Multiple Giants Announce Open-Source Datasets, Accelerating Global Evolution of Embodied Intelligence!
![]() 03/18 2025
03/18 2025
![]() 753
753
Embodied intelligence is advancing on the path of open-source data.
In the realm of embodied intelligence, data serves as the cornerstone for training deep learning models, enhancing, and optimizing robot capabilities. However, factors such as high acquisition costs, low efficiency, and limited versatility of data significantly impede the development of embodied intelligence.
Wang Tianmiao, director of the Robotics Institute at Beihang University, also emphasizes that the lack of data hampers the generalization abilities of humanoid robots. Currently, it is challenging to obtain the three types of generalization data necessary for robot task generalization, perception generalization, and motion manipulation—such as data for tasks like folding clothes or riding bicycles.
Given this, the open-sourcing of datasets has emerged as a crucial 'accelerator' for advancing the embodied intelligence industry collectively.
Since the end of 2024, eight leading embodied intelligence companies and research institutions worldwide have announced the open-sourcing of datasets. These giants are jointly contributing to the construction of the data ecosystem, thereby accelerating the evolution of global embodied intelligence.
Fourier——FourierActionNet
On March 17, Shanghai-based robotics company Fourier officially open-sourced FourierActionNet, a comprehensive dataset for full-size humanoid robots, initially providing over 30,000 high-quality real machine training data.
This dataset encompasses various task trainings for all models in the Fourier GRx series, comprehensively recording the task execution data of robots in real environments. It covers precise picking and placing, pouring, and other operations for various objects such as common tools, household items, and food, as well as generalized execution under different environmental conditions. It includes imitation learning data specifically for hand tasks, adapts to multi-degree-of-freedom dexterous hand tasks, and all data is automatically annotated using a visual language model (VLM) and verified manually for accuracy.
Notably, FourierActionNet contains tens of thousands of real machine training data, including imitation learning data tailored for hand tasks, which is compatible with multi-degree-of-freedom dexterous hand tasks. All data is automatically annotated using a VLM and manually verified to ensure precision and accuracy.
Innovation Center——RoboMIND, “Tien Kung”
On March 12, Tien Kung, a Beijing-based humanoid robot innovation center, released "Huisi Kaiwu," the world's first general embodied intelligence platform featuring "one brain for multiple functions" and "one brain for multiple robots." The application of "Huisi Kaiwu" disrupts the traditional robot application development model based on specialized development for single tasks in single scenarios, filling the gap in general software systems in the field of embodied intelligence.
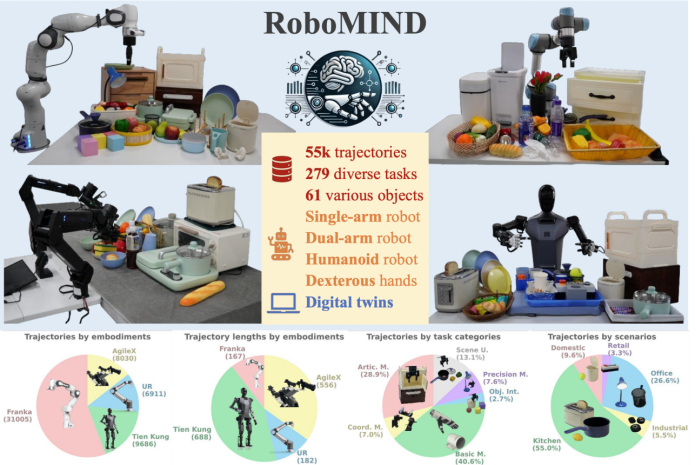
Regarding open-source datasets, the Innovation Center released RoboMIND, the industry's first standardized general embodied intelligence dataset and benchmark, with the first batch of 100,000 open-source data, covering multiple scenarios such as industry, home, and office, demonstrating high versatility and scalability.

