Qualcomm's ambition for a unified PC, mobile, and automotive market
![]() 10/30 2024
10/30 2024
![]() 464
464
Qualcomm aims to reestablish its dominance in automotive chips through Chinese manufacturers.
On October 22, Qualcomm's annual conference was held as scheduled in Hawaii, across the Pacific Ocean. Almost all domestic mobile phone manufacturers chose to attend, following industry norms. However, this time, in addition to numerous mobile phone manufacturers, many Chinese automakers were also present.
Judging from the products launched, Qualcomm seems to have introduced three chips: the Snapdragon 8 Elite for mobile devices and the Snapdragon Ride Elite and Snapdragon Cockpit Elite for automotive systems.
Upon closer inspection, it becomes evident that Qualcomm has, for the first time, unified its naming convention for mobile and automotive chips. Instead of following a numerical sequence, automotive chips now share the same 'Elite' naming as mobile chips.

This was the conference's highlight: Qualcomm achieved architectural unity across smartphones, intelligent vehicles, and autonomous driving chips, realizing a unified PC-mobile-automotive layout.
Particularly, by bridging the gap between cockpit and autonomous driving chips, Qualcomm offers automakers an 'all-in-Qualcomm' option, aiming to break the monopoly in autonomous driving chips.
Revolutionizing Itself
Qualcomm's newly launched intelligent cockpit chips represent a complete revolution within the company.
Qualcomm currently holds an unshakeable market position in cockpit chips. Starting with the 8155 chip, Qualcomm successfully established itself as the leading provider of automotive chips and extended this advantage to the 8295 chip. Even if Qualcomm continued with its previous product roadmap, it would maintain its leading position.
However, Qualcomm chose the seemingly challenging path of introducing a unified chip core, erasing the generational gap between mobile and automotive chips.

Automotive chips require extended stability validation to ensure automotive-grade performance, leading to a generational gap between Qualcomm's automotive and mobile chips.
For instance, the 8155 chip corresponded to the Qualcomm Snapdragon 855, a flagship mobile chip introduced in 2018, while the 8155 was released in 2019 and only widely adopted in vehicles in 2023, a five-year difference.
This resulted in the user experience of even the best automotive chips feeling less fluid than mobile devices, especially as automotive functions continue to expand. Consumers desire a unified experience across devices.

