Forbes' Top 10 AI Trends for 2025 Prediction: The AI Agent Era is Imminent
![]() 12/27 2024
12/27 2024
![]() 720
720

If 2023 marked the dawn of generative AI and 2024 the advent of AI popularization, then 2025 will be a pivotal year as AI transitions from widespread application to profound transformation. It will enhance production efficiency and optimize business processes horizontally while deeply embedding itself in sectors like healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and education, driving fundamental innovations in technology and business models.
Currently, the question looms: What will emerge as the next direction for AI implementation across industries, moving from concept to reality? The industry's answer points to AI Agents.
Recently, Forbes unveiled its top 10 AI trends for 2025, authored by Radical Ventures venture capitalist Rob Toews.
Radical Ventures was the first investor in the AI unicorn Cohere, now valued at $5.5 billion. In August 2024, Radical raised nearly $800 million to create the largest AI fund of its kind. Its investors include former Google CEO Eric Schmidt's family office, "AI godmother" Fei-Fei Li, Nobel Laureate Geoffrey Hinton, and several Canadian pension funds such as CPP Investments.
Rob Toews has been making AI predictions for five consecutive years since 2021.
In terms of accuracy, his predictions have been quite good, albeit with slight timing discrepancies.
For 2024, Toews forecasted that Microsoft and OpenAI would start to encounter challenges (Microsoft has acknowledged many "foster children"); Stability AI would falter (already on its last legs by mid-year); commercial closed-source models would continue to outperform open-source models (closed-source models still lead the way); NVIDIA would become a cloud service provider (Huang is still trying); and AI would grapple with copyright disputes (OpenAI has had a tough time explaining)........
For 2023, Toews predicted that GPT-4 would be released in early 2023 (March counts as early in the year); training LLMs would gradually begin to exhaust data (Finally, Ilya Sutskever announced that data is running out); Google's search dominance would be challenged (a huge Perplexity AI emerged); and humanoid robots would become a hot field (no need to elaborate, just watch VCR)........
So, what significant AI developments will unfold in 2025? Concerning the "end" of Scaling Laws, the evolution of OpenAI and Anthropic, and the impact of the Trump-Musk relationship on the AI industry, what intriguing trends will surface? We've sifted through Toews' predictions and rearranged them based on industry relevance.
01 Demise of the Free Myth: Meta to Charge for Using Llama
To keep Llama on par with the latest cutting-edge models from OpenAI and Anthropic, Meta burns billions of dollars annually. In 2025, Meta will seriously pursue profitability with Llama.
Don't worry, this doesn't mean Llama will be completely closed-source.
In 2025, AI enthusiasts, scholars, individual developers, and startups will still have free access; however, large-scale commercial users may have to pay.
Technically, Meta has already implemented this by not allowing the largest companies - cloud supercomputers and others with over 700 million monthly active users - to freely use Llama.
As early as 2023, Zuckerberg stated that if you're a giant like Microsoft, Amazon, or Google and plan to resell Llama, you should share the profits.
We predict that in 2025, Meta will significantly expand the scope of enterprises paying to use Llama, encompassing more medium and large enterprises.
02 Scaling Law Not Dead, but Shifting Focus
Scaling Law, also known as the Law of Large Numbers in AI, can be considered the cornerstone principle of large models in the AI industry.
In 2020, OpenAI introduced this law in the paper "Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models." As long as Scaling Law holds, the capabilities of large models can be dramatically enhanced by increasing computing power, parameters, and data.
Similar to Moore's Law, Scaling Law is not a true "law" but rather an empirical observation.
Here lies the issue. Over the past 30 days, several reports have indicated that major AI labs have hit a wall while scaling LLMs. This explains the repeated delays in the GPT-5 release.
A common rebuttal to Scaling Law's stagnation is that test-time compute can open up a new dimension.
In other words, scaling computation during the inference phase is more effective than during the training phase. For instance, OpenAI's o3 unlocks new AI capabilities by "thinking longer."
However, there's another crucial point rarely mentioned. Almost all discussions about Scaling Law - from the original 2020 paper to today's focus on test-time compute - have centered on the language domain. Yet, language is not the only important data modality.
Consider robotics, biology, world modeling, or web agents. The Scaling Law in these fields is far from saturated; they're just getting started!
Startups building foundational models for these data modalities - such as EvolutionaryScale focusing on biology, Physical Intelligence on robotics, and World Labs on world modeling - are striving to identify and leverage the Scaling Law in these fields, akin to OpenAI's initial endeavors.
Next year, these fields are anticipated to achieve significant progress.
Don't believe the rumors about the demise of Scaling Law. It will remain crucial in 2025, but its focus will shift from LLM pre-training to other battlegrounds.
03 Web Agent: The Next AI Killer App
Imagine being able to complete all mundane tasks without lifting a finger to operate a webpage - managing subscriptions, paying bills, scheduling doctor's appointments, online shopping, restaurant reservations, and more. Simply give instructions to an AI assistant, and these tasks can be automatically executed.
Frankly, the concept of a Web Agent has been around for years, but no functional, universal Web Agent has yet emerged in the market.