On December 27, 2024, the Innovation Center and the School of Computer Science at Peking University jointly launched RoboMIND, a large-scale multi-configuration embodied intelligence dataset and benchmark, based on mature standards for data collection and validated through multiple model trainings, supporting multiple robots and tasks with versatility.
According to statistics, the dataset released by the Innovation Center employs various robot forms including single-arm robots, dual-arm robots, and humanoid robots for data collection, encompassing 279 different tasks across multiple scenarios and covering up to 61 different objects. It features multiple robots, multiple skills, and multiple applications, making it China's first versatile embodied intelligence dataset validated by models.
On November 11, 2024, the Innovation Center announced the "Tien Kung Open Source Plan," which will gradually open-source technical achievements in robot bodies, datasets, motion control, and other areas to the industry.
It is reported that based on the whole-body cooperative intelligent cerebellum platform, "Tien Kung" boasts an average tested speed of up to 10 km/h, with the maximum running speed increased to 12 km/h. It can also navigate smoothly on various complex and generalized terrains such as slopes, stairs, grass, gravel, and sand.
The multi-functional embodied agent platform "Kaiwu" equipped on "Tien Kung" includes an embodied brain driven by AI large models for task planning and an end-to-end skill execution embodied cerebellum driven by data, capable of "one brain for multiple robots" and "one brain for multiple functions." In the future, it will feature 200,000 robot trajectory data, compatible with over 20 robot bodies, reducing embodied capability development time by 90%.
In terms of the data ecosystem, the Innovation Center's data collection spans 6 types of robot bodies and 7 typical scenarios, with daily data production reaching 10TB.

Physical Intelligence——π0
In February this year, Physical Intelligence (PI), a renowned US embodied intelligence startup, open-sourced their vision-language-action embodied model π0, releasing the code and weights of π0 on GitHub. They also stated that, based on their own experiments, 1 to 20 hours of training data is sufficient for π0 to adapt to various tasks.
π0 has a pre-trained foundation based on a 3 billion-parameter pre-trained visual language model (VLM), adjusted to achieve robot control. In task performance, π0 outperforms other baseline models on multiple robot tasks, including tidying up desktops, folding clothes, and assembling cardboard boxes. The model can also accept natural language instructions and execute tasks while supporting fine-tuning for complex tasks.
The open-source content of the π0 base model includes: code and model weights for running the base pre-trained π0 model; multiple checkpoints fine-tuned for simple tasks on robot platforms such as ALOHA and DROID; example code for running inference on multiple real-world and simulated robot platforms; code for fine-tuning the base π0 model for specific tasks and platforms.

Shenzhen Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Research——MultiPlan
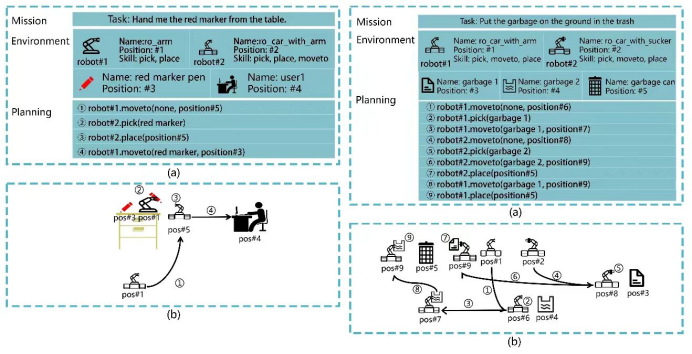
In January this year, the AIRS Intelligent Control Center team led by Professor Ji Xiaoqiang from the Shenzhen Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Research proposed MultiPlan, the world's first heterogeneous multi-robot collaboration control dataset for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs), along with the error diagnosis indicator MRED. MultiPlan defines task content, environment description, and motion planning based on a natural language task description framework, providing a concise and deployable intelligent collaboration solution combined with the robot's underlying SDK.
Compared to traditional methods, the fine-tuned 7B-parameter model demonstrates significant superiority in planning and control capabilities for complex tasks over closed-source large models such as GPT-4o. The MultiPlan dataset covers 100 common indoor and outdoor living scenarios, ensuring data generalization and diversity through a data pipeline of template generation and manual review. Experiments were deployed in two scenarios: office services and urban street cleaning, demonstrating the effectiveness and robustness of the method.
Wisdom Motor——AgiBot World
On December 30, 2024, Wisdom Motor announced the open-source project AgiBot World, a million-scale real robot dataset. Wisdom Motor introduced that AgiBot World is the world's first million-scale real robot dataset based on comprehensive real-world scenarios, versatile hardware platforms, and full-process quality control. Compared to Google's open-source Open X-Embodiment dataset, AgiBot World boasts a 10-fold larger long-range data scale, a 100-fold broader scenario coverage, and data quality upgraded from laboratory-grade to industrial-grade standards.
AgiBot World originated from Wisdom Motor's self-built large-scale data collection factory and application experimental base, with a total space area exceeding 4000 square meters, containing over 3000 real items and over 100 highly realistic scenarios distributed across home (40%), catering (20%), industry (20%), supermarkets (10%), and offices (10%), comprehensively covering typical application needs of robots in production and life.

