Waymo accelerates expansion, surpassing Luobo Express: A peak confrontation between China and the US in autonomous driving
![]() 08/23 2024
08/23 2024
![]() 586
586
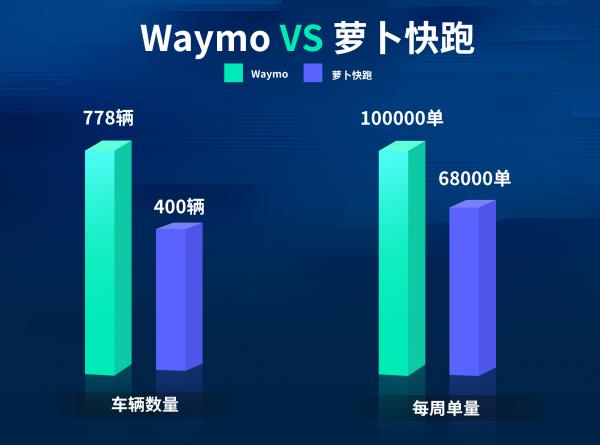
On August 20th, Eastern Time, Waymo, the autonomous taxi platform owned by Google, announced that its autonomous taxi service has exceeded 100,000 weekly paid trips in the US, doubling from the 50,000 reported in May.
This also means that Waymo has surpassed Luobo Express, China's largest autonomous driving platform. According to public data, Luobo Express recorded approximately 899,000 autonomous driving orders in the second quarter of 2024, a 26% year-on-year increase, with approximately 75,000 weekly orders.
This is not merely a commercial competition. Autonomous driving, with its highly intelligent, unmanned, and digital characteristics, represents a significant breakthrough in information technology and is a typical example of "new productive forces." Its development level directly affects the international competitiveness of the automotive industry and the global industrial division of labor among manufacturing powers. To maintain global leadership, countries are fiercely competing in legislation, capital, and application scenarios.
China and the US are at the center of this competition. Luobo Express's launch and service in Wuhan previously earned the city the reputation of being the "first global city in autonomous driving." However, with Waymo's increasing order volume and service expansion, this status may be shaken.
In the current US market, "dominant" Waymo has expanded its services from San Francisco to three new regions in California: Daly City, Broadmoor, and Colma. China is also conducting autonomous driving demonstration tests and services in cities such as Beijing, Wuhan, Chongqing, and Shenzhen. Autonomous vehicles are rapidly being deployed in both countries.
Describing the current autonomous driving competition between China and the US as an "arms race" is no longer accurate; a more fitting term would be "final showdown."
The Peak Confrontation in Autonomous Driving between China and the US
Globally, autonomous driving is sparking a wave of technological competition.
In the US, with Cruise, a subsidiary of General Motors, needing to regain regulatory trust due to various safety incidents, Waymo now dominates the market. In late July, Alphabet (Google's parent company) announced an additional $5 billion investment in Waymo, meaning Waymo has raised over $10 billion in internal and external funding since 2020.
Alphabet's Chief Financial Officer Ruth Porat believes this new round of funding will maintain Waymo's position as the world's leading autonomous driving company.
Waymo, which began operations in 2009, has been considered a bellwether in the autonomous driving industry, attracting investors such as Silver Lake, Mubalada, AutoNation, Andreessen Horowitz, Temasek, and Tiger Global.
Elon Musk has criticized Waymo's service, arguing that its business is fragile. Tesla's self-driving technology should work anywhere globally, not just in prioritized areas. It is rumored that Tesla's Robotaxi will be unveiled on October 10th, with plans to enter the Chinese market by the end of 2024, targeting global operation within the year.
In addition to domestic autonomous driving applications, US tech companies are also active in financing autonomous driving enterprises worldwide.
In the UK, Wayve, founded in 2017, announced a new funding round of $1.05 billion in May 2024, led by SoftBank, with participation from NVIDIA and existing investor Microsoft. UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak congratulated Wayve on the funding, noting it as the largest single funding round for a UK AI company.
In June, Canadian autonomous trucking company Waabi announced the completion of its $200 million Series B funding round, with investors including Uber and NVIDIA. The company plans to deploy generative AI-powered autonomous trucks by 2025.
Domestic exploration of autonomous driving is also in full swing.
As the most "out-of-the-box" autonomous driving platform, Luobo Express has opened manned test services in over ten Chinese cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Chongqing, Wuhan, Chengdu, Changsha, Hefei, Yangquan, and Wuzhen. It also conducts fully unmanned autonomous driving services in Beijing, Wuhan, Chongqing, Shenzhen, and Shanghai.

At the policy level, 54 provinces, municipalities, and autonomous regions in China have issued normative documents on open roads and demonstration applications. Among them, 28 cities support autonomous driving commercial exploration, and 24 support unmanned autonomous driving tests.
At the industrial chain level, China's autonomous driving industry chain is highly complete, covering L2 assisted driving to L4 autonomous driving and passenger cars to logistics vehicles, with participants including startups, internet giants, and traditional automakers.
However, as the two countries with the largest number of autonomous driving companies globally, China and the US are increasingly competing fiercely in this field. Compared to San Francisco's full-time and full-area open unmanned taxi services, China's open scenarios and regions for unmanned driving are relatively conservative.
