Global Semiconductor Startups, Q3 Funding Overview
![]() 10/18 2024
10/18 2024
![]() 544
544

Compiled and translated by Semiconductor Industry Vertical (ID: ICVIEWS)
The funding landscape for semiconductor startups in Q3 was particularly noteworthy.
Numerous new companies emerged in Q3 2024, including startups planning to offer customizable RISC-V-based IP for applications ranging from microcontrollers to data centers, high-speed data center interconnects, memory-computing LLM inference chips, and SoCs for surveillance cameras. Although no funding details were reported, AheadComputing also launched in the previous quarter to develop RISC-V core IP.
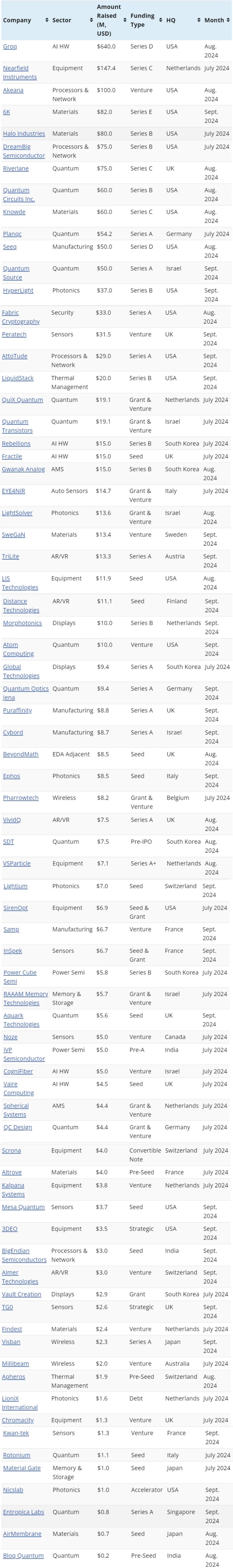
One of the largest funding rounds this quarter went to a company developing inspection and metrology equipment. Other areas attracting significant investment included SiC wafer processing, chiplet interconnects, and quantum computing. This report highlights 75 companies that collectively raised $2 billion in Q3 2024.
Chip Companies
Akeana stood out from obscurity with a $100 million funding round from investors including Kleiner Perkins, Mayfield, and Fidelity Ventures. Akeana offers customizable RISC-V-based IP. Its portfolio includes 32-bit RISC-V cores for applications ranging from embedded microcontrollers to edge gateways; 64-bit RISC-V cores with rich OS support and MMU; higher single-threaded performance 64-bit RISC-V cores optimized for next-generation devices, laptops, data centers, and cloud infrastructure; and a compute engine designed to offload matrix multiplication operations for AI acceleration. Akeana also provides a range of IP blocks necessary for creating processor SoCs, including coherent cluster caches, I/O MMUs, interrupt controller IP, and scalable mesh and coherence hub IP. Founded in 2021, the company is headquartered in Santa Clara, California, USA.
DreamBig Semiconductor raised $75 million in its Series B funding round, led by Samsung Catalyst Fund and the Sutardja Family, with participation from new investors Hanwha Corporation, Event Horizon, and Raptor Capital, as well as existing investors UMC Capital, BRV, Ignite Innovation Fund, and Grandfull Fund. DreamBig provides an interconnect fabric platform for chip-based designs, eliminating the need for a silicon interposer, and features open-standard interfaces and architecture-agnostic support to enable customers to combine CPUs, AIs, accelerators, IOs, networks, and memory chips in a single package. Its architecture weaves HBM interfaces into the chip hub fabric, enabling direct access from all chips to 3D-stacked HBM, DDR, CXL, and SSD memory layers. DreamBig also offers DPU/SmartNIC network accelerator chips. The startup has optimized its platform for Silicon Box's panel-level packaging technology. Founded in 2019, the company is headquartered in San Jose, California, USA.
