Amid the cyclical recovery of the broader market, how will Innoscience narrate its new story?
![]() 07/19 2024
07/19 2024
![]() 638
638
The semiconductor industry has embarked on a cyclical recovery.
According to iFinD statistics from Tonghuashun, as of now, 37 semiconductor stocks have disclosed their first-half performance forecasts, with 27 stocks reporting positive outlooks, either turning losses into profits or expecting growth, representing a positive outlook rate of over 70%. Changchuan Technology leads the pack with the highest forecasted net profit growth, temporarily ranking as the "King of Forecasted Net Profit Growth" among semiconductor stocks in the first half of the year.
In response, China Minmetals Securities believes that "the semiconductor cycle typically lasts 3-5 years, and we are currently in the upswing of the fifth cycle." As the broader market warms up, Innoscience, the global leader in the third-generation semiconductor silicon-based gallium nitride (GaN) field, is also sprinting towards the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. It has recently appointed CITIC CLSA Securities Limited, Huatai Financial Holdings (Hong Kong) Limited, and Jefferies Financial Group Hong Kong Limited as its overall coordinators.
Overall, the company boasts impressive development credentials. It is a leading enterprise in the global third-generation semiconductor silicon-based GaN field, having raised over RMB 6 billion in total funding since its inception and achieving a valuation of RMB 23.5 billion.
However, the flip side of the coin is significant profit pressure, coupled with an overall low industrial penetration rate. In this context, how will Innoscience unlock the key proposition of development?
Is Innoscience's development moat secure amidst industrial competition?
Power semiconductors are an "old concept."
Since the 1950s, this industry has evolved from silicon rectifiers to thyristors and then to insulated gate bipolar transistors. Since the turn of the century, wide-bandgap semiconductor materials, represented by silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), have gradually emerged. Due to their outstanding performance in extreme environments such as high voltage, high temperature, and high frequency, these materials are considered "stars of the future" in the power semiconductor field.
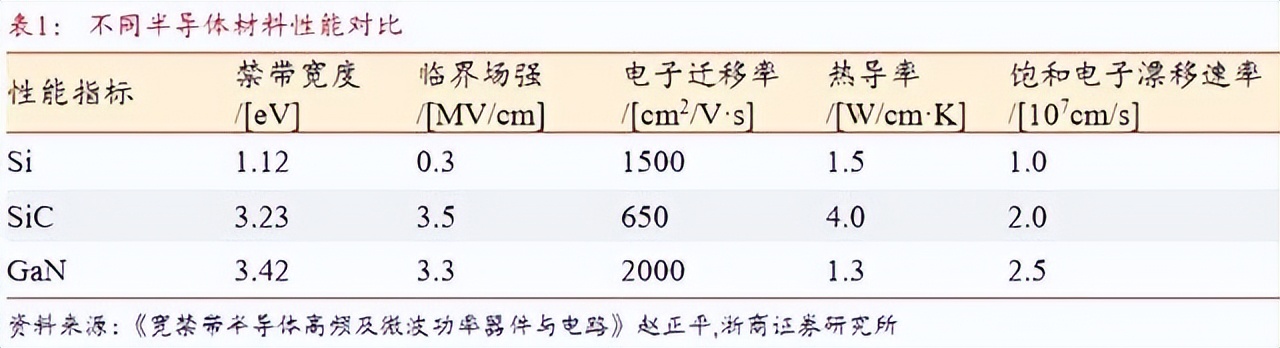
Among them, GaN semiconductors, with their advantages of large bandgap, high thermal conductivity, faster electron saturation speed, and stronger radiation resistance, are more suitable for applications in consumer electronics, new energy vehicles, 5G communications, and other fields, with continuously rising market value. According to Yole, an international authoritative research institution, the market value of GaN power devices will grow from USD 126 million in 2021 to USD 2.04 billion in 2028, with a compound annual growth rate of 49%.
The industry's heat has also propelled GaN power semiconductor companies like Innoscience into a period of rapid growth. The prospectus shows that from 2021 to 2023, Innoscience recorded revenues of RMB 68.215 million, RMB 136 million, and RMB 593 million, respectively, with a compound annual growth rate of 194.8%.
