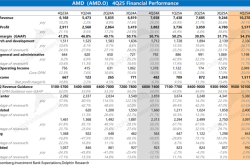
Robotaxi Hits the Fast Lane: Global Fleet Size Surges, Multiple Cities Launch Commercial Operations
![]() 08/04 2025
08/04 2025
![]() 593
593
Source: Zhiche Technology

Giants Lead the Way, Global Robotaxi Market Accelerates Recovery
Robotaxi is reaching a pivotal milestone. Last month, Waymo's inaugural batch of Robotaxis arrived in New York, the "Big Apple," to commence gathering urban mapping and high-precision map data, and to seek testing permits. By 2027, Waymo's annual mileage is projected to surpass 320 million miles, transporting over 48 million passengers and generating revenue exceeding $1.3 billion. As early as 2020, Waymo introduced fully driverless Robotaxi services in Phoenix, and with years of accumulated data, technology, and compliance experience, it currently dominates the US market.
Tesla is also stepping up its efforts. After unveiling the fully autonomous Robotaxi Cybercab in October 2024, it launched a trial operation in Austin, USA, on June 22 this year, with an initial deployment of around 10 Model Y vehicles, planning for mass production in 2026. In July, Tesla applied to test and operate Robotaxis in Arizona, aiming to enter the Phoenix metropolitan area. If approved, this will be a crucial step in promoting commercialization in multiple US cities. Tesla aims to achieve large-scale deployment through a more cost-effective technological path, keeping pace with Waymo.
The Chinese market is equally vibrant. On July 14, Pony.ai announced the road testing of BAIC Arcfox Alpha T5 Robotaxis equipped with its seventh-generation autonomous driving system, marking that Pony.ai's seventh-generation Robotaxis have entered mass production for multiple models and commenced public road testing. Previously, WeRide signed cooperation agreements with Dubai's Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) and Uber, the world's largest mobility and delivery technology company. Currently, WeRide and Uber have initiated Robotaxi road testing in Dubai under the guidance of RTA.
In essence, automakers, autonomous driving technology companies, and operating platform companies form the golden triangle of Robotaxi, corresponding to the three core competencies of vehicle manufacturing, technology, and operation, respectively.
There are also new developments at the capital level. Hello Inc. jointly established "Shanghai Zaofu Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd." with Ant Group and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL), with a total initial investment exceeding RMB 3 billion, focusing on L4 autonomous driving technology research and development, safe application, and commercialization. Hello Inc. continues to deepen its mobility business, expand overseas markets, promote the application of AI in the mobility sector, and accumulate experience for entering the Robotaxi sector, having already recruited a group of technical talents to build a core team. Ant Group's technological layout in large models, reinforcement learning, and other fields, as well as its experience in security and privacy protection, can provide support for Hello Inc.'s autonomous driving business. CATL's leading power battery technology and intelligent skateboard chassis technology provide a solid foundation for autonomous driving.

The Landscape Gradually Becomes Clear, Leading Enterprises Showcase Their Strengths
After intense competition in 2024, the landscape of the autonomous driving sector in 2025 has gradually crystallized. As the first Robotaxi stock globally, WeRide is experiencing rapid growth. Its first-quarter 2025 financial report revealed that its Robotaxi revenue was RMB 16.1 million, accounting for a significantly increased 22.3% of total revenue, with an ultra-high gross margin of 35%, firmly positioning it at the forefront of the global autonomous driving industry. Its services span 10 cities in three countries, including China, the United Arab Emirates, and Switzerland, with fully driverless testing or operations in Abu Dhabi, Beijing, and Guangzhou, and deployment plans already in place for the Canton of Zurich in Switzerland, Dubai in the United Arab Emirates, and 15 new cities, making it the only autonomous driving technology company globally that has achieved commercial Robotaxi operations in both the Chinese and overseas markets with the widest range of landing services. On May 6, WeRide and Uber expanded their strategic cooperation, planning to deploy an additional 15 international cities over the next five years. On May 8, Uber invested an additional $100 million, demonstrating its recognition of WeRide's technology.
In recent years, Chinese Robotaxi companies have welcomed a wave of overseas expansion. Baidu plans to expand its Robotaxi service, Robotaxi Go, to Europe and is currently in talks with PostAuto, a subsidiary of the Swiss Post, to expand to Switzerland. It also plans to expand to Turkey and has previously announced expansions to Dubai and Abu Dhabi, obtaining an autonomous driving test permit from the Hong Kong Transport Department at the end of last year.