Fabric Cryptography raised $33 million in its Series A funding round led by Blockchain Capital and 1kx Management, with participation from Offchain Labs, Polygon Labs, and Matter Labs. Fabric Cryptography is developing a Verifiable Processing Unit (VPU), a custom silicon chip using a crypto-specific instruction set architecture that enables it to accelerate any cryptographic algorithm. By using hardware-software co-design techniques, the startup aims to improve the speed and cost of running advanced cryptographic workloads such as Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP), Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE), and Multi-Party Computation (MPC). Founded in 2023, the company is headquartered in San Francisco, California, USA.
AttoTude announced the completion of its $29 million Series A funding round, with investors including Sutter Hill Ventures, Canaan Partners, and Wing Venture Capital. AttoTude is developing interconnect technology for AI and hyperscale datacenter applications, claiming to enable high-speed data communication at speeds ranging from 112 Gb/s to 448 Gb/s or higher over a single channel. The solution supports high radix, high-density architectures and can utilize existing manufacturing processes. Founded in 2024, the company is headquartered in Menlo Park, California, USA.
BigEndian Semiconductors received $3 million in seed funding from investors including Vertex Ventures SEA & India. BigEndian is developing surveillance camera SoCs for enterprise and consumer applications, with a focus on manageability and flexible design approaches. The company expects to soon release its first chipset. The funding will be used for hiring, R&D, and scaling operations. Founded in 2024, the company is headquartered in Bangalore, India.
Groq secured $640 million in its Series D funding round led by BlackRock Private Equity Partners, with additional investors including Neuberger Berman, Type One Ventures, Cisco Investments, Global Brain, and Samsung Catalyst Fund. Groq offers a generative AI inference platform available through the cloud or on-premises, utilizing its proprietary LPU (Language Processing Unit) chips. Founded in 2016, the company is headquartered in Mountain View, California, USA.
Fractile stood out with $15 million in seed funding led by Kindred Capital, NATO Innovation Fund, and Oxford Science Enterprises, with participation from Inovia Capital, Cocoa.VC, and angel investors. Fractile develops large language model inference chips that integrate memory and processing capabilities into a single component. By eliminating the time spent moving parameters from memory to the processor, the startup claims it can significantly reduce the time required to generate words. The funding will be used for further validation and production test chips. Founded in 2022, the company is headquartered in London, UK.
Rebellions received $15 million in Series B funding from Saudi Aramco's Wa'ed Ventures. Rebellions develops domain-specific AI processors and optimized software. The company states that it has redesigned AI processors to integrate complex deep learning capabilities through silicon-specific DL cores. It currently offers a product targeting the financial industry, aimed at improving transaction speed and reducing latency for high-frequency trading. It has also developed a chip focused on accelerating AI inference in datacenters. It is currently developing a third AI chip focused on large language models for generative AI. Rebellions recently announced plans to merge with Sapeon, another well-funded Korean AI chip startup. Founded in 2020, the company is headquartered in Seongnam, South Korea, and has raised over $225 million to date.
CogniFiber raised $5 million led by Chartered Group and Eastern Epic Capital. CogniFiber has developed an all-optical analog neuromorphic processor AI that uses in-fiber computing. The technology transforms multicore optical fibers into programmable photonic processors. As data travels through the fiber, it scans all elements physically embedded in the neural network, enabling computations to be performed as photons pass through the fiber. The startup claims that its approach provides a significant boost to AI inference while reducing cost, energy, and space. Founded in 2018, the company is headquartered in Rosh Ha'ayin, Israel.
Vaire Computing raised $4.5 million in seed funding led by 7percent Ventures, with participation from Seedcamp, Tagus Capital, Page One Ventures, B Heroes, Italian Angels for Growth, Übermorgen Ventures, Yes VC, and numerous individual investors. Vaire is developing chips that enable adiabatic reversible computing. Through time-reversible computing, the original input can be determined from the output. Since the input is not lost in creating the output, the energy from the input can be recovered within the system. The startup claims that this approach is designed to generate very little heat, thus wasting almost no power. Vaire is currently targeting generative AI and always-on edge device applications and expects to produce prototype chips within a year. Founded in 2021, the company is headquartered in Bellevue, Washington, USA, and London, UK.
