Raising HK$1 Billion: The Dawn of the Robot Golden Age and URobot's Pioneering Role
![]() 07/23 2025
07/23 2025
![]() 584
584
URobot, a global leader in collaborative robots, has announced a significant financing plan to raise over HK$1 billion through a discounted new share placement. This move aims to accelerate technology research and development (R&D) and expand its global market presence.

On July 15, URobot (02432.HK) unveiled plans to place 19.1 million new H shares under general mandate at HK$54.3 per share. This price represents a discount of approximately 9.5% compared to the closing price of HK$60 on the last trading day prior to the announcement and a 6.2% discount to the five-day average price.
Recently, URobot successfully completed this private placement, raising a total of HK$1.037 billion. After deducting issuance costs, the net proceeds amounted to HK$1.022 billion.
The newly placed shares account for roughly 4.73% of the company's current issued share capital, which will be slightly diluted to 4.51% upon completion.
Notably, URobot's listing on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange was just seven months ago. On December 23, 2024, it became the third professional technology company to list under Chapter 18C of the Hong Kong Listing Rules, raising approximately HK$752 million with net proceeds of HK$681 million.
This aggressive financing strategy underscores URobot's commitment to accelerating its robot business expansion, indirectly confirming that the commercialization of the entire robot sector is indeed transitioning from nascent to mature stages.
Investors are equally optimistic about the advancement of industrial commercialization. According to ITJuzi data, the robot sector's financing amount reached RMB 23.2 billion in the first five months of 2025, surpassing the entire year's total of RMB 20.9 billion in 2024. URobot's share price has surged, up 173% year-to-date.
Industrial and commercial robots have witnessed substantial growth, with URobot's commercialization efforts being particularly impressive.
According to the prospectus, URobot, founded in 2015, is a pioneering enterprise specializing in the development, manufacture, and commercialization of collaborative robots.
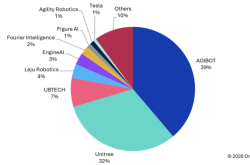
A report by Cinno Research indicates that, in terms of shipments in 2023, URobot ranks among the top two in the global collaborative robot industry and first among all Chinese collaborative robot companies, with a global market share of 13.0%.
Its leading market position is further evidenced by its impressive 2024 performance report: revenue for the year reached HK$374 million, a 30.3% year-on-year increase. More importantly, the adjusted net loss narrowed significantly by 55.4% year-on-year, while the gross margin jumped from 38.2% in 2023 to 46.6%.
Given that losses are currently common in the robot industry, with most humanoid robot products still in the scenario exploration phase and not yet ready for large-scale mass production, URobot's ability to achieve revenue growth and narrow losses simultaneously signifies that its large-scale commercialization is taking effect, and the company is rapidly approaching the profitability inflection point.
Analyzing the revenue structure reveals clear growth drivers for URobot: its core product, the six-axis collaborative robot, contributed 55.9% of revenue, with a year-on-year growth rate of 55.5%. Revenue from composite robots integrating mobile robot technology grew even faster, reaching 64.7%. Notably, revenue from commercial service scenarios surged 111.6%, thanks to the large-scale deployment of new applications such as automated coffee stations and medical assistant robots.
URobot's robotic arms are moving from factories to milk tea shops and hospitals – this is how Liu Peichao, the founder and CEO of URobot, succinctly expressed it in an interview. Among the three categories he divides robotic arms entering human life scenarios into, industrial scenarios with relatively structured and rule-based needs serve as the "basic disk" and were the first to land. Commercial scenarios act as the "growth engine," primarily replacing repetitive labor. Finally, there are household scenarios. He believes that "in the future, robotic arms will definitely enter households to help you fold clothes, cook meals, and do housework. I think such scenarios can be realized in just about three years."
The 2024 performance report confirms the forward-looking nature of this strategy – industrial automation demand has become a pillar business, while commercial service robots have emerged as a new growth curve.
As a technology enterprise, a robust technical barrier is essential for URobot. It adheres to the "full-stack self-research" approach, with a self-research rate of key components exceeding 90% and a total of 961 patents. The first humanoid robot, Dobot Atom, launched in 2025, is equipped with a self-developed neural drive dexterous operating system (NDS), achieving millimeter-level operating accuracy and having verified its functions in scenarios such as precision assembly in the automotive industry and fully automated coffee making.
Leveraging these technical supports, URobot recently launched a hexapod bionic robot dog, becoming the world's first robot platform encompassing "robotic arms + humanoids + hexapods." It even launched a humanoid robot and high-speed collaborative robot CR 30H in Japan to accelerate global delivery and consolidate its industry position with a "technological bombardment."
The global layout provides a "double insurance" for growth. Currently, URobot's products cover over 80 countries and regions, serving more than 80 Fortune 500 companies, with overseas revenue accounting for up to 59%. This "China R&D + global sales" model not only mitigates the risk of fluctuation in a single market but also enhances brand premium by serving high-end customers in industries such as medical and automotive.