Pony.ai recently reached a global strategic cooperation with Uber, with its Robotaxi services and fleet set to be integrated into the Uber platform in the second half of this year. The cooperation will initially be launched in the Middle East market and gradually expanded to more international markets. Pony.ai has established R&D centers in China, the United States, and Luxembourg, obtaining qualifications and licenses in multiple locations in China and the United States, and is also cooperating with enterprises and governments in Singapore, South Korea, the United Arab Emirates, and other places to accelerate the commercialization process.

Accelerated Large-Scale Deployment, Multiple Cities Join the Operation Ranks
A Bank of America Securities in-depth research report indicates that the autonomous driving (AV) market holds vast prospects, with an estimated potential scale of $1.2 trillion by 2040, encompassing multiple fields. Currently, the deployment of commercial AVs has commenced on a large scale, with Robotaxis available in seven cities worldwide, with another 20 cities set to follow soon, indicating that the industry's inflection point has arrived.
In the commercialization process of Robotaxis, the total number of vehicles operated by leading players is not significantly different. Robotaxi Go's fleet size exceeds 1,000 vehicles, while Waymo, which was the earliest to deploy, has less than 2,000 vehicles. Tesla and Pony.ai aim to expand their fleets to thousands of vehicles by the end of 2025.
Many companies view 2025 as a "year of significant expansion," accelerating scale and regional expansion, and enhancing mass production capabilities. Musk expects Tesla's Robotaxi operations in the US market to exceed 100,000 vehicles by the end of 2026.
The US Robotaxi industry is led by technology giants. After Apple abandoned car manufacturing and General Motors ceased funding Cruise, the main players are Waymo, Zoox, and Tesla. As of May 2025, Waymo had a fleet of 1,500 vehicles, serving San Francisco, Los Angeles, Phoenix, and Austin, completing over 250,000 paid rides per week, with plans to expand to seven US cities by the end of 2026. In June, Uber introduced Waymo services in Atlanta. Zoox is conducting road tests in multiple US cities and plans to commence commercial operations in Las Vegas in 2025. Its Hayward, California, factory has an annual production capacity of over 10,000 vehicles, making it the first factory in the US designed specifically for mass production of autonomous vehicles.
Domestic Robotaxi is dominated by startups, with leading enterprises such as Pony.ai, WeRide, and Baidu's Robotaxi Go already operating in pilot regions. In May, Li Yanhong disclosed that Robotaxi Go covers 15 cities globally, deploys over 1,000 driverless vehicles, and provided over 1.4 million travel services in the first three months of this year, a year-on-year increase of 75%. WeRide has deployed a full matrix, with over 1,200 autonomous vehicles in operation globally and over 500 Robotaxis. Pony.ai has over 250 Robotaxis, expects mass production in the second quarter, and plans to deploy tens of thousands within three years.
Each enterprise has distinct focuses in its layout. Pony.ai concentrates on super-tier cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, achieving rapid progress in obtaining licenses; WeRide focuses on Beijing and Guangzhou, with broader overseas expansion plans; Robotaxi Go is based in Beijing and Wuhan, gradually expanding outward, with the largest fleet in operation.
As Robotaxis enter the inflection point of large-scale mass production, domestic players are striving to establish partner ecosystems and explore international markets, with the Middle East becoming a popular destination for overseas expansion.

Strong Policy Drive, Collaborative Development of Robobus
Policy support is the core driving force behind the large-scale deployment of Robotaxis. In July 2024, China's Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and four other departments jointly released the first batch of 20 "Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration" pilot cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, Chongqing, and other cities, to promote the construction of intelligent roadside facilities, cloud control platforms, and in-vehicle terminals, accelerating Robotaxi testing and operations.
For instance, Beijing's High-Level Autonomous Driving Demonstration Zone has expanded to 600 square kilometers, opening up eight major scenarios such as airport shuttles, and realizing an autonomous driving commute route from Yizhuang to Daxing Airport. Many local governments have also issued supporting policies. For example, the "Regulations on Autonomous Driving Vehicles in Beijing" clearly supports innovative applications such as Robotaxis, gradually building a commercial closed loop and laying a legal foundation for commercialization.