At the conference, Qualcomm chose to bridge the traditional generational gap by unifying mobile and automotive chips. Qualcomm developed the new Oryon CPU in-house, enhancing chip performance and unifying chip deployment.
Compared to the previous generation, the new Elite chips offer a threefold increase in CPU performance, a 12-fold increase in NPU-related AI computations, and a threefold increase in GPU graphics processing capabilities.
They support up to 16 screens in the vehicle, with a maximum resolution of 4K, covering all currently available models with ample performance redundancy.
Crucially, these chips are manufactured using TSMC's second-generation 3nm process, the industry's most advanced, matching Apple's A18 Pro chip, resulting in superior energy efficiency.
While this energy efficiency may seem insignificant for electric vehicles, it optimizes in-car design by eliminating the need for a dedicated cooling system for the infotainment system, reducing cockpit development costs.
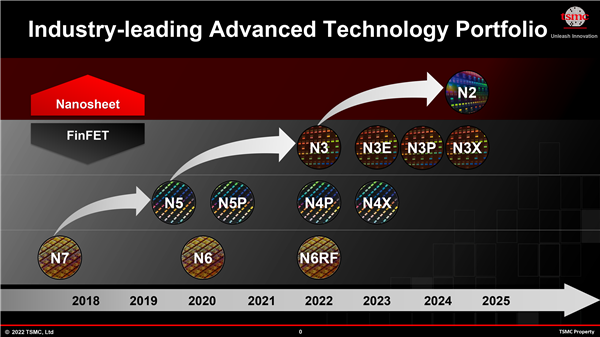
In intelligent cockpit chips, Qualcomm has revolutionized itself, showcasing superior performance and advanced manufacturing processes that underscore its dominance in automotive chips. Through multiple generations of chip market validation, Qualcomm has established itself as a leader in automotive chips.
Yet, Qualcomm aims higher, seeking breakthroughs in autonomous driving chips. With the 8295 chip, Qualcomm planned to bridge cockpit and autonomous driving functions, reducing chip deployments through L2-level autonomous driving computations.
However, this strategy has not gained traction, with mainstream automakers opting for NVIDIA's chip solutions, even if requiring multiple chips for sufficient computing power.
Despite setbacks, Qualcomm identified a new direction. As NVIDIA shifted focus to high-performance computing chips, many automakers chose in-house chip development for advanced autonomous driving, though limited by technology, these chips lacked industry-leading processes.
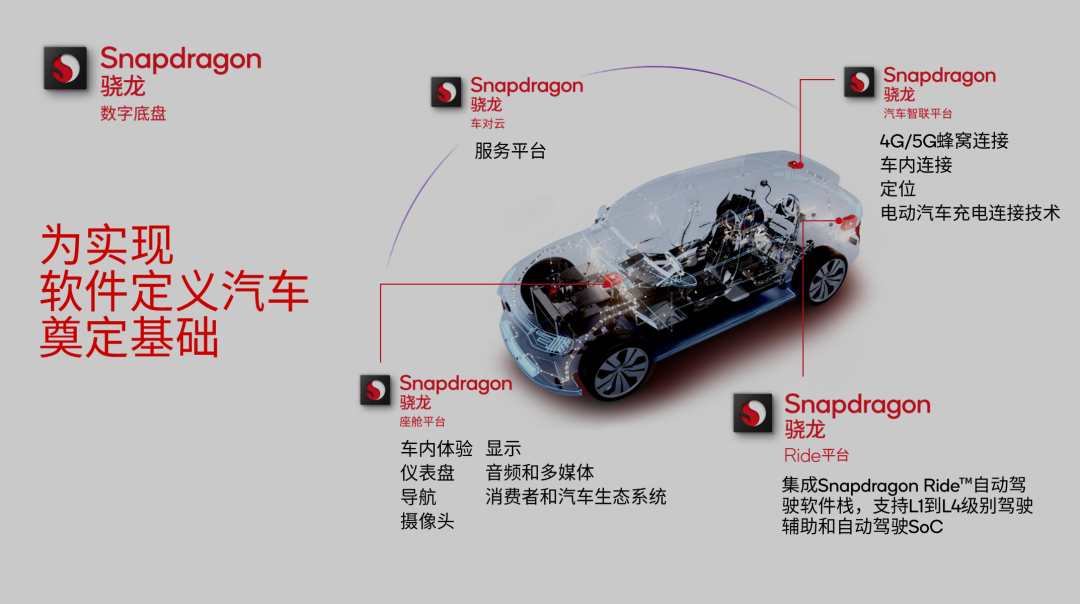
As one of TSMC's largest partners, Qualcomm can leverage the most advanced manufacturing processes, a significant advantage for automakers. The technological gap between advanced processes is difficult to bridge through technical means, particularly in the fiercely competitive automotive market where superior parameters confer advantages.
The Snapdragon Cockpit Elite platform enables simultaneous deployment of intelligent cockpits and autonomous driving systems, with automakers free to choose either or both, offering flexibility in configuration.
In autonomous driving, the Snapdragon Ride Elite chip supports over 40 sensors, including multiple 16MP exterior cameras, 360° panoramic infrared cameras for passengers, radar, and LiDAR fusion computations, covering mainstream autonomous driving solutions.
At this conference, Qualcomm is fully committed to the automotive market, actively expanding its automotive applications while maintaining orderly mobile market iterations.
Challenges and Breakthroughs
Another highlight of the Qualcomm conference was the presence of not only mobile and consumer electronics executives but also automotive industry leaders, such as Great Wall Motors' CTO Wu Huixiao, who delivered a keynote speech as a partner representative.
Beyond Great Wall Motors, NIO and Mercedes-Benz will be among the first automakers to adopt Qualcomm's new chips, with sample vehicles expected as early as 2025.
From the launch of the Snapdragon Digital Chassis in 2023 to the autonomous driving-specific chip platform in 2024, Qualcomm has deepened its automotive presence, seemingly continuously pushing boundaries.
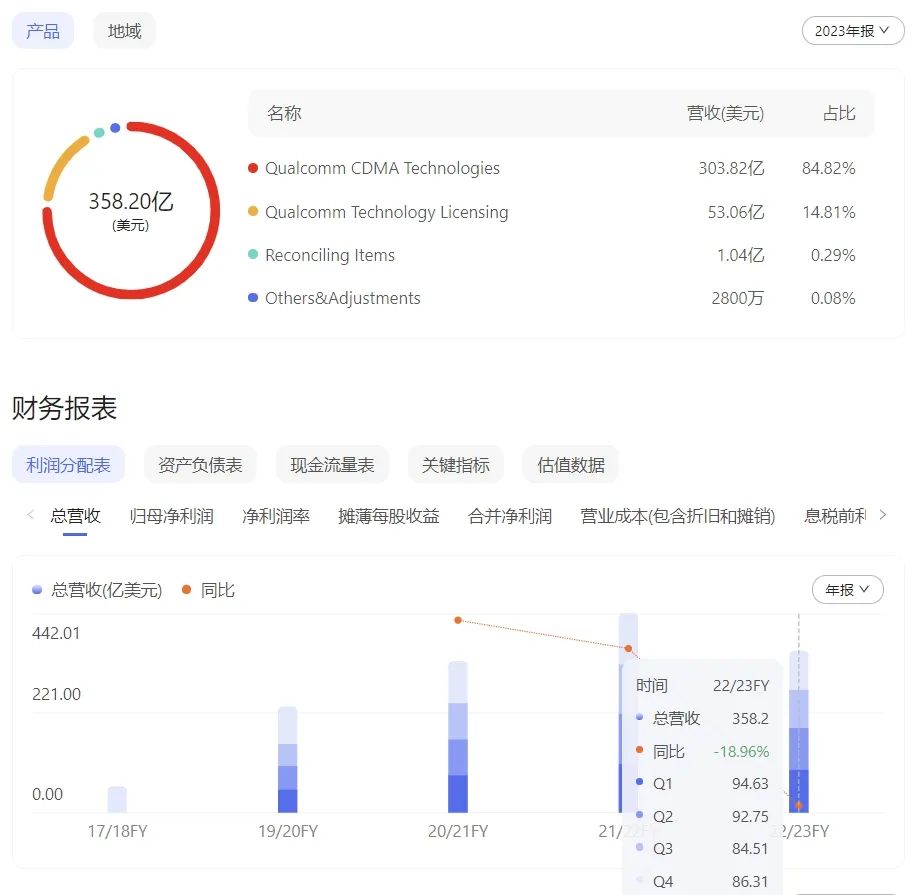
However, these moves stem from Qualcomm's declining core business. Qualcomm's 2023 fiscal year revenue declined 18.96% YoY to $35.82 billion, with mobile chip revenue down 12% YoY to $22.14 billion.
More concerning than revenue decline is profit erosion; net income fell 44% YoY to $7.232 billion, nearly halving Qualcomm's profitability.
This is largely attributed to the global smartphone market downturn, with 2023 global sales down ~3% YoY. Competitors like Apple have strengthened their position, with iPhone market share reaching 23% in the premium segment.
Meanwhile, MediaTek's growth has pushed its market share to 15%, particularly in the mid-to-low end, while Huawei's self-sufficiency in chip supply has deprived Qualcomm of 4G SoC orders, contributing to its mobile chip revenue decline.

