Baidu's Intelligent Driving Expert Li Zhenyu Ventures Out, Another Star Team Emerges in Embodied AI
![]() 12/23 2024
12/23 2024
![]() 745
745

Author | Lingxiao, Baixue
Another star team has emerged in the realm of embodied AI.
Li Zhenyu, the former Senior Vice President of Baidu Group and President of the Intelligent Driving Group (IDG), has embarked on a fresh journey in embodied AI.
He has joined Tashizhihang, an embodied intelligent robot company founded by Chen Yilun, the former Chief Scientist of Huawei's BU, and Ding Wenchao, a former Huawei Genius.

Li Zhenyu
At this juncture, the three founders of Tashizhihang have come into the spotlight.
Tashizhihang is a quintessential startup in the embodied AI race, founded by a combination of "autonomous driving experts + young scientists." Notably, Li Zhenyu, a core technology expert at Baidu for 17 years, held the top position at Baidu IDG and was the Senior Vice President of the group.
With Li Zhenyu's arrival, another highly promising startup has surfaced in the embodied AI sector.
Li Zhenyu Joins Tashizhihang
May Be Responsible for Team Establishment and Management
Li Zhenyu, the former leader of Baidu IDG (Intelligent Driving Group).
He was the architect of Baidu's early autonomous driving efforts and the driving force behind Baidu's open-source autonomous driving ecosystem.
At Baidu, Li Zhenyu spearheaded the autonomous driving business and achieved numerous victories. Among them, two stand out prominently.
The first battle: Uniting talents under the Apollo program to build an ecosystem and harness Baidu's autonomous driving prowess.
Autonomous driving has always been Baidu's strength, but this strength truly flourished and was put into practical use when Li Zhenyu ascended to the top position and took charge of Baidu IDG.
Li Zhenyu, with a background in network technology research and development at Huawei, joined Baidu in 2007 and played a crucial role in establishing the Autonomous Driving Business Unit and managing Baidu Brain. However, before 2017, Baidu's autonomous driving direction was unclear, and internal technical turnover was high.
Li Zhenyu bolstered Baidu's autonomous driving team's morale.
Upon becoming General Manager of Baidu IDG in 2017, Li Zhenyu vigorously promoted the Apollo program, securing contracts and respect through an ecosystem strategy.

Li Zhenyu at the Apollo RT6 launch event
In an internal letter, Li Yanhong once commented on Li Zhenyu: "He excels at resource integration, proactively seeks change, and continually upgrades organizational capabilities, significantly contributing to building Baidu's new growth engine."
This testament underscores Li Zhenyu's leadership prowess.
The second battle was leading Baidu's driverless car team to prominence.
From 2020 to 2024, Baidu's driverless car team and its spin-off service, Luobo Kuaipao, shone brightly in China's Robotaxi industry. Li Zhenyu was a pivotal figure, witnessing Baidu's driverless car project grow from infancy to prominence.
As early as 2016, Li Zhenyu participated in Baidu's first public trial ride in a driverless car. Four years later, with Baidu officially obtaining a test license for autonomous passenger vehicles in Beijing, Baidu Luobo Kuaipao commenced public operations in major cities nationwide.
From the lab to Baidu's first public passenger ride in a driverless car, to Luobo Kuaipao in Wuhan sparking nationwide debate, Baidu's stock price surged by 18% at one point. Driverless cars were no longer a distant dream, and Baidu stood as the only Chinese player on par with Waymo.