Nearfield Instruments raised €135 million ($147.4 million) in its Series C funding round led by Walden Catalyst Ventures and Temasek, with participation from M&G Investments, Innovation Industries, Invest-NL, and ING Corporate Investments. Nearfield Instruments provides inspection and metrology equipment, including semiconductor scanning probe microscope (SPM) systems that can measure 3D surfaces. The company states that its feedforward trajectory planner imaging mode can be used for non-destructive in-line process monitoring of 3nm and below Gate-All-Around FETs (GAA FETs), while the parallel architecture of its mini-SPM improves throughput. It also offers an in-line, non-destructive subsurface metrology system that combines acoustic microscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM) technologies to "listen" to sound waves traveling through wafer layers and measure buried features and defects, such as voids, in advanced memory and logic devices at the nanoscale. The funding will be used to increase production capacity and expand the product portfolio. Founded in 2016 as a subsidiary of research organization TNO, the company is headquartered in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
Cybord raised $8.7 million in its Series A funding round led by Capri Ventures, with participation from Ocean Azul Partners, IL Ventures, NextLeap Ventures, and others. Cybord offers a visual AI component analysis platform that inspects, identifies, and tracks every electronic component in real-time to prevent defective, damaged, or counterfeit components from being assembled onto PCBAs. Founded in 2018, the company is headquartered in Tel Aviv, Israel.
SirenOpt received $6.6 million in seed funding led by Voyager Ventures and Visionaries Club, with participation from Union Labs, Berkeley Skydeck Fund, Wireframe Ventures, Access Industries, Climate Club, and Climate Capital. The company also received a $300,000 grant from the National Science Foundation. SirenOpt offers an advanced material characterization platform that combines cold atmospheric plasma, machine learning, and predictive analytics. The system non-destructively measures and classifies various material properties and performance indicators, such as thickness, density, conductivity, and chemical composition, for advanced coatings, thin films, and nanoscale materials used in batteries, aerospace, semiconductors, electronics, and other advanced manufacturing industries. Founded in 2022 as a spin-off of the University of California, Berkeley, the company is headquartered in Oakland, California, USA.
6K closed the first tranche of its Series E funding round with $82 million from Anzu Partners, Energy Impact Partners, LaunchCapital, Material Impact, and Volta Energy Technologies. 6K manufactures alumina, silica, and ceria-based powders and special particle coatings using microwave plasma technology for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) polishing of semiconductor wafers. The company also applies its technology to the production of additive manufacturing metal powders and cathode active materials for lithium-ion batteries. Founded in 2014, the company is headquartered in North Andover, Massachusetts, USA.
Halo Industries raised $80 million in its Series B funding round led by the US Innovation and Technology Fund, with participation from 8VC and SAIC. Halo Industries uses laser-based tools for grinding, chemical mechanical polishing, and metrology/wafer mapping to process silicon carbide (SiC) wafers. The startup claims that its processing technology improves yield and quality while minimizing waste and production costs. It is also developing laser-based wafer dicing and processing technologies for silicon, diamond, sapphire, lithium tantalate, gallium nitride, and other materials. Founded in 2014 as a spin-off of Stanford University, the company is headquartered in Santa Clara, California, USA.
SweGaN raised nearly €12 million ($13.4 million) in venture capital and strategic funding from investors including Navigare Ventures, Wafer Works, RFHIC, Ignite Innovation, BRV Capital Management, and Lifelike Capital. SweGaN manufactures custom gallium nitride on silicon carbide (GaN-on-SiC) epitaxial wafers for RF and power devices used in telecommunications, defense, and satellite communications. Its approach utilizes a "distorted heteroepitaxy" process involving vacancy ordering to perfectly transform the in-plane lattice atomic structure from the SiC substrate to the AlN nucleation layer. The company states that its QuanFINE structure combines the benefits of GaN and SiC without the need for a traditional thick C-/Fe-doped buffer layer, bringing the thermal channel closer to the heat sink SiC substrate, reducing buffer-related traps, and using an ultra-wide bandgap AlN nucleation layer as an effective back barrier. It is a spin-off of Linköping University, founded in 2014, and is headquartered in Linköping, Sweden.
