As SoC and memory prices rise, smartphone prices increase
![]() 11/11 2024
11/11 2024
![]() 450
450

This article is a comprehensive report by Semiconductor Industry Insights (ID: ICVIEWS)
In the first half of 2024, sales of smartphones priced at $1,000 and above increased by 18% year-on-year.
According to Counterpoint Research's market outlook report, the global average selling price (ASP) of smartphones is expected to increase by 3% year-on-year to $365 in 2024 and further increase by 5% in 2025. This growth can be attributed to various factors, including the ongoing transition to 5G technology, enhanced computing capabilities, and a significant shift towards premium smartphones.
In 2025, the growing consumer interest in Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) will primarily support the trend towards premiumization, as GenAI requires significant enhancements in SoC capabilities in terms of CPU, NPU, and GPU functionality. Additionally, in mature smartphone markets with longer replacement cycles, manufacturers are adopting advanced technologies such as GenAI to drive upgrades in the premium segment.
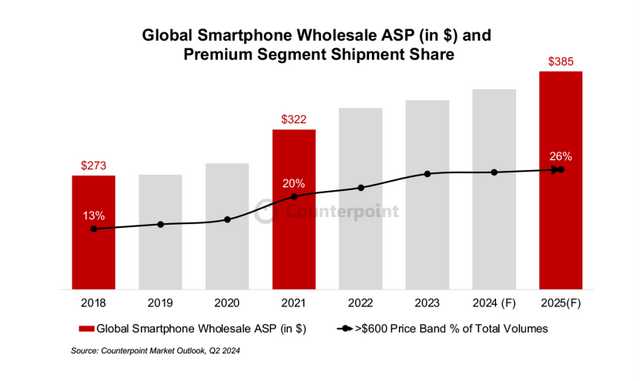
In the first half of 2024, sales of smartphones priced at $1,000 and above increased by 18% year-on-year. As consumers seek devices with advanced features and performance, major smartphone OEMs are integrating GenAI technology into their models, marking the advent of the AI smartphone era.
For example, the prices of flagship Android models are rising. Xiaomi's latest release, the Xiaomi 15, equipped with the Snapdragon 8 Elite, as well as a new Oryon CPU and Hexagon NPU, is priced approximately $70 higher than its predecessor. This trend suggests that the upward momentum in ASP may continue as more brands leverage cutting-edge technology innovations to enhance their products.
Key drivers of cost increases: SoC and memory
The increase in ASP is closely related to the rise in bill of materials (BoM) costs. The SoC is a primary factor contributing to this increase. As manufacturers adopt more advanced process nodes (e.g., 4nm and 3nm), it is expected that wafer fabrication-related costs will rise starting from 2025. This growth will affect the pricing of some Qualcomm and MediaTek products that utilize GenAI, resulting in single-digit percentage increases.
The latest SoC products launched by companies like Qualcomm and MediaTek are not only more expensive but also more powerful in terms of functionality.
Enhanced AI capabilities, particularly in the NPU, enable these chips to perform complex tasks more efficiently. For instance, the MediaTek Dimensity 9400, equipped with the NPU 890, Cortex-X925, and Immortalis-G925, offers performance improvements of 40%, 30%, and 40%, respectively, and is priced more than 20% higher than its predecessor, the Dimensity 9300+.
While SoC price increases contribute to the overall rise in smartphone costs, memory prices are also a critical factor. In the third quarter of 2023, memory chips ended their price decline cycle and entered a new upcycle. From the third quarter of 2023 to the second quarter of 2024, spot prices for DRAM and NAND increased by an average of more than 60%. The GenAI trend may drive the adoption of higher-performance DRAM and NAND, such as LPDDR5x 9600 and NAND UFS 4.0, which are relatively more expensive compared to previous solutions. The price gap between LPDDR5x and LPDDR5 is expected to narrow, further impacting overall costs. However, demand for higher-capacity chips like 1TB is decreasing, and their prices are expected to decline slightly by the end of 2024 and possibly continue into 2025.
As we enter the era of AI smartphones, the integration of GenAI features is expected to continue this upward trend. The interaction between cost increases and consumer expectations will shape the competitive landscape of the smartphone industry in the coming years.
Smartphone ODM Rate Rankings: Apple Leads with In-House Research and Development, Huawei Ranks Fifth
Recently, Counterpoint Research released the latest data on the ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) mobile phone industry for the first half of 2024, revealing the true situation regarding outsourced design and manufacturing among major smartphone manufacturers. Apple tops the list with a 0% ODM rate, while Xiaomi ranks second to last with a 78% ODM rate.
The ODM design ratios of mainstream smartphone manufacturers in the first half of 2024 are as follows: Apple has a 100% in-house research and development design rate and a 0% ODM design rate, with all models designed internally without relying on ODM. Motorola (under the Lenovo Group) relies on ODM for 90% of its designs, with only 10% developed in-house. Samsung has a 22% ODM design rate, a decline from 28% in 2022. OPPO, Honor, and Huawei have ODM design rates of 39%, 40%, and 44%, respectively, none exceeding 50%. Xiaomi has a 78% ODM design rate, ranking second to last, ahead of only Motorola.
These data reveal the degree of autonomy in design and manufacturing among major smartphone brands, with Apple maintaining the highest in-house research and development rate, while other brands rely on ODM partners for their product designs.
ODM phones are designed and manufactured by original design manufacturers (ODMs) based on the requirements of smartphone manufacturers and then sold under the smartphone manufacturer's brand label. This cooperation model is increasingly common in the mobile phone industry, especially for brands focused on cost control and rapid market response.
Data shows that well-known global ODM manufacturers such as Wintek, Huaqin Technology, Longcheer Technology, and Huawei's subsidiary Zhongnuo Communications design and manufacture an astonishing number of mobile phones annually, reaching nearly 400 million units, accounting for 35%-40% of global mobile phone sales. This proportion highlights the important role of the ODM model in the global mobile phone industry chain.
However, major smartphone manufacturers adopt vastly different strategies regarding outsourcing. Apple tops the list with a 0% ODM rate, indicating that it insists on designing all its smartphone products in-house without relying on any third-party design agencies. This strategy aligns well with Apple's consistent product philosophy and brand positioning.
In contrast, Samsung adopts a more flexible strategy with a 22% outsourced design rate, suggesting that while maintaining in-house research and development capabilities, Samsung also actively leverages external resources to enrich its product line.
Among domestic smartphone brands, Motorola has the highest ODM dependency rate at 90%, making it the brand most reliant on the ODM model. Brands like VIVO, Huawei, Honor, and OPPO also utilize the ODM model but at relatively lower rates, ranging from 40%-50%. These brands typically insist on in-house research and development for high-end products while leveraging the ODM model more in the mid-to-low-end market to reduce costs and improve market response speed.
Huawei has a 44% outsourced design rate, which may be related to its current market strategy and product layout. Huawei may include some non-core models or smart selection models in this statistic, thereby pushing up the overall rate.
*Disclaimer: This article is originally created by the author. The content reflects the author's personal views. Our republication is solely for sharing and discussion purposes and does not represent our endorsement or agreement. For any objections, please contact us.