This time, his two younger colleagues in this venture are also formidable.
Dr. Chen Yilun holds a Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering from the University of Michigan and bachelor's and master's degrees from Tsinghua University's Department of Electrical Engineering.
He worked at Huawei for four years, serving as CTO and Chief Scientist of the BU's Autonomous Driving System. He left in 2022 and is currently the Chief Expert in Intelligent Robotics at Tsinghua University's Institute for AI Industry Research (AIR).
Ding Wenchao earned his bachelor's degree from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and his Ph.D. from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. He was selected for Huawei's "Genius Young Program".
In 2020, Ding Wenchao joined Huawei and served as a research scientist and technical leader for Intelligent Driving Solutions (ADS), working alongside Chen Yilun during his Huawei tenure. He was a core technical expert in Huawei's first-generation intelligent driving system.
In February 2023, Ding Wenchao departed to join Fudan University's Institute of Engineering and Applied Technology as a young researcher and head of the Clustered Robotics System Laboratory (Magic Lab).
Notably, Fudan MagicLab unveiled the elderly care humanoid robot "Guanghua No. 1" this July. "Guanghua No. 1" can walk, read people's micro-expressions, and generate corresponding emotional responses.
Currently, Tashizhihang's team members are primarily Ph.D. students from Tsinghua and Fudan Universities.
The three founders are currently conducting intense interviews, directly managed by Li Zhenyu, focusing on AI algorithms and hardware positions.
It is understood that Tashizhihang sets high standards for talent selection, preferring young, innovative AI talents with successful product experience. According to insiders, several potential candidates have expressed eagerness to join the new company due to the founders' allure.
Next, Li Zhenyu may lead the establishment, management, and business expansion of the Tashizhihang team. Chen Yilun and Ding Wenchao will likely concentrate on technological research and development.
For startups, the founding team's strong academic backgrounds and practical experiences are crucial in attracting funding and talent.
With Li Zhenyu, a seasoned technology expert, on board, Tashizhihang's team can be deemed a luxury lineup in embodied AI, starting from a high point with considerable investment prospects.
Insiders revealed that Tashizhihang is currently in its first round of funding.
Public information indicates that Tashizhihang was established in July this year, with a business scope encompassing artificial intelligence software development, hardware sales, and the research and development, as well as sales, of intelligent robots, industrial robots, and service consumer robots.
Intelligent Driving + Embodied AI
A New Racetrack for Seasoned Captains
It's not uncommon for intelligent driving experts to shift to embodied AI.
Since 2022, many technical and business talents in the intelligent driving field have entered the embodied AI industry to venture out on their own. They include Wang Gang, former Vice President of Alibaba and head of the Alibaba DAMO Academy's Autonomous Driving Lab, Zhang Li, former COO of WeRide, Liu Fang, former head of autonomous driving product technology and mass production at Xiaomi, and Yu Yinan, former Vice President of Horizon Robotics.
Even leading companies in the intelligent driving supply chain, such as Bosch, Horizon Robotics, and RoboSense, are increasing their investments.
According to incomplete statistics, at least 15 leading companies in the intelligent driving supply chain have ventured into the embodied AI industry, primarily through three methods: forming teams, collaborating with humanoid robot companies for research and development, and developing robot technology and components.
In addition to talents and intelligent driving supply chain companies, automakers have also joined the embodied AI fray. Tesla, Xiaomi, XPeng, and Changan Automobile are all developing humanoid robots.
Embodied AI (Embodied AI) integrates AI into physical entities like robots, endowing them with the ability to perceive, learn, and interact dynamically with their environment.
In layman's terms, embodied AI is an AI brain combined with a mechanical body.
Therefore, embodied AI can manifest in various forms, such as robotic arms, bipedal robots, humanoid robots, and more.
Their commonality is possessing a smart brain capable of assisting or even replacing humans in various tasks.
In 2022, significant breakthroughs in AI technology, exemplified by large models, made it possible for robots to possess smart brains, gradually popularizing the concept of embodied AI.
Why are intelligent driving talents flowing towards embodied AI? There are two primary reasons.
First, the underlying operational logic of intelligent driving and embodied AI is consistent, encompassing perception, decision-making, and execution.
Due to the commonality of technology, software and hardware from intelligent driving can be transferred to embodied intelligent robots.
Software technologies such as autonomous driving systems, large models, end-to-end neural networks, motion planning algorithms, and core automotive components like batteries, motors, steering gears, and brakes can all be reused.
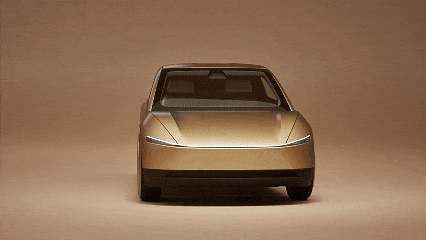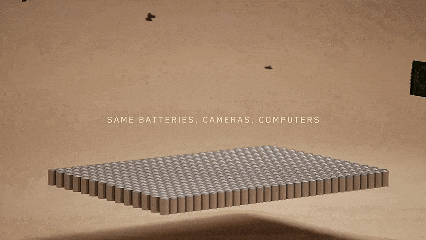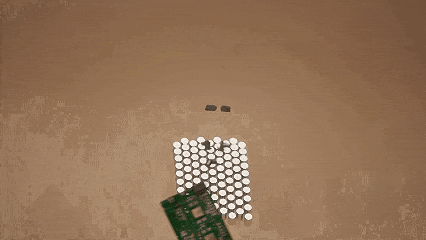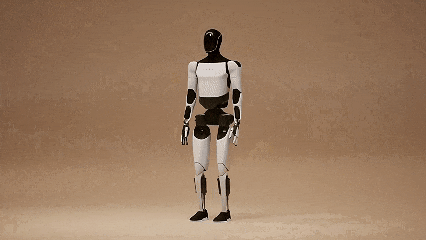
Reuse of Tesla's automotive battery components in the humanoid robot Optimus
Furthermore, leaders transitioning from intelligent driving to embodied AI possess rich experience in technology research and development, hardware manufacturing, or business operations.
Second, the embodied AI market is still nascent and may hold even greater potential than the autonomous vehicle market.
After more than eight years of development, the intelligent driving industry's leading players have been established, and a substantial market share has been captured by relatively mature enterprises.
The embodied AI field is still in its infancy, with no company having truly completed a business closed loop, and market share remains to be captured.
The vast market share gap corresponds to the enormous potential of embodied AI in the future.
Taking humanoid robots, the hottest segment in the embodied AI field, as an example:
Musk once predicted that by 2030, Tesla's market value would reach $30 trillion, with humanoid robots contributing $25 trillion of that value, surpassing the value contributed by its autonomous vehicles.
Jensen Huang, CEO of NVIDIA, also stated that robots will become one of the world's most important industries. He believes that only two types of robotic systems can be easily deployed globally: autonomous vehicles and humanoid robots.
Tempted by the immense market potential, capital is pouring into the embodied AI sector.
According to incomplete statistics from the GGII (Gaogong Robot Industry Research Institute), from January to October 2024, there were 69 financing events for humanoid robots globally, totaling over 11 billion yuan. Among them, 56 events occurred in China, totaling over 5 billion yuan.
In the first half of 2024, global financing for humanoid robots exceeded 7 billion yuan, surpassing the total financing for the entire year of 2023.
Besides humanoid robots, embodied intelligent robots may take various forms, holding unlimited development potential.
Embodied AI and intelligent driving are like two distinct sailboats on the same sea.
The intelligent driving sailboat has sailed into a fiercely competitive and tumultuous red ocean.
However, some seasoned captains who once dominated the intelligent driving field have chosen to sail a new embodied AI sailboat towards new blue oceans.
How much turbulence will these experienced captains stir up in the next vast sea, and what changes will they bring to human society?
The future of embodied AI is promising.