RAAAM Memory Technologies has received a €5.3 million (~$5.7 million) grant and equity funding from the European Innovation Council Accelerator. RAAAM has developed an on-chip memory technology called Gain Cell Random Access Memory (GCRAM). The GCRAM bit cell utilizes decoupled write and read ports, offering native dual-port operation. It is proposed as an embedded SRAM alternative with smaller area and power consumption, manufactured using standard CMOS processes. The company was founded in 2021 and is headquartered in Petah Tikva, Israel.
Gwanak Analog raised ₩18 billion (~$15 million) in Series B funding from investors including Samho Green Investment, KDB Bank, JB Investment, Mirae Asset Venture, GU Equity, and Seoul Techno Holdings. Gwanak Analog develops analog and power SoC and ICs for industrial, consumer, and automotive markets. Its products include edge AI signal processing chips, powerline communication (PLC) modem SoCs, display PMICs, multi-sensor signal conditioners, ultrasonic sensor ICs, and sensor signal conditioning readout ICs with 24-bit delta-sigma ADCs. The company was founded in 2018 and is headquartered in Seoul, South Korea.
Millibeam received A$3 million (~$2 million) in funding from Breakthrough Victoria. Millibeam designs millimeter-wave radio chipsets for 5G/6G communication networks. Its chips utilize smart frequency switching, enabling them to simultaneously use existing 5G spectrum at lower frequencies and 5G spectrum at millimeter-wave frequencies, while improving energy efficiency and radio link range for terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks. The company was founded in 2021 and is headquartered in Sydney, Australia.
HyperLight raised $37 million in Series B funding led by Summit Partners, with participation from Xora Innovation and Foothill Ventures. HyperLight offers thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) photonic ICs. Its products include transmitter engine PICs for data center and telecom optical communications, 110 GHz electro-optic modulators, and application-specific PIC solutions realized through MPW and dedicated wafer runs. The funds will be used to accelerate product development. The company was founded in 2018 and is headquartered in Cambridge, MA, USA.
LightSolver received a €12.5 million (~$13.6 million) grant and equity funding from the European Innovation Council Accelerator. LightSolver has developed a laser-based processing unit for compute-intensive workloads such as CAE, bioscience computations, and optimization problems. The LPU uses all-optical coupled lasers to perform computations without electronics, which the startup claims enables compact footprint, scalability, low power requirements, and room-temperature operation. The company was founded in 2020 and is headquartered in Tel Aviv, Israel.
Ephos secured an $8.5 million seed round led by Starlight Ventures, with participation from Collaborative Fund, Exor Ventures, 2100 Ventures, Unruly Capital, Green Sands Equity, Silicon Roundabout Ventures, Club degli Investitori, the European Innovation Council, NATO DIANA, and angel investors. Ephos designs and manufactures glass-based photonic chips for quantum computing, data centers, communications, and sensing equipment. It uses femtosecond laser writing manufacturing processes to inscribe waveguides in glass, minimizing signal loss and enabling the creation of unique 3D device designs. The company was founded in 2022 and is headquartered in Milan, Italy.
Lightium raised a $7 million seed round led by Vsquared Ventures and Lakestar. Lightium has developed a thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) process for manufacturing and packaging photonic integrated circuits. The startup, which intends to offer foundry services, states that its TFLN platform is capable of supporting data transfer speeds exceeding 1.6 Tb/s. Initially targeting designs for telecom and datacenter applications, it suggests the platform could be applied to markets such as satellite communications, quantum computing, and LiDAR. Funds will be used to optimize its PDK and accelerate the commercialization of its foundry services, which it intends to launch in early 2025. The company was founded in 2023 and is headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland.
