Auto Enterprises: Pursue Humanoid Robot Development or Transform Cars into Embodied Intelligence?
![]() 01/04 2026
01/04 2026
![]() 381
381
Produced by Zhineng Technology
In 2026, regarding the strategies automotive companies should adopt for humanoid robots and embodied intelligence, Li Xiang and He Xiaopeng, the CEOs of two prominent new-energy vehicle firms, hold divergent views.
● Li Xiang, CEO of Li Auto, asserts that over the next decade, the most valuable product in the realm of embodied intelligence will undoubtedly be cars endowed with autonomous and proactive capabilities. He designates 2026 as the inaugural year for embodied intelligence in the automotive sector, predicting the emergence of entirely novel products.
● He Xiaopeng of XPENG Motors envisions a more profound integration between embodied humanoid robots and the automotive industry. By 2026, XPENG's advanced humanoid robots are projected to enter mass production, and XPENG will evolve into a physical AI explorer, transforming into a global embodied intelligence company.

In 2025, a growing number of automakers will commence systematic investments in humanoid robot research. Chinese automakers, seeking a second growth trajectory amidst fierce competition in car manufacturing, are exploring this convergence from both technological and industrial perspectives. Automobiles and robots inherently share a common technological foundation, with one positioned upstream and the other downstream.
◎ Intelligent electric vehicles are essentially large 'robots on wheels'.
◎ Humanoid robots, conversely, can be viewed as 'cars' stripped of steering wheels and equipped with legs.
Both share a highly homologous underlying technology: perception, decision-making, and execution form a common technological triangle, differing only in the form of actuators.
The Chinese automotive industry's accumulated expertise in autonomous driving, three-electric systems, computing platforms, and large-scale manufacturing has laid a crucial foundation for humanoid robots. Let's also take stock of automakers venturing into this field.

01 Automakers Venturing into the Humanoid Robot Arena
● XPENG Motors
When discussing cities, many readers express dissatisfaction on behalf of Guangzhou's XPENG second-generation Iron. Let's delve deeper into XPENG's humanoid robot history.
◎ XPENG's earliest foray into quadrupedal robots dates back to December 2020 when it acquired 'Duogou Robotics' and co-founded 'Pengxing Intelligence' with He Xiaopeng and others, officially entering the robotics sector.
◎ At the 2023 1024 Tech Day, XPENG unveiled its first humanoid robot, PX5 (engineering version). Standing approximately 1.5 meters tall, PX5 adopted a 'straight-knee' stride, enabling complex terrain navigation, obstacle crossing, anti-interference capabilities, as well as soccer playing and balance bike riding. This marked XPENG's transition from quadrupedal to bipedal humanoids, reusing autonomous driving algorithms.
◎ In 2024, at AI Day, XPENG released the first-generation Iron (IRON), shifting from an industrial to a more anthropomorphic design, entering factory training and showcasing interactive movements at exhibitions.
◎ On November 5, 2025, at XPENG Tech Day (AI Day), the latest generation Iron was unveiled. Standing 178cm tall and weighing 70kg, it features human-like spines, bionic muscles, fully covered flexible skin, a 3D curved head display, bionic shoulders, and 22-degree-of-freedom dexterous hands.
Equipped with three self-developed Turing AI chips (totaling 2250 TOPS), a second-generation VLA large model, it supports high-level interactions (such as conversation, walking, and folding clothes), and debuts with all-solid-state batteries, gaining popularity for its 'cat-like' smooth gait.