Parallel to the development of Robotaxis is Robobus (autonomous buses). Taking the autonomous bus providing shuttle services during the Annual Conference of the Zhongguancun Forum as an example, it is equipped with cameras, lidars, and high-precision GPS to achieve 360° perception and high-precision positioning. The onboard intelligent driving platform can convert road condition information to accurately realize automatic start-stop, obstacle avoidance, and other functions. In addition to fully autonomous driving capabilities, it is still equipped with safety officers. Passengers can view driving information through the in-car display, and the intelligent system will automatically announce stops. It uses pure electric drive with a range of 80 kilometers and can be applied to multiple scenarios. Passengers can call vehicles at bus stops, and the operator will dispatch vehicles based on the number of passengers, improving efficiency and reducing waiting time.
Robobus (autonomous buses) is another type of autonomous vehicle with different uses, positioning, and paradigms. According to incomplete statistics, as of July 2025, cities such as Beijing, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Changsha, Shanghai, Chongqing, Hangzhou, and Wuhan have initiated pilot projects, with policy support and test operations progressing simultaneously. More than 20 provinces and cities across the country have planned test routes for driverless buses. Below is the progress of Robotaxi and Robobus deployments in major cities that have been publicly promoted:
Beijing: Beijing's High-Level Autonomous Driving Demonstration Zone has entered the 4.0 phase, covering 600 square kilometers, opening up eight categories of scenarios such as Robotaxis and driverless shuttles, and realizing an autonomous driving commute route from Yizhuang to Daxing Airport. Between Beijing South Railway Station and Beijing Yizhuang, citizens can make appointments for shuttle buses through mobile apps and experience the new autonomous driving route for a fee. The unmanned bus "Dragon Boat ONE" by Lightspeed Autonomous will officially start regular testing in Beijing's High-Level Autonomous Driving Demonstration Zone, providing safe and convenient passenger transportation services between subways and office buildings in the future.
Shanghai: In Lingang, Saic Motor's Robotaxi has set up 50 autonomous driving locations, with an operating range covering the 68 square kilometers of the main urban area of Lingang, including important transportation nodes such as campuses, commercial districts, residential areas, government and enterprise institutions, tourist attractions, and transportation hubs. Shanghai will prioritize the orderly development of large-scale applications of intelligent taxis and intelligent buses in Jiading, Nanhui, and Fengxian New City. The SenseTime Absolute Vision L4 autonomous driving bus is already in daily operation for the public, adopting a "responsive bus" model to respond on demand. The actually put into operation medical shuttle and Shanghai Ocean University shuttle have seen a cumulative number of appointments exceeding 16,000 passengers.
Guangzhou: Huangpu District has opened 334 test roads, and WeRide has opened eight 24-hour Robotaxi operation routes in Guangzhou's core urban area, covering landmarks such as Canton Tower and Zhujiang New Town. As of May 2025, the Robotaxi fleet operated by the Ruqi Travel platform in the Greater Bay Area totaled over 300 vehicles; the safe operation mileage of the self-owned fleet exceeded 2 million kilometers, covering over 3,000 stations. In May 2025, the total number of Robotaxi orders increased by over 413% year-on-year.
Shenzhen: Nanshan District has issued the inaugural batch of pilot licenses for the market-oriented operation of intelligent and connected vehicles, authorizing Pony.ai, Robotaxi Go, and other enterprises to commence commercial Robotaxi services. The city now boasts over 300 driverless vehicles operational across more than 100 community business districts, averaging over 100,000 daily orders. Additionally, the Shenzhen Bus Group has deployed 20 autonomous buses in Qianhai, establishing four autonomous bus routes.
Xiong'an New Area: As China's pioneer in fully deploying intelligent transportation infrastructure, Xiong'an New Area has achieved three nation-leading milestones: establishing the country's first city-wide digital road, operating the first autonomous bus route on a fully open community road, and integrating intelligent and connected buses into the city's regular public transportation system. The area has also unveiled the nation's first large-scale regional digital road, with driverless buses already in operation.
Hangzhou: Cao Cao Mobility and T3 Travel have commenced Robotaxi demonstration services. The self-driving shuttle in Hangzhou's Future Science and Technology City offers a one-way trip lasting approximately half an hour. Two autonomous 6-seat shuttle minibuses are now available at the Pingyao Liangzhu Ancient City Site Park, where tourists can scan codes to book free rides. Furthermore, Hangzhou has officially launched the country's first demonstration line for intelligent and connected vehicles at central urban high-speed railway stations, connecting "Citizen Center" to "Hangzhou East Railway Station," alongside another demonstration line connecting "Citizen Center" to "Xiaoshan Airport" for intelligent and connected Robotaxis.
