Data Indicates: Majority of Enterprises See 5G as Key to Future Competitiveness
![]() 09/16 2025
09/16 2025
![]() 517
517
Recently, Ericsson unveiled a report titled 'The State of Enterprise Connectivity—United States 2025'. In this comprehensive study, Ericsson surveyed a wide range of U.S. enterprises regarding their 5G applications. The findings, based on this survey, highlight that amidst economic uncertainties, talent shortages, and a surge in digital transformation demands, U.S. companies are placing unprecedented emphasis on connectivity technologies, with 5G emerging as a core pillar for future competitiveness. Simultaneously, advancements in AI, automation, and IoT are driving urgent new connectivity needs.
While 5G has been commercially available for over six years, its application effectiveness across various industries has not yet reached the anticipated optimal state. However, after six years of practical deployment, the industrial chain has continuously matured, application costs have steadily decreased, and enterprise acceptance has continually improved, indicating a positive trend in 5G industry applications. As the survey suggests, most enterprises view 5G as a cornerstone of future competitiveness, and in the "second half" of 5G development, its application effectiveness within enterprises is expected to further manifest.
What does the data reveal about 5G's role as the cornerstone of enterprise future competitiveness?
The 'State of Enterprise Connectivity—United States 2025' report states that 93% of enterprises believe secure, high-performance networks like 5G are crucial for the U.S. to maintain its global technological leadership. Meanwhile, 92% state that next-generation connectivity is vital for unlocking business innovation. Enterprises are particularly focused on how 5G can support bandwidth-intensive and latency-sensitive applications, such as AI-driven analytics, automated processes, and massive device connectivity.
Regarding the relationship between 5G and AI, enterprises unanimously view them as symbiotic. The report notes that 88% of U.S. companies believe 5G is essential for optimizing AI applications in the workplace, while 90% state that AI has already enhanced network security by automatically detecting and resolving issues. AI also helps offset persistent labor shortages. Nearly 90% of companies report that AI is improving the skills of network managers by automating analysis and reducing manual tasks. This interaction reflects a virtuous cycle: 5G enables the high-speed data transmission required by AI tools, while AI enhances the performance and security of these networks.
The survey report indicates that with the proliferation of 5G, IoT adoption is accelerating, with 58% of enterprises having already deployed IoT solutions and another 34% planning new investments. Among IoT deployment cases, 54% have implemented security systems, 41% video surveillance, 38% GPS and route management, 37% fleet management, and 35% predictive maintenance.
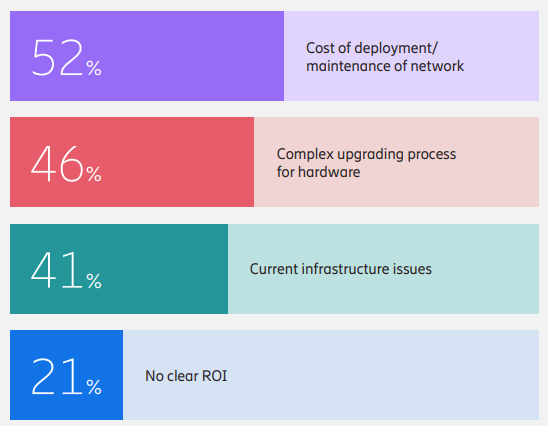
However, numerous obstacles remain for 5G application in enterprises. The report shows that 52% of companies view the cost of deploying and maintaining networks as the biggest hurdle, 46% cite the complexity of upgrading existing hardware systems for compatibility as a significant obstacle, and 41% believe issues with existing infrastructure hinder 5G adoption.
Additionally, nearly 80% of respondents state that delays in spectrum auctions hinder 5G deployment and innovation, highlighting the importance of regulatory policies for competitiveness. Relevant legislators have called for the U.S. Federal Communications Commission to regain spectrum auction rights to provide more spectrum resources for 5G.