● Xiaomi, NIO, Li Auto, and Leapmotor 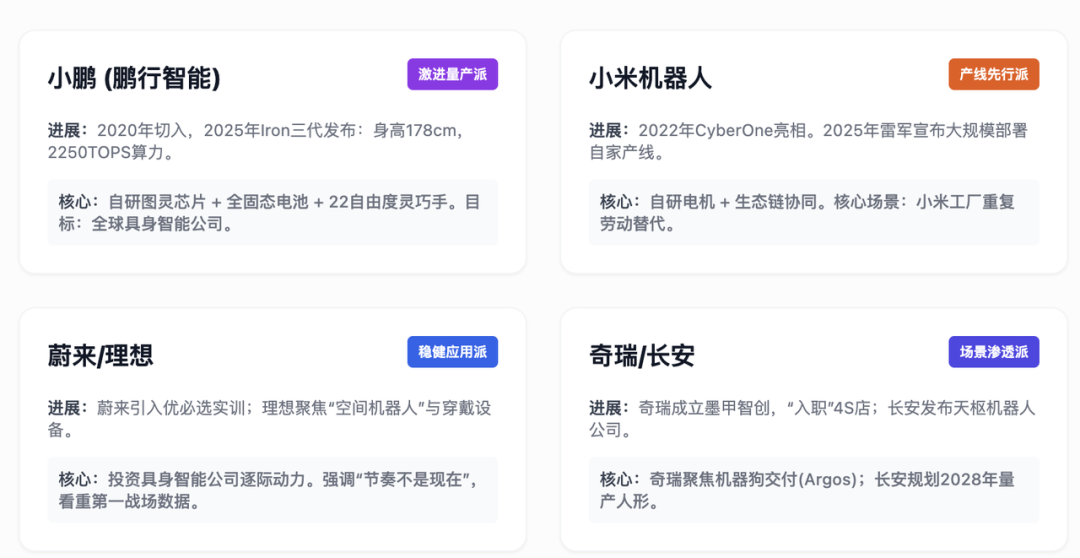
◎ Xiaomi's布局 (strategy) in the humanoid robot sector has been relatively low-key. In September 2021, it established a robotics division in response to Tesla's Optimus.
In August 2022, it unveiled the CyberOne prototype, interacting with Lei Jun on stage. Standing 177cm tall and weighing 52kg, it is a full-sized humanoid bionic robot with 21 degrees of joint freedom and a peak torque of 300Nm (hip joints).
In April 2023, it registered Beijing Xiaomi Robotics Technology Co., Ltd., and in November 2023, participated in the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center's ecosystem layout.
In February 2025, the team announced the phased deployment of CyberOne in its own factory production lines. By the end of November 2025, Lei Jun stated in an interview that humanoid robots would be massively deployed in Xiaomi factories within the next five years to replace repetitive labor, though no significant moves have been made yet.
◎ NIO's approach to humanoid robots has been relatively cautious, focusing on technological research, underlying studies, and factory applications.
In 2023, NIO formed a humanoid robot 'team' and also assembled a team of about 20 people to research robot dog projects, introducing third-party humanoid robots for practical training (such as UBTECH's Walker S for quality inspection, car logo application, and vehicle appearance collection). Leju Robotics' Kuafu series was also used in production and after-sales service.
Of course, NIO Capital invested in the embodied intelligence company LimX Dynamics without directly participating in embodied intelligence, as this money-burning sector is deemed unsuitable for short-term involvement.
◎ Li Auto explicitly stated its future entry into the humanoid robot sector but with a cautious pace. By the end of 2024, CEO Li Xiang's stance was: 'Li Auto will definitely develop humanoid robots, but not now.' With the release of glasses, we observe the emergence of 'spatial robot' and 'wearable robot' divisions, focusing on intelligent spaces and wearable devices.
◎ Leapmotor's involvement in humanoid robots is the most superficial, primarily in the early research stage. In March 2025, founder Zhu Jiangming revealed that Leapmotor had formed a several-dozen-person humanoid robot R&D team, with the project in the research phase. Humanoid robots serve merely as a technological reserve.
● Other Chinese Automakers
◎ Changan Automobile: From 2024 to early 2025, it planned and invested over 50 billion yuan in intelligence, with robots being a part of it.
In September 2025, it launched the Tianshu Intelligent brand and established Changan Tianshu Robotics Co., Ltd. in November. At the Guangzhou Auto Show, it showcased the 'Xiao'an' prototype (with 40 degrees of freedom and over 2 hours of endurance). The first vehicle-mounted component robot is expected in the first quarter of 2026, the first humanoid robot in 2027, and mass production in 2028.