Wuhan: Robotaxi Go has achieved near-complete coverage in Wuhan, excluding certain downtown areas within the outer three ring roads and three remote districts. The company plans to further expand its operations in the future. Additionally, Wuhan has inaugurated the province's first driverless tourist shuttle route in the Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, spanning 24 kilometers and serviced by seven driverless buses.
Chongqing: The Liangjiang New Area and High-Tech Zone have opened autonomous driving test zones. The Robotaxi intelligent shuttle service test route at Chongqing Airport covers a 17-kilometer round trip with 13 shuttle stations. On the 28th, the country's first demonstration project for L4 autonomous driving buses commenced toll operations in Yongchuan District, with the first batch consisting of three Robobuses.
Changsha: Aiming for full Robotaxi coverage by 2025, the city has already opened Baidu Apollo's L4 Robotaxi in collaboration with Hongqi for public trial rides.
Jinan: Two road segments have been designated as test roads for intelligent connected vehicles, with applications submitted by Jinan Public Transport Group Co., Ltd., and Zhongtong Bus Co., Ltd., for BRT dedicated line autonomous driving testing and demonstration applications.
Hefei: The T99 bus route, a V2X technology-based public transport experience route, has been officially launched, equipped with four conventional buses and two driverless buses.
Shaoxing: The autonomous driving bus route in the ancient city of Shaoxing has been officially commenced.
Huzhou: A total of six intelligent driving buses have been put into use in the intelligent driving scenic area of Deqing Geoinformation Town, Huzhou.
Shiyan: Ten 9-seat driverless buses have been deployed for road operations.
Wuxi: Five driverless vehicles are now operational on two regular routes, covering diverse scenarios such as residential areas and commercial complexes.
Nanjing: Three Robotaxis are deployed on Jiangxinzhou Eco-Tech Island, while L4 driverless buses are being piloted in Qinhuai District and Qixia District, focusing on dynamic scheduling to optimize urban traffic efficiency and alleviate congestion.
Jinan: Test roads for intelligent connected vehicles have been opened, with Zhongtong Bus and Yutong Bus participating in the testing application process.
Mianyang: The trial operation of the first batch of 19 driverless buses commenced in June 2024, covering four routes.
Fuzhou: Baidu, Xiamen King Long, and Qingzhou Zhihang have secured the first batch of test licenses for autonomous driving ride-hailing and bus services.

Challenges Remain, but the Prospect is Still Promising
Despite the swift advancement of the Robotaxi industry, it continues to confront numerous challenges. At the technical level, the safety and reliability of autonomous driving remain paramount, necessitating the ability to manage complex road conditions and emergencies to ensure passenger safety.
Regulatory discrepancies across regions pose another hurdle, requiring companies to invest significant time and resources to comply with varying policies, which can hinder the pace of Robotaxi deployment. Socially, some consumers harbor concerns about autonomous driving, necessitating increased promotional efforts and education to bolster public awareness and trust in Robotaxi services.
While the hardware cost of individual vehicles has decreased to the thousand-yuan level, hidden operational and maintenance costs remain high, urging the establishment of a viable business model. Leading firms like Baidu Apollo and Pony.ai are exploring profitability through subscription services, aiming to reduce the cost per mile to $0.25.
It is evident that the potential for Robotaxi to revolutionize future travel remains vast. With ongoing technological advancements, the gradual refinement of regulations, and increased social acceptance, Robotaxi is poised to become a cornerstone of future transportation. It promises to offer more convenient, efficient, and safe travel services, reduce traffic accidents, alleviate urban congestion, and lower travel costs. Simultaneously, the commercial operation of Robotaxi will propel the growth of related industries, generating job opportunities and economic benefits.
Robotaxi is undeniably transforming the future of travel. With the guidance of industry giants, the entry of multiple players, and a gradually emerging landscape, despite the challenges, the future looks bright. We have every reason to anticipate that Robotaxi will enhance our travel experience and usher in a new era of future mobility.
- End -
Disclaimer:
All works on this official account marked as "Source: XXX (non-Intelligent Car Tech)" are reproduced from other media. The purpose of reproduction is to disseminate and share more information and does not represent the endorsement of this platform for the views expressed or responsibility for their authenticity. The copyright belongs to the original author. Please contact us for deletion if there is any infringement.