Riverlane raised $75 million in Series C funding led by Planet First Partners, with participation from ETF Partners, EDBI, and existing investors Cambridge Innovation Capital, Amadeus Capital Partners, the UK National Security Strategic Investment Fund, and Altair. Riverlane has developed a quantum error correction hardware and software stack that transforms unstable physical qubits into error-free logical qubits. It works with multiple qubit types, combining an orchestration layer that coordinates and synchronizes complex activities in real-time, a decoder that identifies errors in the data and sends correction instructions, and an interface that processes qubit readout data from any quantum computer control system. The company was founded in 2016 and is headquartered in Cambridge, UK.
Quantum Circuits Inc. raised $60 million in Series B funding led by ARCH Venture Partners, F-Prime Capital, Sequoia Capital, and Hither Creek Ventures, with participation from Canaan Partners, Fitz Gate Ventures, In-Q-Tel, Osage University Partners, Connecticut Innovations, Tao Capital Partners, and Tribeca Venture Partners. Quantum Circuits is developing a full-stack superconducting quantum computer that uses dual-rail qubits with built-in error correction and a modular scalable architecture. The company is a spin-out of Yale University, founded in 2015, and is headquartered in New Haven, CT, USA.
Planqc raised €50 million (~$54.2 million) in Series A funding led by CATRON Holding and DeepTech & Climate Fonds, with participation from Bayern Kapital, Max Planck Foundation, UVC Partners, Speedinvest, and private investors, alongside a non-dilutive grant from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Planqc is developing a scalable quantum computer based on neutral strontium atoms trapped in optical lattices, capable of operating at room temperature. Quantum information is then processed using quantum gates based on precisely controlled laser pulses. The startup claims that its approach can scale to tens of thousands of qubits. Funds will be used to establish a quantum computing cloud service and develop quantum software for industries such as chemistry, healthcare, climate technology, automotive, and finance. Founded in April 2022 and based on research from the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics and Ludwig Beethoven University of Munich, the company is headquartered in Garching, Germany.
Quantum Source raised $50 million in Series A funding led by Eclipse, with participation from Standard Investments, Level VC, Canon Equity, and existing investors Pitango First, Grove Ventures, 10D VC, and Dell Technologies Capital. Quantum Source is developing large-scale, fault-tolerant, server-rack-sized photonic quantum computers. The approach leverages cavity quantum electrodynamics (cavity-QED) to generate single photons and realize atom-photon entangled quantum gates using individual atoms trapped on a photonic chip, facilitating the construction of complex 3D cluster states that are the backbone of error correction codes. The startup claims that the deterministic nature of the gates minimizes the need for expensive and complex feedforward and switching operations. The company was founded in 2021 and is headquartered in Ness Ziona, Israel.
Atom Computing received a $10 million investment from PensionDenmark, following a DKK70 million (~$10.2 million) investment from Danish Export and Investment Fund (EIFO) in the previous quarter. Atom Computing is building a highly scalable gate-based quantum computer using nuclear spin qubits formed by arrays of optically trapped neutral atoms. All control functions of the neutral atom qubits are mediated by light traveling through free space, rather than individual cables connected to each qubit, reducing complexity. Additionally, the closed outer electron shells of the alkaline earth metal atoms used are insensitive to environmental perturbations, enabling qubit coherence times >40 seconds. The startup has a 100-qubit prototype platform for quantum algorithm development and is building a system with over 1,000 qubits. Funds will support the establishment of a European headquarters in Copenhagen. The company was founded in 2018 and is headquartered in Berkeley, CA, USA.
LiquidStack raised $20 million in Series B funding from Tiger Global. LiquidStack provides liquid cooling solutions for data centers. Its offerings include direct-to-chip cooling, single-phase and two-phase immersion cooling, and modular systems for micro data centers. The company was founded in 2012 and is headquartered in Carrollton, TX, USA.
*Disclaimer: This article is created by the original author. The content reflects the author's personal opinions, and our republication is solely for sharing and discussion purposes. We do not endorse or agree with the views expressed herein. For any objections, please contact us.