◎ Chery Automobile also made an early move in robotics, focusing on cooperation and manufacturing reuse to explore humanoid robots and robot dogs.
In January 2025, it established Anhui Mojia Zhichuang Robotics Technology Co., Ltd., and in March, the Moyin robot made its debut at the Shanghai Auto Show. The first batch of 220 units was delivered globally, and in June, robots began 'working' in 4S stores. By December, the 1000th robot dog, Argos, was delivered. Core scenarios include 4S store guides, supermarket retail, and public services, with a three-step plan to expand into households.
◎ GAC Group: In early 2022, its research institute initiated embodied intelligence R&D. In December 2024, it released the second/third-generation GoMate (with a wheel-foot structure, 38 degrees of freedom, and self-developed dexterous hands/motors), primarily for R&D and exhibition purposes. Small-scale production is expected in 2026, with gradual mass production of complete machines.
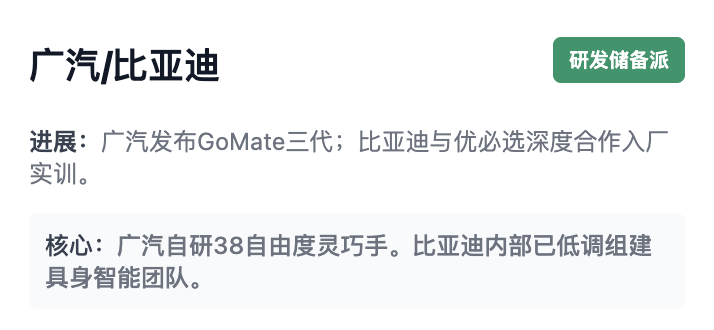
◎ BYD: From 2024 to 2025, it collaborated with UBTECH, with the Walker series entering factory practical training. In 2025, it internally recruited an embodied intelligence team, though no significant moves have been made yet.
02 Characteristics of Automakers Entering the Robotics Sector
Automakers appear to be 'no novices' when venturing into robotics, with the humanoid robot trend set by Tesla.
At the 'brain' and 'cerebellum' levels of humanoid robots, automakers can leverage their accumulated experience in assisted driving systems to transition into embodied intelligence. Automakers have already navigated the most challenging phase in assisted driving, from computing platforms and algorithm stacks to data closures. However, the most difficult aspects remain scenarios and data, which are currently in a research and breakthrough phase for automakers.
At the 'muscle' and 'skeleton' levels, the most expensive core components of humanoid robots require underlying processing capabilities homologous to the new energy vehicle supply chain. The scale effect of the Chinese automotive industry may significantly drive down costs and achieve scaled production of humanoid robots.

Manufacturing capabilities are the forte of the automotive industry, which excels at breaking down complex systems into engineering, testable, and replicable modules, and stably producing them at high rhythms. From an industrialization perspective, humanoid robots can be envisioned as being assembled like consumer electronics. To ensure reliability, they will undoubtedly draw on the automotive industry's experience and be 'manufactured like cars.'
For automakers, humanoid robots do not need to initially face open markets. Their own vehicle manufacturing and component factories are ideal 'first battlefields.'
In roles requiring high repetition, intensity, and increasing flexibility, such as handling, sorting, quality inspection, and assembly, humanoid robots inherently possess value.
Once integrated into production lines, they can form a closed loop of data-training-iteration-redeployment. This 'self-production and self-use' path allows their robot products to move beyond mere demonstrations.
Subsequent investments from automakers may accelerate the commercialization of humanoid robots, bringing technologies previously confined to research or small-scale pilot stages into industrial-grade validation. This can introduce automotive supply chain enterprises into sectors such as motors, precision reducers, dexterous hands, sensors, and control chips, bringing automotive-grade safety, reliability, and quality systems.
Summary
It is quite noteworthy to observe automakers transitioning from being major clients of industrial robots to becoming researchers and manufacturers of humanoid robots.