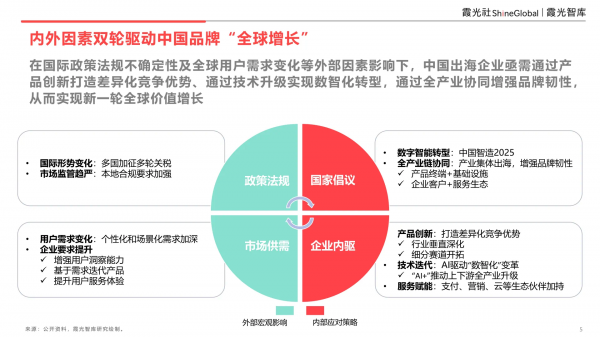
Chinese brands are accelerating their "global growth" driven by both internal and external factors.
Amid external uncertainties such as shifting international policies and regulations, and evolving global consumer demands, Chinese enterprises operating overseas must create differentiated competitive advantages through product innovation, achieve digital and intelligent transformation via technological upgrades, and enhance brand resilience through holistic industry chain coordination. This approach aims to propel a new wave of global value growth.
(III) External Factors Shaping Chinese Brands' Global Growth: International Policy Uncertainty + Shifts in Global Market Supply and Demand
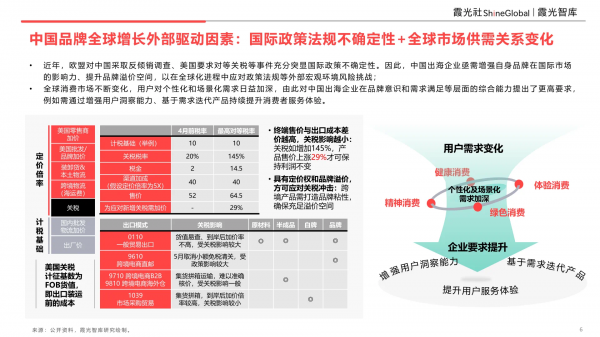
Recent events, including the EU's anti-dumping investigations against China and the US's push for reciprocal tariffs, underscore the unpredictability of international policies. Consequently, Chinese enterprises operating overseas must urgently strengthen their brands' international influence and increase brand premium to navigate external macro-environmental risks and regulatory challenges in the globalization process.
The global consumer market is in constant flux, with users' demands for personalized and scenario-based services intensifying. This poses higher demands on Chinese enterprises' comprehensive capabilities in brand awareness and demand satisfaction. For instance, it is imperative to enhance user insight capabilities and continuously refine consumer service experiences through demand-driven product iterations.
(IV) Internal Drivers of Chinese Brands' Global Growth: National Initiatives + Self-Motivated Enterprises

The nation advocates digital and intelligent transformation for overseas enterprises, promoting the manufacturing industry's evolution towards a digital and intelligent "Made in China 2025," thereby enhancing Chinese brands' international competitiveness.
Against the backdrop of the digital economy's rise and global consumption upgrades, Chinese enterprises have achieved technological breakthroughs and innovations in certain industry sectors, equipping them to compete in the global market. They must now venture overseas to convert these advantages into brand premium, further bolstering Chinese intelligence's overall strength and international market competitiveness through global industrial layouts, optimized resource allocation, and reduced overseas operating costs such as logistics and channels.
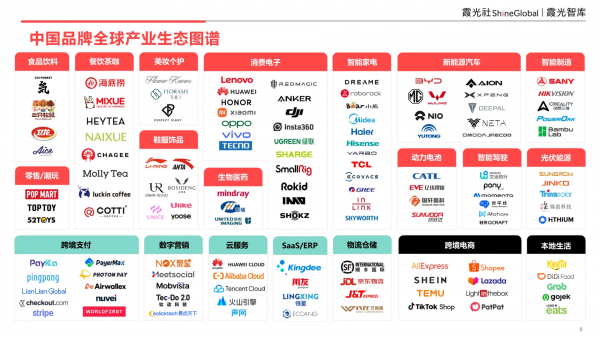
(V) The Global Industrial Ecosystem Map of Chinese Brands