Wang Xiaojing, Chief Scientist of the National Intelligent Transportation Systems Engineering Technology Research Center, believes that autonomous driving can provide an application testing ground for cutting-edge technologies represented by AI, support AI technology research and development, and link future industrial competition and economic growth. China has institutional and market advantages not found in many developed countries, and citizens and society are more tolerant of new things. Therefore, China must seize the opportunity for unmanned driving development to embrace the convergence of AI and the transportation industry.
The Dividend of the Era of "New Productive Forces"
Any technological revolution will inevitably impact existing ecosystem participants in the short term. Amid the booming development of autonomous driving, some taxi drivers express concerns about "technological unemployment," fearing their driving skills will become obsolete.
Wang Xiaojing notes that similar concerns arose when ride-hailing apps emerged, leading to resistance from traditional taxi drivers. However, China subsequently introduced the world's only national ride-hailing management system, which not only survived but thrived, creating the world's largest ride-hailing industry in terms of scale, users, and practitioners.
Throughout human history, the rise of new productive forces has always been accompanied by the survival pressure of those dependent on old production systems. However, this pressure is not irreversible. For instance, while the automobile's widespread adoption rendered horse-drawn carriage drivers obsolete, it did not deprive them of the right to drive cars. In fact, their road experience often made them invaluable drivers.
Recruitment demands for autonomous driving safety officers from companies like Luobo Express, Pony.ai, and Didi indicate that drivers with experience in passenger/freight transportation, such as ride-hailing, taxis, and buses, have priority.
Gu Dasong, Executive Director of the Transportation Rule of Law and Development Research Center at Southeast University, believes that while autonomous driving may reduce the demand for traditional drivers in the long run, this substitution is not simply a disappearance of jobs but an upgrade of the employment structure, promoting profound transformation in the labor market.
Driving skills are not a "secure job," especially as the ride-hailing market becomes saturated. Since 2024, many regions in China have issued risk warnings for the ride-hailing industry, indicating that ride-hailing capacity is reaching saturation, urging caution for businesses and individuals considering entering the market.
Moreover, job postings for autonomous driving safety officers suggest higher technical requirements, enhancing the core competitiveness of practitioners.
Autonomous driving creates jobs beyond safety officers. The Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security has officially recognized several new occupations related to autonomous driving, including "Intelligent and Connected Vehicle Testers" and "Intelligent and Connected Vehicle Installation, Adjustment, and Operation & Maintenance Personnel."
Zhang Lianqi, a member of the Standing Committee of the National Committee of the CPPCC, has stated that as a representative of new productive forces, autonomous driving is a new business model with immense potential. Its application scenarios offer ample imagination, creating new market demands and industrial opportunities in areas such as sensor manufacturing, algorithm development, and system integration. These industrial chains are bound to generate numerous new job opportunities.
While the wheel of the times keeps turning, the application of new productive forces does not mean abandoning participants in old production systems. Adapting to social changes is the true "secure job." Each upgrade in productive forces unleashes significant dividends, allowing those involved to experience income and productivity improvements while becoming part of social progress.
Embracing a New Round of Global Technological Competition
According to People's Daily, fully unmanned autonomous vehicles have been operating across the Yangtze River in Wuhan since late February 2024. Luobo Express alone has over 300 unmanned vehicles on Wuhan's streets. This innovative application is genuinely changing people's travel habits.
What was Wuhan's traffic situation like before?
Internet users often criticize Wuhan's traffic conditions, citing issues like drivers failing to signal lane changes, two-lane roads turning into four due to congestion, and drivers not slowing down at crosswalks. The city's complex road network has even inspired a trending hashtag, "Everyone in Hubei."
Since Luobo Express's operation in Wuhan, while some may criticize autonomous vehicles for being overly cautious compared to experienced human drivers, no one disputes their rule-abiding nature. Their strict adherence to traffic rules has earned them the endearing nickname "naive radish" among Wuhan residents, who joke that they are the city's own "road judges."
As autonomous driving applications expand and related technologies advance, this standardized and civilized driving behavior will gradually influence other road users, significantly enhancing the city's driving culture and civilized travel standards. This is a testament to how new productive forces transform citizens' lives.

Expanding the perspective, autonomous driving technology not only transforms human lifestyles but also serves as a crucial engine for national technological strength. According to ARK Invest, autonomous vehicles are projected to become the most significant technological innovation driving GDP growth in history, potentially contributing an additional 20% to global GDP over the next decade. Its economic impact could surpass that of steam engines, robots, and information technology combined.
Autonomous driving is a product of the integration of AI and transportation and represents the largest application scenario for AI globally. It is also an emerging technological force driving the transformation and upgrading of traditional real economies.
In the autonomous driving competition, China and the US, as the two countries with the largest number of autonomous driving enterprises and highly similar technologies and applications, have entered a decisive stage. The pace of advancing policies, regulations, and pilot applications has accelerated to compete for the dominant position in this field.
Earlier deployment and operation, especially in bustling and complex urban areas, means earlier access to real-road data, accumulation of operational experience, and enhancement of autonomous driving capabilities, giving a competitive edge in this "final showdown."
Therefore, "Luobo" must not only run fast but also accelerate, striving to lead the global race.