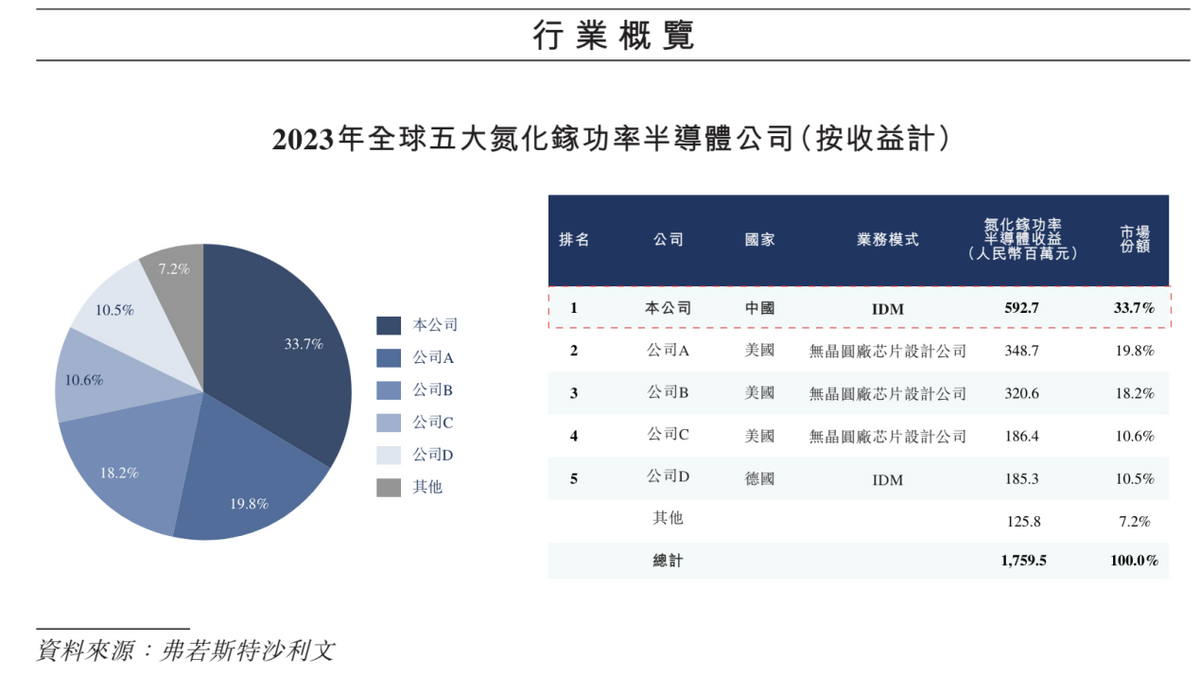
Furthermore, in terms of revenue, Innoscience ranked first among all GaN power semiconductor companies globally in 2023, accounting for 33.7% of the GaN power semiconductor industry's market share.
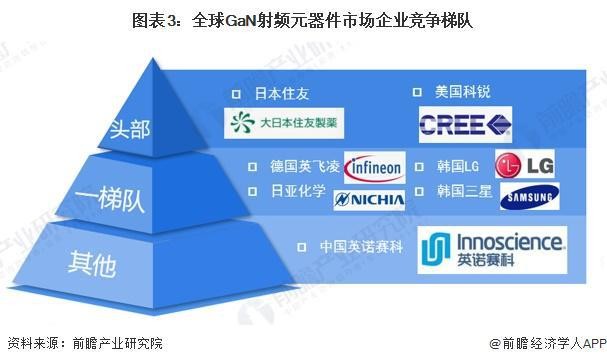
It is worth mentioning that as market interest climbs, competition in the GaN semiconductor industry is becoming increasingly fierce. From a supply chain perspective, the GaN supply chain can generally be divided into upstream substrates and epitaxial wafers, midstream devices and modules, and downstream systems and applications.
Currently, Innoscience primarily focuses on the GaN device segment, where foreign companies such as Japan's Sumitomo Electric, the US' Cree, Germany's Infineon, and South Korea's LG and Samsung have established leading positions. Domestically, in addition to Innoscience, companies like San'an Optoelectronics, Wente Technology, CEE, Jucan Optoelectronics, and QL Photonics are also actively deploying in this segment.
It can be said that it will not be easy for Innoscience to break through, so what development secrets does it possess, given its current market position and revenue performance?
Currently, Innoscience primarily derives its volume from the domestic market. The prospectus shows that from 2021 to 2023, Innoscience's domestic revenue was RMB 68 million, RMB 130 million, and RMB 535 million, accounting for 99.7%, 95.5%, and 90.2% of its total revenue for the respective years.
Focusing on the domestic market has a certain degree of rationality. Specifically, China is the world's largest consumer of power semiconductors, contributing about 40% of the power semiconductor market. Additionally, with the rapid development of consumer electronics, new energy vehicles, photovoltaics and energy storage, and data computing centers, the domestic GaN industry is also experiencing rapid growth. Data indicates that the GaN penetration rate is expected to reach 40% by 2026.
Overall, the domestic GaN power semiconductor market has considerable growth potential, and compared to the overseas giants, the competitive landscape is still relatively fragmented, which presents significant breakthrough opportunities for Innoscience.