Observation 1: Overseas Market Boundaries Continue to Expand, with Increasing Scale and Volume Yearly
Diverse categories spawn varied expansion paths, gradually encompassing global core markets.
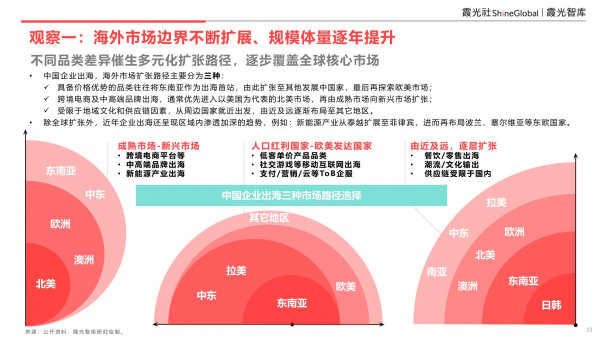
Chinese enterprises venturing overseas primarily adopt three expansion paths:
- Price-advantaged categories often initiate their overseas journey in Southeast Asia, expanding into other developing countries before exploring European and American markets.
- Cross-border e-commerce and mid-to-high-end brands typically prioritize entering the North American market, represented by the US, before expanding from mature markets to emerging ones.
- Due to geographical, cultural, and supply chain considerations, enterprises start in neighboring countries, gradually expanding to other regions from near to far.
Apart from global expansion, overseas enterprises have recently shown a trend towards deeper intraregional penetration. For instance, the new energy industry has expanded from Thailand and Vietnam to the Philippines, and further to Eastern European countries like Poland and Serbia.
Transitioning from rapid growth to a stable phase, the need for refined operations drives the comprehensive growth of the overseas service ecosystem.
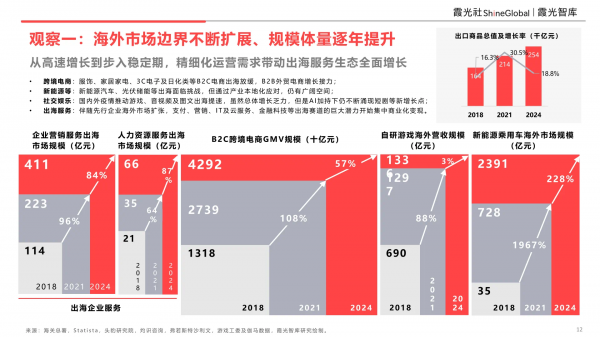
Whether cross-border e-commerce, enterprise marketing services, human resources services, or new energy vehicles, their overseas market revenue has surged significantly in recent years:
- Cross-border e-commerce: Growth in B2C e-commerce for clothing, home appliances, 3C electronics, and daily chemicals has slowed, with B2B foreign trade e-commerce taking over the growth baton.
- New energy, etc.: New energy vehicles and photovoltaic energy storage face challenges overseas but still have ample room for growth through industrial localization.
- Social entertainment: The domestic and international pandemic has accelerated the overseas expansion of games, audio and video, and graphic content. While overall growth is sluggish, new growth points like short dramas continue to emerge, supported by AI.
- Overseas services: As pioneering enterprises expand overseas, the vast potential of sectors like payment, marketing, IT and cloud services, and fintech has begun to be commercialized and monetized.
Observation 2: Chinese Brands Expand the Scope of Global Business Operations
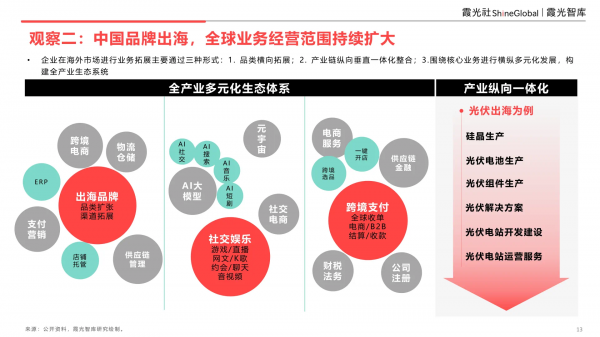
Enterprises primarily expand their overseas business through three forms:
- Horizontal category expansion
- Vertical integration of the industrial chain
- Diversified development in both horizontal and vertical directions around core businesses to build a comprehensive industrial ecosystem
Taking the overseas expansion of photovoltaic products as an example, enterprises expand from upstream silicon crystal production to the manufacture of photovoltaic cells and modules, eventually developing a comprehensive set of photovoltaic solutions encompassing photovoltaic power station development, construction, and operation services.