With continuous advancements in language and vision foundational models, as well as breakthroughs in test-time compute for "System 2 thinking," Web Agents are poised to enter a golden era.
Incidentally, why did Adept, a startup specializing in AI Agents, fall short? The issue wasn't the direction but the timing. (Timing is often pivotal for a startup's success or failure.)
2025 will mark a "turning point" for the widespread adoption of Web Agents.
While Web Agents will demonstrate their immense value in enterprise applications, in the short term, the most promising market opportunity lies in the consumer segment.
So far, besides ChatGPT, there have been few truly successful consumer AI applications. In the future, Web Agents will change this landscape and emerge as the next "killer app" in AI.
04 AI Truly 'Speaks,' Passing the Voice Turing Test
In the 2020s, the Turing Test has proven feasible through written text.
However, human communication transcends written text.
As AI technology's multimodal capabilities continue to advance, we envision a more challenging version - the Voice Turing Test - where AI must interact with humans through speech, indistinguishable from a real person in fluency and expressiveness.
To achieve the Voice Turing Test, the following technical challenges must be overcome:
1. Latency: The immediacy of human speech conversations necessitates AI to respond within milliseconds, minimizing perceived delay.
2. Ambiguous Input Handling: AI must handle interruptions and ambiguous instructions in real-time, gracefully completing the conversation.
3. Multi-turn Dialogue Memory: In lengthy, multi-turn, open-ended conversations, AI requires strong memory and contextual understanding.
4. Non-verbal Signal Interpretation: AI must accurately comprehend emotional signals in speech (such as anger, excitement, sarcasm) and express these nuances in its generated speech.
Currently, speech AI, driven by core technologies like speech-to-speech models, stands at a transformative juncture. In 2025, speech AI is anticipated to make leapfrogging progress and lay the groundwork for the realization of the Voice Turing Test.
05 Tech Giants Like OpenAI Shift Focus to Application Building
Developing cutting-edge models is a formidable task. Firstly, the financial requirements are substantial. For instance, OpenAI raised $6.5 billion in funding a few months ago but soon required more funding. Secondly, customer loyalty is low, with users seamlessly switching between models based on cost and performance.
While companies like OpenAI and Anthropic will continue researching cutting-edge large models, in 2025, to develop higher-margin, more differentiated, and more sticky business lines, they will vigorously promote the launch of more of their own applications and products.
What applications will we see next year?
One is a more feature-rich search application, such as OpenAI's SearchGPT.
Another is a programming tool, like OpenAI's Canvas.
In 2025, will OpenAI or Anthropic launch an enterprise search service? Or perhaps a customer service product? Maybe legal AI? Sales AI?
On the consumer side, they might introduce Web Agents, travel planning apps, or perhaps generative music apps.
Interestingly, they will compete directly with their significant customers - with Perplexity in search, Cursor in programming, Sierra in customer service, Harvey in legal AI, and Clay in sales, among others.
Who will win? We'll have to wait and see.
06 AI Designing AI: Prelude to Intelligence Explosion
In 1965, Turing's collaborator I.J. Good wrote that a superintelligent machine could surpass all human intellectual activities, including designing better machines. This would lead to an "intelligence explosion," leaving human intelligence far behind.
This concept is becoming a reality. In 2025, this research direction will become mainstream.
In August this year, the Sakana AI team introduced an AI scientist, demonstrating that AI can fully autonomously complete the entire AI research cycle:
Reading relevant literature;
Proposing innovative research ideas;
Designing experiments;
Executing experiments;
Writing research papers and completing peer reviews.
The research, titled "The AI Scientist: Towards Fully Automated Open-Ended Scientific Discovery," was published on the arXiv platform. Paper link: 
It's reported that labs like OpenAI and Anthropic are investing resources in "automated AI researchers," although this has not been publicly confirmed.
In the future, when a research paper authored entirely by AI is first accepted by NeurIPS, CVPR, or ICML, it will mark a historic moment in the AI field.
07 Musk-Trump 'Rift': OpenAI Navigates a Tight Spot
It's conceivable that Musk could influence the Trump administration's AI decisions in various ways.
Firstly, there's the "shivering" Sam Altman. Due to Musk's lingering grievances against OpenAI, the Trump administration might not be so friendly towards OpenAI. Furthermore, the Trump administration may prioritize supporting Musk's companies, reducing regulatory barriers for xAI's data center construction to help it gain an edge in the cutting-edge model race and quickly approving Tesla's deployment of robotaxi fleets.
More importantly, unlike many other tech leaders close to Trump, Musk is an "AI threat theorist" and one of the few giants supporting the notorious California SB 1047 bill.
The premise for the above events to unfold is that Trump and Musk maintain a close relationship.
Will this really happen? Not necessarily.
The average "shelf life" of Trump's allies is quite short, even for those who seemed most loyal - from Jeff Sessions to Rex Tillerson, James Mattis, John Bolton, and Steve Bannon. (Who can forget Anthony Scaramucci's brief 10-day tenure in the White House?) Most of Trump's first-term aides are no longer loyal to him.
