Blocked by the EU's high tariffs, SAIC's path to globalization becomes rugged
![]() 09/02 2024
09/02 2024
![]() 518
518
Introduction | Lead
Recently, several domestic automakers have successively released their semi-annual reports. As SAIC, which used to be the leading domestic automaker for a long time, its financial performance was not impressive due to the lackluster performance of its joint ventures. With the implementation of EU tariffs, SAIC faces increasingly significant challenges.
Produced by | Heyan Yueche Studio
Written by | Zhang Dachuan
Edited by | Heyanzi
Total words: 2405
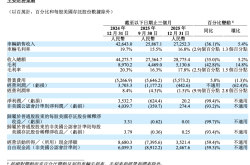
Recently, SAIC released its performance report for the first half of 2024. In the first half of the year, SAIC's revenue reached RMB 284.69 billion, with a net profit attributable to shareholders of RMB 6.63 billion. In comparison, BYD's net profit attributable to shareholders for the same period was RMB 13.631 billion, making it clear that SAIC lags behind BYD. When excluding non-recurring gains and losses (i.e., excluding the proceeds from the sale of SAIC's stake in its Indian subsidiary), the actual net profit was only RMB 1 billion, a year-on-year decline of 82%.

△SAIC's net profit significantly declined in the first half of the year
From a sales perspective, SAIC delivered 2.115 million vehicles to end-users in the first half of this year. Among them, 524,000 were new energy vehicles, and 548,000 were delivered to overseas markets. Among SAIC's various overseas markets, the European market undoubtedly plays a pivotal role. From January to June this year, MG brand delivered over 120,000 vehicles to end-users in the European market, maintaining its position as the sales champion among Chinese automotive brands in Europe for twelve consecutive years. For the full year, the European market has already reached a scale of 200,000 vehicles. However, whether SAIC can maintain its volume in Europe remains questionable.
Impact of Reverse Globalization
After the EU began imposing tariffs on electric vehicles (EVs) manufactured in China, sales of Chinese EVs exported to Europe declined significantly in July.
According to statistics from Dataforce, a globally renowned consulting firm, the number of Chinese EVs registered in Europe dropped significantly by approximately 45% compared to June. Specifically, MG brand sales declined by 20%, while Polestar sales dropped by 42%. From a country-specific perspective, except for the UK, which has left the EU and is therefore unaffected by the tariffs, Chinese-made EVs are affected in other major countries such as Germany and France.

△Registrations of Chinese EVs exported to Europe declined sharply in July
However, the most critical test for Chinese automakers lies in the European Commission's official vote on import tariffs for Chinese EVs in October. For China, if it fails to secure opposition votes from 15 out of the EU's 27 member states, accounting for 65% of the EU's total population, the current temporary tariffs on Chinese-made EVs will become a long-term policy lasting five years.
Global protectionism is on the rise. Following the United States' announcement of impending tariffs on China and the EU's imposition of tariffs on Chinese goods, the Canadian government has also taken action against Chinese EVs. From October 1, 2024, all Chinese-made EVs exported to Canada will be subject to a 100% surcharge, covering electric and some hybrid passenger cars, trucks, buses, and cargo vehicles. This follows a surge in Chinese automotive exports to Canada, with the number reaching 44,400 vehicles in 2024, valued at CAD 2.2 billion (approximately USD 1.6 billion), up from CAD 100 million in 2022.

△Canada will also impose tariffs on Chinese EVs
Why is SAIC Subject to the Highest Tariff in the EU?
Excluding Tesla's 9% tariff, BYD faces the lowest additional tariff among Chinese companies in the EU, at just 17.4%, while Geely faces 19.9%, and SAIC faces a staggering 37.6%. Other Chinese manufacturers not subject to the sample survey face a uniform weighted average tariff of 20.8%, while those not participating in the investigation face a tariff of 37.6%. Opinions vary as to why SAIC faces the highest tariff.

△SAIC faces a significantly higher tariff rate in the EU than BYD and Geely
As the largest Chinese automaker in Europe with annual sales exceeding 200,000 vehicles, SAIC wields considerable influence in the European market, surpassing that of BYD and Geely. For the EU, imposing a higher tariff on SAIC's MG brand can swiftly curb the expansion of Chinese EVs in Europe. However, regardless of this factor, SAIC has been at a disadvantage in negotiations with the EU, leading overseas media to speculate differently from SAIC's perspective.
According to SAIC, it did not disclose relevant data to the EU due to the protection of core data, including battery formulas. Although it is unclear whether SAIC, BYD, and Geely received identical questionnaires, it is possible that the EU deliberately targeted SAIC due to its significant presence and scale in Europe. However, both BYD and Geely adhere to Chinese laws and regulations on cross-border transmission of critical data and consider their commercial interests, making it unlikely they would easily disclose core secrets to the EU. Furthermore, in terms of battery R&D, BYD and Geely are not inferior to SAIC. If SAIC is unwilling to share its battery formula data, there is no reason why BYD and Geely would do so either.

△BYD and Geely are no less capable than SAIC in battery technology
Foreign media reports attribute SAIC's high tariff to its lackluster response to the EU. In contrast, BYD and Geely were more proactive, hiring international law firms and conducting thorough internal data collection. BYD even engaged Brussels-based policy experts to actively communicate with the EU. International law firms can better understand the context and objectives of EU investigations, enabling a more nuanced approach to filling out questionnaires. Without experienced third-party assistance, SAIC may have been at a disadvantage in filling out questionnaires and communicating with the EU.
Integrating into Overseas Markets Takes Time
For SAIC, as the US market has closed its doors to Chinese-made vehicles, the European market is a crucial overseas market that cannot be abandoned. After facing the highest punitive tariffs in the EU, SAIC began shifting its primary exports to Europe from the MG4 pure electric model to plug-in hybrid models.

△SAIC shifts its primary European exports from pure electric to DMH models
This strategic adjustment is reasonable, given the EU's current slowdown in demand for electric vehicles. However, if SAIC or other domestic automakers cannot effectively communicate with the EU, the bloc may block not only pure electric vehicles but also plug-in hybrids made in China.
Another phenomenon that has attracted international media attention is that at The Battery Show Europe 2024, Chinese companies accounted for more than one-fifth of all exhibitors. However, during the three-day conference, there were virtually no Chinese speakers. Clearly, Chinese automakers need more time to adapt to overseas markets, including understanding media demands, advertising, and joining industry associations. Influential local journalists and commentators in Europe can significantly impact European consumers' purchasing decisions.

△Few heavyweight Chinese speakers at The Battery Show Europe 2024
Commentary
Previously, SAIC's MG4 and MG ZS EV were popular in Europe due to their high cost-effectiveness. For SAIC to truly establish itself in the European market, it must elevate its brand rather than relying solely on low prices. In the future, how to avoid trade frictions, better present itself, integrate into local societies, and actively communicate with the EU and national governments to maximize its interests is a crucial international lesson that SAIC and other domestic autonomous brands must learn as they venture overseas.
(This article is originally created by Heyan Yueche Studio and may not be reproduced without authorization)