So, what is the key to breakthrough? Innoscience's answer is "8-inch silicon-based GaN wafers + IDM production model."
It is understood that Innoscience is the world's first company to mass-produce 8-inch silicon-based GaN wafers and the largest manufacturer of 8-inch silicon-based GaN devices globally.
Compared to 6-inch silicon-based GaN wafers, 8-inch wafers offer significant advantages, including an 80% increase in die output and a 30% reduction in single-device costs, which is conducive to achieving greater economic benefits for enterprises. However, the production difficulty is also exponentially increased, considering challenges such as warpage, defect and dislocation densities, and leakage. Few domestic enterprises have attempted this, but Innoscience has successfully established this product line, largely thanks to its IDM model support.
Specifically, under the IDM business model, enterprises enjoy prominent operational autonomy, enabling them to coordinate design, manufacturing, packaging and testing, sales, and application support, thereby leveraging strong resource integration capabilities to facilitate rapid product iteration and achieve large-scale mass production.
According to the prospectus, as of the end of 2023, Innoscience's designed capacity reached 10,000 wafers per month, with cumulative shipments of GaN discrete devices exceeding 500 million units.
Industry insiders have recognized Innoscience's production model: "Once IDM enterprises establish a stable competitive landscape, their future development potential should not be underestimated." However, this model is not without flaws. IDM semiconductor enterprises are traditionally asset-intensive, with substantial upfront capital expenditures and long profit cycles.
In this context, what anchor points should Innoscience seize to achieve greater growth?
The Future of Innoscience: Building on Existing Strengths, Racing towards Incremental Growth
Innoscience's operating losses over the past three years have exceeded the total amount of its five rounds of funding since inception. According to the prospectus, Innoscience recorded annual losses of RMB 3.399 billion, RMB 2.206 billion, and RMB 1.102 billion from 2021 to 2023, respectively.
Innoscience explained that these losses were primarily due to significant depreciation of production equipment, as well as substantial R&D and sales and marketing expenditures. The prospectus data also reveals that from 2021 to 2023, Innoscience's R&D expenditures were RMB 662 million, RMB 581 million, and RMB 348 million, respectively; while sales and marketing expenditures were RMB 28.4 million, RMB 69.3 million, and RMB 90.1 million, respectively.
Of course, from an industry perspective, these investments are necessary. Firstly, the capital intensity of power semiconductors stems mainly from technology intensity. Experts point out that GaN excels in power density, bandwidth, reliability, and high-temperature tolerance compared to other materials, but its disadvantage lies in high product costs, which hinder mass production.
Focusing on Innoscience, it primarily engages in the development of 8-inch GaN-on-Si wafers. As mentioned earlier, products of this size pose greater challenges in technological development and process manufacturing, and Innoscience is continuously advancing towards mass production, which entails considerable expenses.
Secondly, a non-negligible issue is that the current market penetration rate of Innoscience is actually not high. Yole data shows that in 2022, GaN power devices accounted for only 0.3% of the total power semiconductor (power chips, power discrete devices, and modules) market.
Coupled with increasingly fierce market competition, especially with foreign companies like Infineon leading in technological strength and production capacity, the necessity for domestic manufacturers like Innoscience to strengthen market expansion through product development and sales continues to be prominent.
In this light, profit pressure is a prevalent phenomenon in the power semiconductor industry. Looking at other companies in the industry, for example, in 2023, CR Microelectronics' net profit attributable to shareholders decreased by 43.48% year-on-year, while R&D investment increased by 25.30%; San'an Optoelectronics' net profit attributable to shareholders fell by 46.49% year-on-year, while sales expenses increased by 10.63% and R&D expenses by 35.84%.
However, "how to profit" remains an unavoidable development proposition for these companies, especially for Innoscience, which is sprinting towards an IPO. It needs to unleash its commercial potential to a greater extent to gain broader capital recognition. In fact, from an industry prospect and enterprise competitiveness perspective, Innoscience has a solid growth foundation, and the future depends on how it amplifies its development certainty on this basis.
Currently, actively expanding into downstream markets with broader prospects, such as consumer electronics and automotive electronics, has become a necessary step for Innoscience and other companies seeking incremental growth.
According to Yole's report, the consumer electronics and automotive industries are the most significant growth segments in the GaN power semiconductor application market. It is expected that from 2022 to 2028, the former's market size will increase from USD 146 million to USD 1.307 billion, with a CAGR of 44%; while the latter's market size will grow from USD 6 million to USD 504 million, with a CAGR of 110%.
