OpenAI strikes hard! Transforms ChatGPT into a search engine and invests $5 billion in developing custom AI chips
![]() 11/04 2024
11/04 2024
![]() 622
622
On October 31, OpenAI announced the upgrade of its popular ChatGPT service into a powerful search engine, marking the boldest move taken by the company to compete with Google.
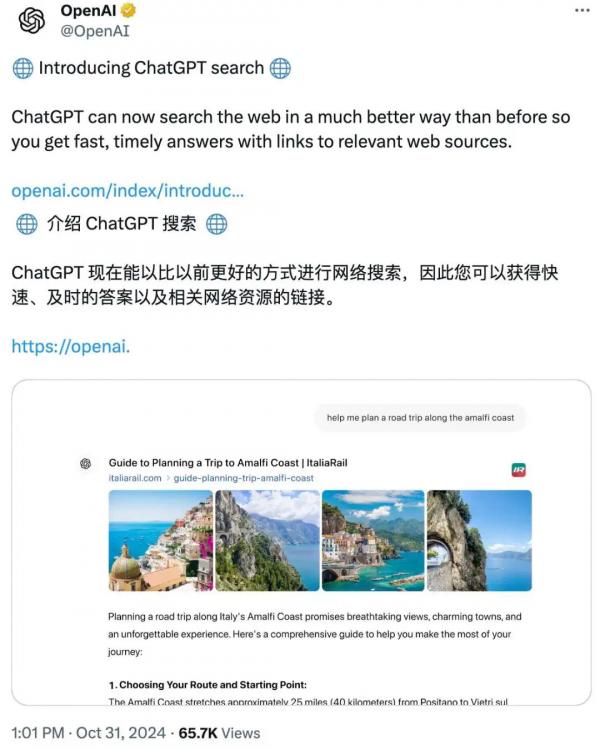
After the upgrade, users can ask questions in simple English and receive real-time information on news, sports, stocks, and weather, all previously requiring separate search engines.
An OpenAI spokesperson said, "We believe search should be as natural as a conversation. We will first roll out this feature to paying users and plan to expand it to free users in the coming months."
01. How does OpenAI's new AI search work?
Unlike traditional search engines (like Google and Microsoft Bing) that return lists of links, ChatGPT can now process queries in natural language, provide curated answers, and clearly label information sources.
Users can click to access the original source or ask follow-up questions to delve deeper into the topic.
This technology builds on OpenAI's SearchGPT experiment in July this year, where 10,000 users tested the search functionality, helping OpenAI refine how AI processes web information and attribution sources.
The system is specifically tuned based on OpenAI's latest GPT-4o model. OpenAI trained it on vast amounts of web data, fine-tuned it, and refined its ability to understand context in long conversations.
02. Major news publishers collaborate with OpenAI
Major news organizations such as The Associated Press, Axel Springer, and Vox Media have partnered with OpenAI to provide content.
These collaborations aim to address long-standing concerns, such as AI systems using unlicensed or unpaid publisher works.
Pam Wasserstein, President of Vox Media, said in a statement, "ChatGPT search is expected to better highlight and summarize news sources, thereby benefiting audiences."

"This also expands the influence of high-quality news publishers. Meanwhile, publishers can choose not to use their content for AI training but can still appear in search results."
03. OpenAI bets $5 billion on custom chips and AI infrastructure
This announcement comes as OpenAI builds its own technology infrastructure.
OpenAI recently announced agreements with AMD, Broadcom, and TSMC to develop custom AI chips by 2026, aiming to reduce dependence on NVIDIA's expensive processors.
These investments are substantial. Microsoft, as OpenAI's largest backer, has invested nearly $14 billion.
Microsoft stated this week that the collaboration would reduce its quarterly profits by $1.5 billion. Simultaneously, OpenAI expects its computing costs to reach $5 billion this year.
The massive investment in custom silicon and infrastructure heralds a crucial shift in OpenAI's strategy.
While most AI companies still rely on Nvidia chips and data centers from cloud computing providers, OpenAI is ambitiously pursuing technological independence.
This is a risky bet that could deplete the company's resources or give it an insurmountable advantage in the AI race.

By controlling its chip destiny, OpenAI could potentially halve computing costs by 2026. More importantly, custom chips optimized for GPT models can achieve functions unattainable by general-purpose AI processors.
This vertical integration from chips to models to consumer products mirrors Apple's dominant approach in the smartphone sector.
The new search feature will appear on ChatGPT's website and mobile app. Enterprise customers and educational users will access these features in the coming weeks, gradually rolling out to OpenAI's millions of free users.
Currently, Google remains the dominant force in search. However, with AI advancements, more users are becoming accustomed to conversational interfaces, and online information search competition seems poised for its biggest change in decades.

The Chinese content is compiled by the MetaverseHub team. For reprints, please contact us.