The "Second Half" of 5G Begins: Enterprises Leverage 5G for Digital Application Effectiveness
In a previous article, 'Google's Former CEO Claims "5G Race: U.S. Lags Behind China," But Don't Overlook America's Late-Mover Advantage!', I argued that U.S. 5G development was relatively slow in previous years, primarily constrained by limited radio spectrum, a small number of equipment and terminal vendors, and an immature ecosystem. However, the commercialization of 5G is a marathon, with its ultimate goal lying in application—enabling various sectors of the national economy to adopt 5G technology for digital transformation and enhancing industrial strength. Delays in early infrastructure construction do not necessarily imply future 5G application lags. Ericsson's survey report reveals a continuous rise in U.S. enterprise demand for 5G, laying the foundation for future 5G application deployment. The U.S. already possesses certain conditions for 5G application development, and its late-mover advantages will become evident as infrastructure continues to improve, primarily including:
First, Technological Integration: Applying 5G across various industries is essentially a process of integrating diverse technologies. 5G must combine with various ICT technologies such as AI, cloud computing, and big data to achieve industry applications. The U.S. holds an absolute advantage in comprehensive technological strength, with leading positions in AI, cloud computing, and big data. Although 5G infrastructure was previously a weakness, by referencing existing experiences, it can rapidly form integrated technological applications, demonstrating its late-mover advantage.
Second, Industrial Foundations: Applying 5G in various industries requires a solid foundation within those sectors, including their technological base and existing digitalization levels, which determine the effectiveness of 5G industry applications. The U.S. digital economy ranks first globally, with industrial digitization accounting for over 80%, indicating that U.S. industries have broad and deep applications of core digital economy technologies and leading digitalization levels. With this foundation, if industries demand 5G applications, rapid deployment is feasible, thus leveraging 5G's late-mover advantage.
Third, Industry Promotion: The U.S. industrial sector is also promoting 5G technology and deployment progress through various other means. U.S. companies in the 5G-related industrial chain have not waited passively for operators' slow 5G deployment but have actively advanced it through multiple approaches, including promoting CBRS shared spectrum bands, providing enterprise private network spectrum authorizations, and facilitating private network deployment. Many vendors have continuously innovated, introducing 5G cloud core networks and edge computing solutions to assist operators and enterprises in rapidly implementing 5G applications.
U.S. companies view 5G as the cornerstone of future competitiveness. Against the backdrop of China's global leadership in 5G infrastructure construction, 5G should also become a crucial pillar of enterprise competitiveness in the future. Data shows that as of the end of July this year, China has cumulatively built 4.598 million 5G base stations and 30.532 million gigabit ports, achieving "gigabit connectivity in every county, 5G in every township, and broadband in every village." Over the past few years, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has organized and implemented the '5G Application "Sailing" Initiative', promoting large-scale industrial internet applications. Nationwide, there are over 20,000 '5G+Industrial Internet' construction projects, with new models and formats such as "driverless mines," "dark factories," and "smart ports" gradually expanding. In the consumer sector, new information consumption products and models like smart terminals, e-commerce livestreaming, immersive shopping, and digital cultural tourism are flourishing. 5G applications have been implemented and promoted in over 500 top-tier hospitals, covering pre-hospital emergency care, inpatient treatment, and post-discharge rehabilitation processes.
Building on this foundation, 5G should play a more significant role in empowering enterprise digitalization. In my view, 5G development has entered its "second half." In the first half, "human connectivity" developed rapidly, but constrained by factors such as the maturity of 5G IoT technology standards, industry user acceptance, application costs, and enterprise investment pressures due to slowing economic growth, the scale of 5G IoT connections remains limited, and deep industry application penetration still needs strengthening. In the second half of 5G, "IoT connectivity" must be prioritized, bringing 5G capabilities into various scenarios and processes across all sectors of the national economy through deep IoT penetration, truly enabling 5G to empower industries.
For development in the second half, on the one hand, we can fully promote the construction of 5G private networks, enriching IoT connection scales in private network environments and bringing more application scenarios to enterprises. On the other hand, 5G development should fully integrate into major initiatives like 'AI+' and 'Data Factor X'. AI has become a new production tool, and data has become a new production factor, jointly constituting important drivers of new quality productivity. Various industries are deeply engaged in 'AI+' and 'Data Factor X' initiatives, and various IoT applications should fully integrate with these initiatives, leveraging IoT's differential advantages in sensing and transmission to create a multiplier effect, jointly promoting industry transformation and upgrading.
The competition in 5G is not just a short-term contest over 5G technology and infrastructure construction. As an enabling technology, 5G's ultimate goal is to facilitate the digital transformation and competitiveness enhancement of various sectors of the national economy. We anticipate that the "second half" of 5G will become a significant source of core competitiveness for enterprises across industries.