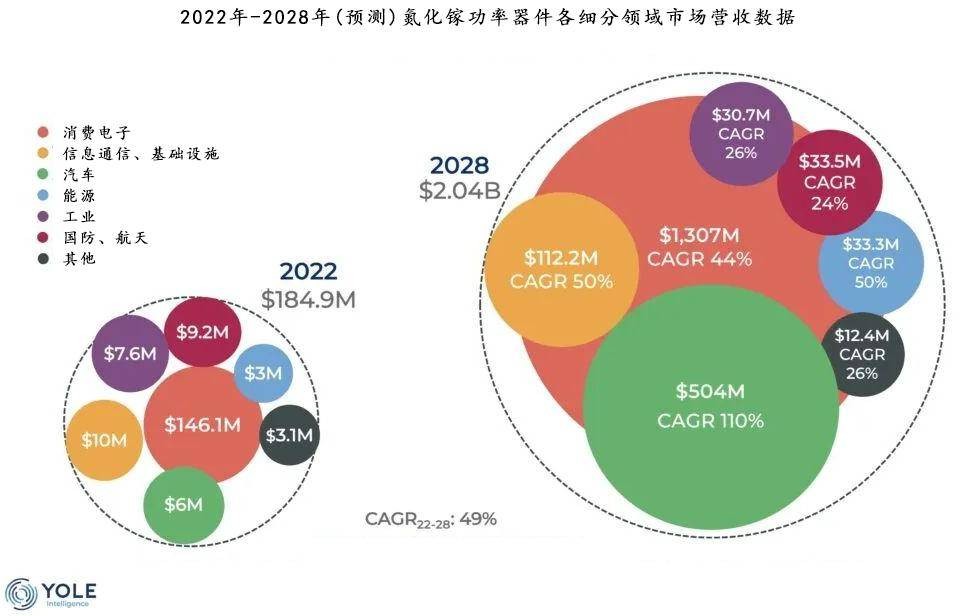
In consumer electronics, GaN technology is primarily used to meet the charging needs of mobile phones, computers, and other products. Chargers equipped with GaN power chips offer advantages such as high switching speed, high charging efficiency, fast heat dissipation, and compact size. Based on these product characteristics, the market size of GaN chargers is continuously expanding. According to BCC Research, the global GaN charger market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 90% from 2020 to 2025, reaching over RMB 60 billion.
Currently, consumer electronics brands like Xiaomi, OPPO, vivo, Honor, and Lenovo are also intensifying their layout of GaN chargers. Innoscience has established cooperative relationships with these manufacturers, and as its customer base continues to expand and partnerships tighten, Innoscience's position in the consumer electronics supply chain is expected to rise.
Moreover, the adoption of GaN semiconductors in automobiles is also a new trend, with technology as the core driver. Philip Zuk, Senior Vice President of Business Development and Marketing at Transphorm, once pointed out, "GaN power semiconductor technology, with its better performance, higher manufacturing yield, and lower material and manufacturing costs, aligns with the performance and cost structure required for automotive ODM and OEM success."
In this context, many companies in the supply chain are making relevant layouts. For example, CR Microelectronics' overall new energy sector (automotive and renewable energy) business accounted for 39% of its total revenue in 2023, and it has passed the highest level of ISO 26262 ASIL D certification for automotive functional safety management systems.
In 2024, Innoscience also officially launched its 100V automotive-grade GaN device, INN100W135A-Q, which has passed AEC-Q101 certification and is suitable for lidar in autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems, high-power density DC-DC converters, and Class D audio applications. In the future, the cooperation space between Innoscience and the electric vehicle market is worth looking forward to.

Of course, both the consumer electronics market and the new energy vehicle market are undergoing intelligent upgrades, with AI products and autonomous driving as concrete manifestations. In this context, for suppliers like Innoscience, keeping pace with downstream market demands and strengthening technological innovation and iteration remain essential actions to pursue.
After being fully honed in the domestic "training ground," there will be greater momentum for overseas expansion. Currently, Innoscience is strengthening its overseas market development. According to the prospectus, Innoscience has established subsidiaries in Silicon Valley, Seoul, and Belgium. From 2021 to 2023, the company's overseas market revenue accounted for 0.3%, 4.5%, and 9.8% of its total revenue for the respective years, indicating the growing importance of its overseas business and sending a positive signal to the market to a certain extent.
However, considering issues such as patent protection, the path to overseas expansion is destined to be long. The patent dispute between Innoscience and Efficient Power Conversion Corporation (EPC) in the US is a testament to this.
Overall, in the new era, the GaN semiconductor industry is on the rise, with both "established players" and "upstarts" striving to gain an advantage in the new round of competition. The race has just begun, and Innoscience, which is sprinting towards an IPO, has many stories yet to tell.
Source: Hong Kong Stocks Research Society