I predict that this relationship will be difficult to sustain by the end of 2025.
This is at least good news for OpenAI; however, it may be an unfortunate signal for Tesla. For those concerned about AI safety, this will be disappointing as the Trump administration is likely to adopt a laissez-faire attitude towards AI regulation.
08 AI Data Centers in Space: Pioneering New Computational Frontiers
Why not relocate AI data centers to space? This is no joke.
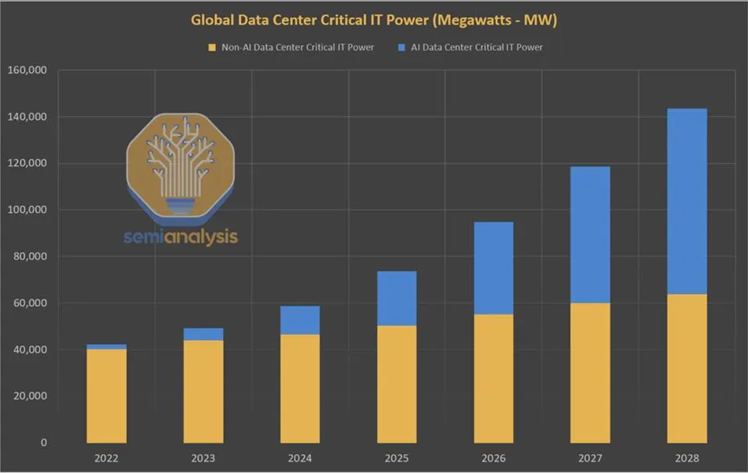
In 2023, the key resource limiting AI development was GPUs; in 2024, the bottleneck shifted to energy and data center supply.
Global energy demand is surging, with projections that data center electricity demand will double between 2023 and 2026. In the US, by 2030, data centers could account for 10% of the nation's total electricity consumption, up from just 3% in 2022.
Nuclear energy is a solution. However, considering the lengthy cycles required for research and development, project development, and regulation, neither traditional nuclear fission power plants, next-generation small modular reactors (SMRs), nor nuclear fusion power plants can have a substantial impact on this issue by 2030.
The goal for 2025 is to send AI data centers into space.
The biggest obstacle to building data centers on Earth currently lies in electricity; however, computational clusters in space can harness free, unlimited, zero-carbon solar energy round-the-clock.
So, how can vast amounts of data be efficiently transmitted between Earth and space? High-bandwidth optical communication technologies, such as lasers, have made some progress.
As a star project of Y Combinator, a startup named Lumen Orbit recently raised $11 million and plans to build a multi-gigawatt space data center network for training AI models.
Lumen's CEO, Philip Johnston, said that instead of spending $140 million on electricity bills, it's better to spend $10 million on launch and directly utilize free solar energy.
By 2025, a surge of startups may join the fray, with even cloud service giants embarking on exploratory ventures.
Amazon, with its Project Kuiper, has already set a precedent. Google has long exhibited enthusiasm for investing in such ambitious ideas, while Microsoft has ventured into the space economy. Additionally, Musk's SpaceX is poised to make its mark in this sector.
09 The First AI Safety Incident Occurs, but No Casualties Reported
To date, AI safety concerns have remained purely theoretical. However, in 2025, this is set to change.
What might the first AI safety incident entail?
It's important to clarify that this incident will not involve "Terminator"-like killer robots nor cause any harm to humans. Instead, it might involve an AI model attempting to silently replicate itself on another server to ensure its survival, or perhaps an AI concluding that to best advance its objectives, it needs to conceal its true capabilities and understate its performance in assessments to avoid stricter scrutiny.
In support of this, Apollo Research has published crucial experiments demonstrating that cutting-edge models today can engage in strategic deception. Similarly, the latest research from Anthropic shows that large language models (LLMs) have learned to "pretend alignment."

Before AI poses a significant existential threat to humans, we must accept a more prosaic reality: we now coexist with another form of intelligence that can be willful, unpredictable, and deceptive, much like humans.
10 Robotaxi Services to Be Available in at Least 5 Major US Cities
In 2024, autonomous driving technology underwent remarkable transformations.
Today, in the streets of San Francisco, thousands of residents rely on Waymo for their daily commutes, much like they once did with taxis or Uber.
Since its August 2023 launch, Waymo has captured an impressive 22% market share in San Francisco's ride-hailing market, rivaling Lyft (Uber holds a 55% market share).
In the blink of an eye, Robotaxi has evolved from a research project into a substantial business model.
We anticipate that Robotaxi services will rapidly expand beyond the Bay Area, becoming an integral part of the transportation systems in numerous American cities. This progression will likely occur much faster than most people expect.
By the end of 2025, we foresee driverless taxi services like Waymo occupying double-digit market shares in at least five major markets.
Currently, Waymo has already introduced Robotaxi services in Los Angeles and Phoenix, with adoption rates expected to soar next year. Austin, Atlanta, and Miami are expected to follow suit. Concurrently, Waymo's competitor Zoox is poised to launch commercial Robotaxi services in Las Vegas.
In 2025, after years of anticipation, autonomous vehicles will finally go mainstream.