Beyond mobile chips, Qualcomm's other businesses, including IoT and technology licensing, have also seen revenue declines of over 10%.
Only the automotive business showed positive growth, contributing $1.64 billion (less than 5% of total revenue) with a 60% YoY increase in FY2023.
Entering FY2024, Qualcomm's mobile business has shown some recovery but remains below expectations. While Q2 and Q3 saw YoY growth, sequential declines persisted, indicating a bottleneck.
In contrast, Qualcomm's automotive chip business, part of the QCT segment, maintained double-digit growth, with revenue exceeding $600 million for four consecutive quarters, peaking at $811 million in Q3, accounting for over 10% of total revenue.

Focusing on the automotive market is Qualcomm's most prudent strategy. To expand revenue, Qualcomm cannot rely solely on market forces and must accelerate automotive R&D and market expansion.
Beyond automotive chips, Qualcomm foresees the future of autonomous driving chips. As NVIDIA shifts focus, Qualcomm seeks to capitalize on this opportunity, integrating cockpit and autonomous driving chips to deepen automotive customer relationships.
While Qualcomm's advanced automotive chip processes seemingly address mobile chip shipment declines, they also leverage TSMC's 3nm capacity, efficiently used due to Qualcomm, MediaTek, and Apple's dominance.
Qualcomm aims to create premium pricing for automotive chips through advanced processes, as Qualcomm is currently the only company capable of developing and manufacturing 3nm automotive chips.

Market dominance will drive premium pricing for Qualcomm, which has established itself as an industry leader in automotive chips. For automakers, premier chip launches enhance their reputation, akin to mobile manufacturers' chip premieres.
However, it remains unclear how much market share Qualcomm can capture from NVIDIA. For NVIDIA, Qualcomm's moves may be insignificant, given Qualcomm's $132.1 billion market cap versus NVIDIA's $3.42 trillion.
For the market, Qualcomm's conference appears aimed at attracting more customers. While many automakers attended, only NIO and Mercedes-Benz announced early adoptions, reflecting Qualcomm's lesser influence in the automotive sector compared to mobile.
One certainty is Qualcomm's deeper commitment to the automotive market, as it lacks better alternatives.
Note: Some images are sourced from the internet. Please contact us for removal if infringement occurs.