Behind the HK$1 billion fundraising is the charge for the "humanoid robot war."
Timing this placement is closely linked to URobot's intent to seize the increasingly clear industrial trend of humanoid robots and respond to the strategic layout of global competition.
The "golden age" of the collaborative robot sector is accelerating. According to Cinno Research data, the global market size increased from US$470 million in 2019 to US$1.03 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate of 22.2%. It is projected to reach US$4.95 billion by 2028, with the growth rate soaring to 36.6%.
The core logic behind this growth is that collaborative robots, with their flexibility and ease of use, are filling the market gaps that traditional industrial robots cannot cover – from small-batch, multi-variety production in the 3C electronics industry to service scenarios in medical care and catering, to daily household chores. Almost all "non-standardized" needs have become battlegrounds for collaborative robots.
The HK$1 billion raised this time serves as the "ammunition depot" prepared by URobot for this war, encompassing preparations for more intense competition in terms of R&D iteration speed, capacity expansion, and market coverage.
According to URobot's disclosure, the funds raised will primarily be invested in four strategic directions: increasing investment in core technology R&D, especially in cutting-edge fields of intelligent robots (such as humanoid robots and AI training platforms); actively seeking opportunities for industrial chain integration, including potential investments, acquisitions, or strategic alliances to strengthen ecological synergy; expanding global sales channels to enhance product penetration and competitiveness in overseas markets; and using funds for daily operating capital to support the rapid deployment and commercialization of emerging application scenarios such as medical and commercial services.
In terms of capital market feedback, market analysts generally believe that high-discount placements may cause short-term stock price fluctuations but, in the long run, this crucial funding is expected to accelerate the company's progression towards the profitability inflection point.
Shenyin & Wanguo Securities analysis points out that URobot's dual-wheel drive strategy of "collaborative robots + embodied intelligence" is gradually becoming clear, which may drive the reshaping of the company's valuation system.
Taking the lead before the outbreak
By efficiently leveraging more capital resources, URobot aims to build barriers in three dimensions: technological leadership, ecological synergy, and market penetration.
At the technological level, humanoid robots are considered the "ultimate form" of collaborative robots. Unlike industrial robotic arms, humanoid robots require capabilities such as environmental perception, autonomous decision-making, and multi-task execution, placing higher demands on AI algorithms, sensors, and precision control. URobot's Dobot Atom has taken the lead in verification in scenarios such as automotive assembly and coffee making. If the technology can be reused in a broader range of commercial scenarios, such as logistics sorting and household services, it may become a core advantage distinguishing URobot from competitors like Universal Robots.
At the ecological level, URobot is constructing a closed loop of "hardware + software + services." Its embodied intelligence robot X-Trainer, launched in 2024, collects task data through remote control operations and uses neural networks to train end-to-end control models, essentially "installing a 'brain' for robots with AI." This model not only enhances the efficiency of a single robot but also forms a "getting smarter with use" network effect through data accumulation, ultimately constructing an unreplicable ecological moat.
Practical applications demonstrate X-Trainer's success. It has been deployed in leading enterprises across multiple industries, including 3C, automotive, and cosmetics, covering over 20 application scenarios such as cosmetic packaging, wire harness terminal plugging and unplugging, and automotive part gripping, accumulating a vast typical task parameter set totaling over 2 billion.
At the market level, global competition has reached a "white-hot" stage. International giants like Universal Robots enjoy a first-mover advantage, while domestic enterprises such as JAKA and AUBO are also accelerating their pursuit. URobot's advantage lies in its dual-wheel drive of "technology + globalization." In terms of global layout, URobot has made early inroads into incremental markets such as Europe, the United States, and Southeast Asia. In China, URobot has collaborated with top-tier automakers, electronics manufacturers, coffee shops, and will achieve trial production and mass production in mid-2025, continuously expanding market share and enhancing brand influence.
However, challenges persist. The most pressing is profit pressure – in 2024, R&D expenses amounted to HK$77.52 million, accounting for 20.7% of revenue. While high-intensity investment widens the technology gap, it also compresses short-term profit margins, which need to be effectively diluted through broader scale applications.
Another challenge is scenario verification risk: the payback period for single stores deploying commercial service robots (like coffee robots) and the clinical compliance of medical robots require time to verify. Although there is an optimistic outlook for household scenario popularization within three years, consumers' willingness to pay still needs to be cultivated.
In essence, URobot's eagerness to raise funds aims to secure a leading position before the industry outbreak.
Conclusion
From a "small workshop" in 2015 to ranking among the top two in the global collaborative robot industry with a 13% market share in 2024, and then to the "humanoid robot charge" after raising HK$1 billion through private placement in 2025, URobot's growth trajectory epitomizes the entire humanoid robot sector's acceleration from the laboratory to the production line.