During their overseas expansion, enterprises must address the challenge of upstream supply not meeting downstream demand. With experience, they can vertically expand their business to serve other similar overseas enterprises, offering services like warehousing and IT systems.
Cross-border e-commerce enterprises form a replicable model based on "small front-end" + "large middle platform," aiding brands in horizontal cross-category development, becoming brand incubation centers. Typical representatives include Anker Innovation and Savvy.

Observation 3: Technological Strength Significantly Enhances Product Power
The AI technology revolution is driving consumer electronics to evolve from "functional entities" to "intelligent entities."

Insta360, a recently listed company that began as an imaging equipment maker, combined its hardware technology with AI. This not only diversified product functionalities but also allowed users to personalize photos or videos on intelligent imaging equipment, propelling Insta360 into a beloved sports camera brand among overseas consumers.
Building a smart lifestyle for global users centered around smart home living scenarios.
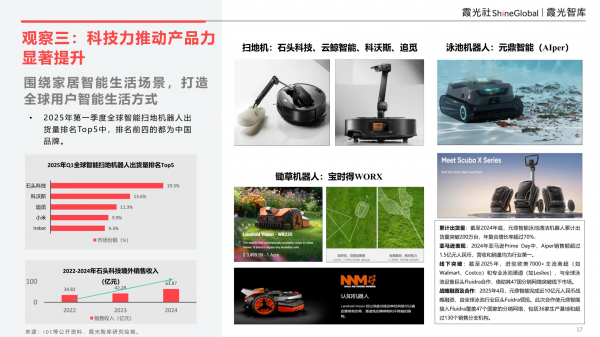
In addition to Insta360, smart glasses brand Rokid, robot vacuum cleaner brands Stone Technology and NARWAL Robotics, pool robot brand Yuanding Intelligence, etc., all focus on smart home living scenarios to create a smart lifestyle for users. Public data reveals that in Q1 2025, the top four brands in global smart robot vacuum cleaner shipments were all Chinese.
Observation 4: Marketing Power Significantly Enhances Brand Power
It's not about functional value but emotional value.

Public data projects that the global healing economy market will reach $7 trillion by 2025. German philosopher Byung-Chul Han once observed, "Today, what we ultimately consume is not the commodity itself but emotions. Commodity consumption may have an end, but emotional consumption is boundless." As a crucial aspect of the global healing economy, emotional consumption will usher in a vast market.
In April 2025, Pop Mart launched Labubu 3.0, which swiftly became a top-tier IP in the global fashion toy market due to its "ugly cute" design, "hunger marketing," and star effect, sparking a buying frenzy in South Korea, Australia, the US, and beyond, with temporary stockouts and price speculation emerging. In Q1 2025, Pop Mart's overseas revenue surged nearly 480% year-on-year, with a growth rate of about 900% in North America, and its share price rose by 191% cumulatively in 2025.
From product globalization to cultural globalization, new Chinese tea drinks drive the growth of cultural value, which in turn enhances the brand's commercial value.

The rise of emotional consumption has also fueled the rapid growth of new tea drinks that blend Eastern culture and tea culture overseas, propelling Chinese culture globally and enhancing the brand's commercial value.
Jasmine Milk White, a new tea brand venturing overseas, opened its first overseas store in New York, USA, in April 2024, making a splash and occupying a brand highland. Subsequently, Jasmine Milk White turned to Southeast Asia, choosing to open its first Southeast Asian store at Siam Paragon, a core business district in Thailand. From mature markets to emerging ones, the "Oriental Modern" design concept and cultural heritage provide Jasmine Milk White with a continuous driving force for overseas market expansion.