Unitree Robotics——G1 Operating Dataset
On November 13, 2024, Unitree Robotics announced the open-sourcing of the G1 humanoid robot operating dataset to propel the global embodied intelligence industry forward, encompassing data collection, learning algorithms, datasets, and models, with stated plans for continuous updates.
In this open-source release, Unitree Robotics published teleoperation control code for the G1 humanoid robot, including code tutorials for teleoperation control, hardware configuration diagrams, bills of materials, installation instructions, etc. Simultaneously, Unitree Robotics also open-sourced the G1 humanoid robot's operating dataset, covering five operations: screwing bottle caps and pouring water, stacking tricolored building blocks, placing cameras into packaging boxes, collecting and storing items, and grasping red wooden blocks with dual arms and placing them into black containers. It records the seven-dimensional state and action data of the robot's arms and dexterous hands.

Tsinghua University——RDT
On October 18, 2024, Tsinghua University open-sourced RDT (Robotic Diffusion Transformer), the world's largest diffusion large model for dual-arm robots. RDT is the world's largest diffusion foundation model for dual-arm robot manipulation tasks, launched by the TSAIL team at Tsinghua University's Computer AI Research Institute. With 1.2 billion parameters, RDT can autonomously complete complex tasks without human intervention. Based on imitation learning, RDT can imitate human actions, demonstrating strong generalization capabilities and manipulation precision, capable of handling unseen objects and scenarios.
It is understood that RDT was pre-trained on the largest multi-robot dataset to date and scaled to 1.2 billion parameters, making it the largest diffusion-based robot manipulation foundation model. RDT was fine-tuned on a self-built multi-task dual-hand dataset containing over 6000+ sets, enhancing its manipulation capabilities. RDT possesses the largest fine-tuned dual-arm dataset to date, with the Tsinghua team constructing a dataset including over 300 tasks and 6000+ demonstrations.

Google——Open X-Embodiment
In October 2024, Google DeepMind collaborated with 21 internationally renowned institutions, including Stanford University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, NVIDIA, New York University, Columbia University, the University of Tokyo, the RIKEN, Carnegie Mellon University, ETH Zurich, and Imperial College London, to integrate 60 independent robot datasets and create Open X-Embodiment, an open, large-scale standardized robot learning dataset.
It is reported that Open X-Embodiment is the largest open-source real robot dataset to date, covering 22 different types of robots from single-arm robots to dual-arm robots and quadruped robots, containing over 1 million robot trajectories and 527 skills (160,266 tasks). Researchers have demonstrated that models trained on data from multiple robot types perform better than those trained on data from a single robot type.

Note: The featured image is from the official website of the Nationally and Locally Co-built Embodied Intelligent Robot Innovation Center








