Stellantis, World's Fourth Largest Auto Group, Suffers 70% Profit Plunge Amidst Chinese Automakers' Rise
![]() 03/14 2025
03/14 2025
![]() 635
635
Recently, Stellantis, the world's fourth largest automotive conglomerate, unveiled its 2024 financial report, revealing a distressing picture.
The figures are indeed alarming. Revenue stood at €156.9 billion, marking a year-on-year decline of 17%, while net profit plummeted by an astonishing 70% to €5.5 billion. Furthermore, the operating profit margin nosedived from 12.8% to 5.5%, and operating cash flow plummeted to €4 billion, a decrease of 82%.
In terms of sales, Stellantis sold a total of 6.4 million vehicles globally in 2023, but this figure dropped to 5.42 million in 2024, a decline of over 1 million vehicles or 15%.
In summary, the entire financial report can be described in one word: dire.
For those unfamiliar with Stellantis, it is a vast collection of automotive brands, encompassing 15 names such as Peugeot, Citroen, Fiat, luxury offerings like Maserati and Alfa Romeo, as well as Jeep, DS, and Chrysler. Primarily, it comprises a range of European automotive brands.
Historically, these brands operated independently. However, in 2021, amidst a decline in European car sales, Italy's FCA Group (Fiat Chrysler Automobiles) merged with France's PSA Group (Peugeot Citroen), integrating other brands to form Stellantis.
Currently, Stellantis ranks fourth globally in sales.
So, what explains its dire performance? The answer lies, in part, with Chinese automakers, who have significantly impacted Stellantis.
In the past, brands like Peugeot, Citroen, Fiat, Jeep, Dodge, and Chrysler enjoyed considerable success in China, boasting a loyal fan base. Consumers valued their cars for their combination of affordability and quality, particularly Peugeot and Citroen, renowned for their superior chassis quality.
However, with the ascendancy of Chinese automakers, especially in the realm of new energy vehicles, sales of these traditional brands have waned in China. For instance, Fiat, Dodge, and Chrysler have exited the Chinese market entirely.
While Peugeot and Citroen continue to sell in China, their performance has deteriorated significantly, with sales plunging. They have resorted to steep price cuts to barely maintain some market presence.
Moreover, they have made minimal progress in transitioning to new energy vehicles, relying heavily on gasoline vehicles, which has made them increasingly uncompetitive.
Additionally, Chinese automakers are exporting in large numbers to Europe and other regions, further eroding the market share of these brands in Europe and beyond, leading to declines in sales, revenue, and profits...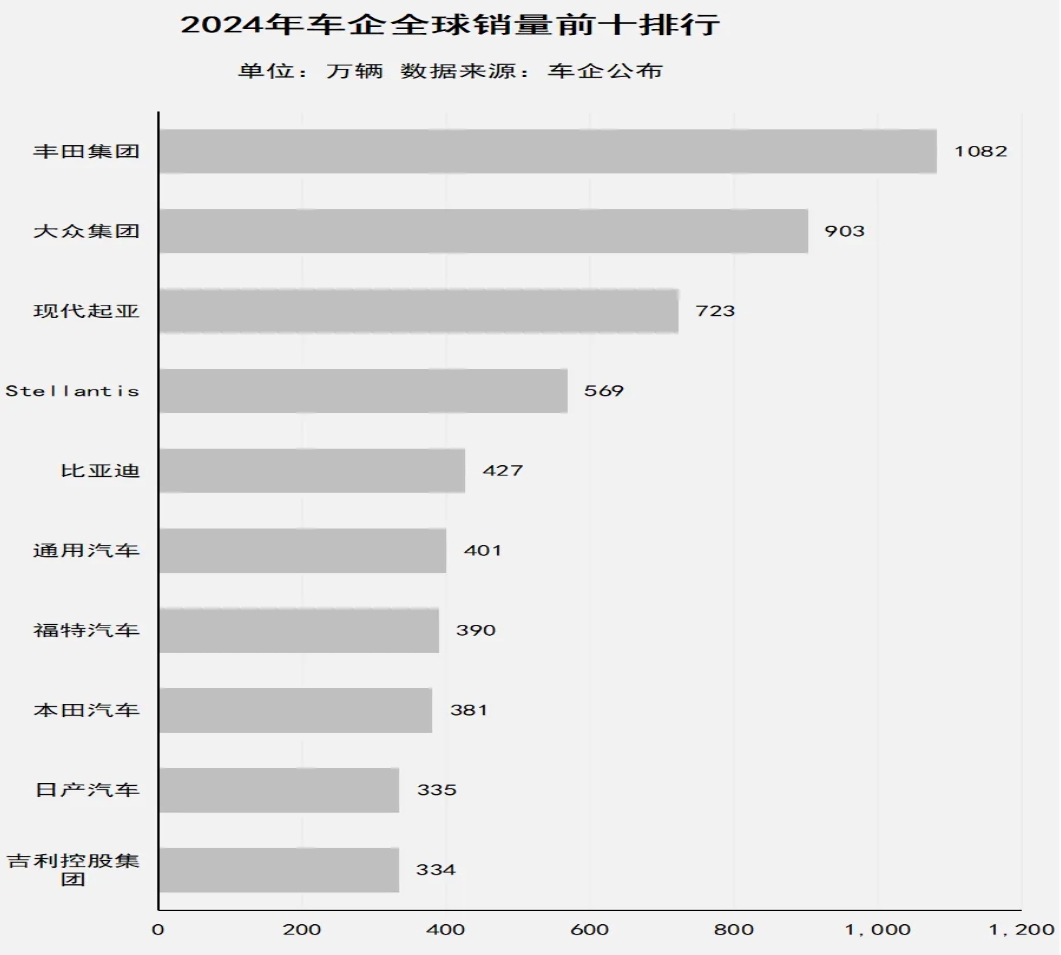
Based on 2024 data, while Stellantis retains its fourth-place global ranking, it trails BYD by a slim margin of approximately 1.4 million vehicles. Some institutions predict that by 2025 or 2026, Stellantis may lose its global fourth position and be surpassed by BYD.