Observation 5: Achieving Efficiency and Resilience in Parallel Through Holistic Industry Chain Integration
China's new energy vehicles: From "selling globally" to "taking root globally"
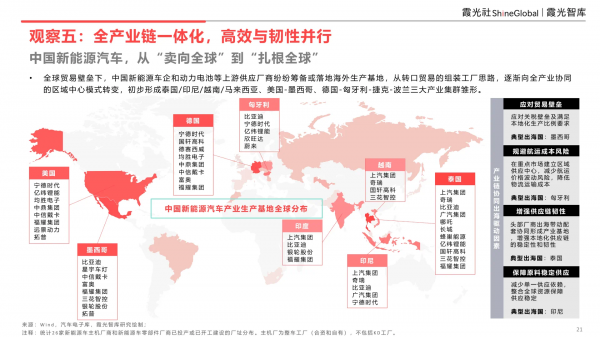
Amid global trade barriers, Chinese new energy vehicle enterprises and upstream suppliers like power batteries are preparing or establishing overseas production bases, gradually shifting from the idea of assembly factories for entrepot trade to a regional hub model with industry-wide coordination. This has initially formed the prototype of three major industrial clusters: Thailand/Indonesia/Vietnam/Malaysia, the United States-Mexico, and Germany-Hungary-Czech Republic-Poland.
The localization of Chinese enterprises' overseas market layouts has deepened further.
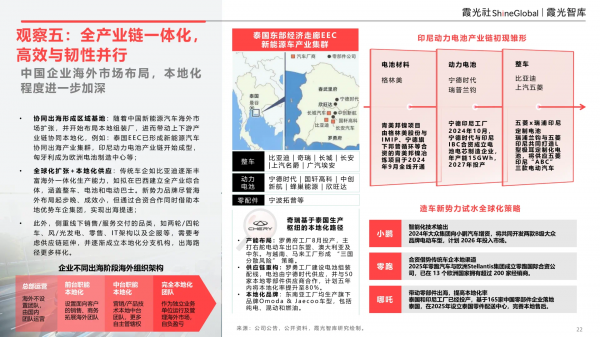
Collaborative overseas expansion forms regional bases: As China's new energy vehicle market expands overseas and local assembly plants are established, this has further driven the localization of upstream and downstream industrial chains. For example, the EEC in Thailand has formed a new energy vehicle collaborative overseas industrial cluster, the Indonesian power battery industrial chain has started to take shape, and Hungary has become a European battery manufacturing center.
Global expansion + local supply: Traditional automakers like BYD are gradually enhancing their overseas integrated production capabilities, such as planning to establish an industrial complex in Brazil encompassing complete vehicles, batteries, and electric buses. While new force brands have a later start and smaller overseas footprints, they achieve accelerated overseas expansion through joint ventures and collaborations, leveraging local advantageous automotive groups.
Observation 6: Behind Every Great Brand, There Lies a Formidable Industry Leader
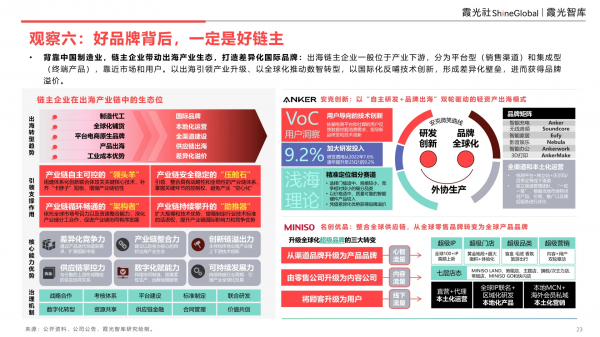
Overseas-bound chain master enterprises are typically positioned in the downstream sector of their respective industries, categorized into platform-based (sales channels) and integrated (end products) enterprises, closely aligned with market and consumer demands. Ultimately, a brand's success hinges on an enterprise's mastery over the supply chain. In the past, companies could build robust brands within a single market by leveraging marketing and channel strategies to boost popularity. However, in today's globalized landscape, brands confront a complex and diverse market. A lack of robust supply chain control renders it impossible to guarantee consistent product power and quality. This compels enterprises to assume the role of chain masters, exercising control over the entire supply chain process.

Observation 7: Deep Integration from "Content E-commerce" to "Intelligent Social E-commerce"
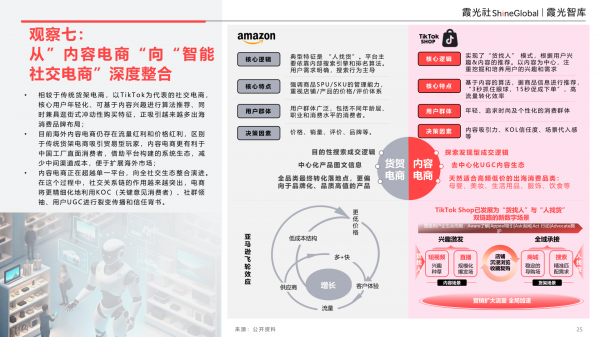
In contrast to traditional shelf e-commerce, content e-commerce platforms like TikTok boast a younger user base. They make algorithmic recommendations based on content interests and exhibit window-shopping-like impulse purchasing characteristics, attracting a growing number of overseas consumer brands. Content e-commerce is evolving beyond a single platform to encompass a comprehensive social ecosystem. In this evolution, the significance of social relationship chains is becoming increasingly pronounced. E-commerce platforms are now more precisely leveraging KOCs (Key Opinion Consumers), community leaders, and user-generated content (UGC) for viral marketing and brand trust endorsement. For instance, private domain operations via WhatsApp communities, brand community building on Discord, and viral TikTok challenges facilitate the integration of "social fission + trust conversion," transcending the confines of closed-loop transactions within content platforms like TikTok Shop and Instagram Shopping.
Observation 8: "Omni-channel Operation" Becomes the Core Competitiveness

As consumers seek both efficiency and experience, "omni-channel operation" becomes indispensable. This approach enables the connection of cross-platform data, establishing a unified data mid-platform that integrates data from third-party cross-border e-commerce platforms, DTC independent stations, social media, advertising platforms, and more. This comprehensive user persona guides omni-channel marketing and operational decisions. Furthermore, the overseas expansion of consumer goods relies heavily on online e-commerce channels, where marketing customer acquisition and product mix are crucial for market growth. Leveraging AI technology applications and cloud platforms, overseas enterprises can accurately identify localized categories, achieve intelligent marketing, and foster sustainable global business growth. Overseas technology service providers, such as vertical SaaS platforms, are also expanding into foreign markets, following the footsteps of retail, manufacturing, and logistics. They are beginning to provide solutions for local enterprises, taking root locally, and achieving dual growth by serving both Chinese enterprises and expanding overseas.

For overseas enterprises reliant on offline channels, achieving offline omni-channel operation necessitates deep integration of physical business and digital tools, encompassing the entire chain from localized operations to global collaboration.

Observation 9: Intelligence Empowers the Entire Industrial Upgrading of Chinese Overseas Enterprises
Emerging technologies such as large models and generative AI are empowering supply chain decision optimization, emerging as key drivers in the transformation of China's overseas supply chains.
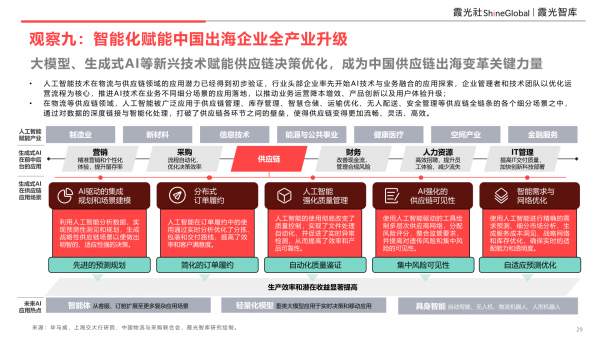
The potential applications of artificial intelligence in logistics and supply chain management have been initially validated. Industry leaders are pioneering the integration of AI technology and business operations. Enterprise managers and technical teams are focused on optimizing operational processes, promoting the application and implementation of AI technology across various business segments. This drives cost reduction, efficiency enhancement, product innovation, and user experience upgrades. In supply chain sectors like logistics, AI is extensively used in various segments of the entire supply chain, including supply chain management, inventory management, smart warehousing, transportation optimization, unmanned delivery, and safety management. By deeply linking and intelligently processing data, AI breaks down barriers between different supply chain links, fostering a smoother, more flexible, and efficient supply chain.


Observation 10: Service Ecology Empowers and Symbiosis Drives Growth
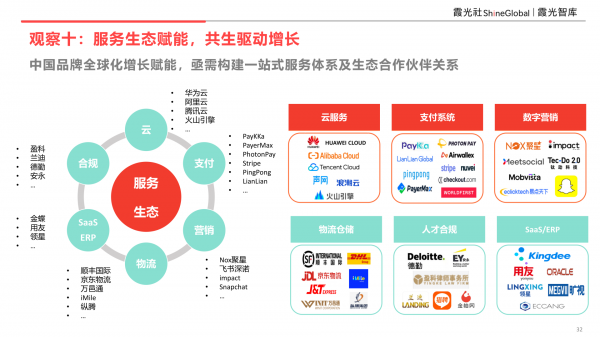
Currently, Chinese enterprises face escalating challenges when expanding overseas, ranging from infrastructure such as cloud services, network infrastructure, logistics, and warehousing to various links like payment systems, digital marketing, and talent compliance. The required capabilities are becoming increasingly specialized and systematic, often beyond the scope of a single enterprise. As the service provider ecosystem gradually matures, the business ties between service enterprises and overseas brands have deepened, and the resulting growth impact will become increasingly pronounced.

(1) Payment System: PayKKa
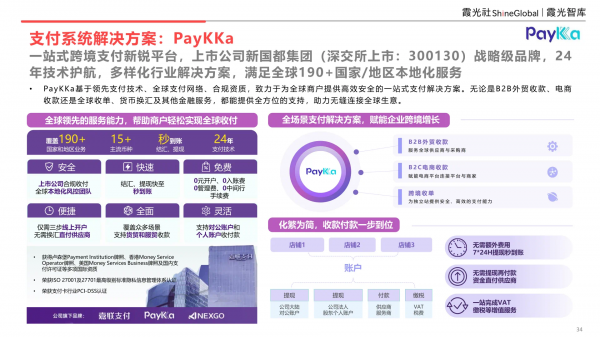
Payment is a pivotal aspect of commerce, influencing the smoothness of the transaction experience. PayKKa is a payment platform with profound technical expertise. Leveraging cutting-edge payment technology, a global payment network, and compliance qualifications, PayKKa provides efficient and secure one-stop payment solutions to global merchants. Currently, this solution supports localized services in over 190 countries/regions worldwide. Whether it's B2B foreign trade collection, e-commerce collection, global acquisition, currency exchange, or other financial services, PayKKa offers comprehensive support, facilitating seamless global business connectivity.
(2) Influencer Marketing: Nox Influencer
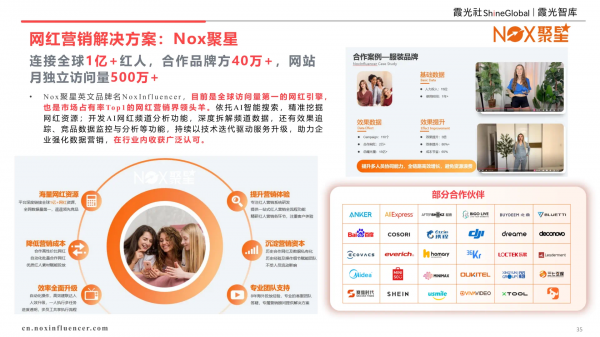
Content e-commerce is evolving from a single platform to an integrated social ecosystem. Within this ecosystem, influencer marketing is garnering increasing attention from overseas brands. Nox Influencer, currently the world's most visited influencer engine and the market leader in influencer marketing, leverages AI-driven intelligent search to accurately mine influencer resources and deeply analyze channel data, empowering enterprises with data-driven marketing strategies.
(3) Cloud Service: Alibaba Cloud
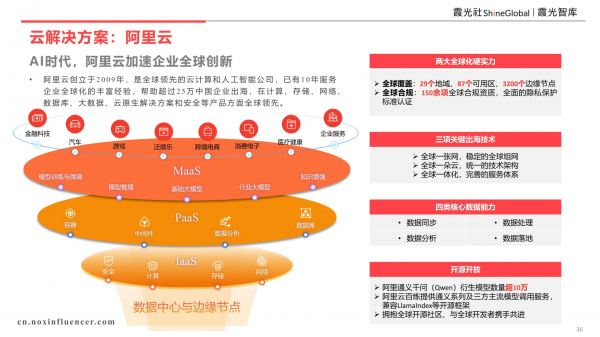
2025 marks a year of significant enthusiasm for AI. From the start of the year, various AI large model products have showcased an explosion of intelligence. Consequently, many platforms or overseas brands have begun exploring AI integration. However, the prerequisite for utilizing AI is cloud computing support. Established in 2009, Alibaba Cloud is a global leader in cloud computing and artificial intelligence, boasting a decade of rich experience in serving enterprise globalization. It has assisted over 250,000 Chinese enterprises in their overseas expansion and is globally renowned for its products in computing, storage, networks, databases, big data, cloud-native solutions, and security.







