From Huawei Mate60 to the tri-fold MateXT, 100% Chinese-made RF chips
![]() 10/14 2024
10/14 2024
![]() 443
443
As we all know, since October 2020, Huawei's Kirin chips have become a thing of the past, with no more foundries available for production.
Subsequently, Huawei faced not only issues with mobile SoC chips but also with 5G RF chips, which it could no longer source from abroad. Consequently, for a long period, Huawei could only launch 4G phones.
Without 5G SoC and 5G RF chips, it is impossible to manufacture 5G phones.

From 2021 to 2023, as 5G technology developed rapidly, Huawei watched as other phone manufacturers launched 5G phones while it could only offer 4G models. The psychological impact on Huawei can be imagined.
However, by the end of 2023, the Huawei Mate60 debuted. This phone was not labeled as 5G or 4G, and even the chip was not specified.
But after testing, it was confirmed that the phone's internet speed met 5G standards, and its chip performance was on par with Qualcomm's 5nm Snapdragon 888.

Given the circumstances at the time, it was essentially confirmed that Huawei had resolved issues related to both 5G SoC and RF chips, eliminating the need for foreign imports.
Following the Mate60, Huawei introduced the Pura70 and the tri-fold MateXT, all of which are 5G phones powered by Kirin chips. It is evident that Huawei, in collaboration with domestic supply chains, has overcome the entire 5G component challenge.
Recently, an organization disassembled the Huawei MateXT phone and compared it with earlier models like the Pura70 and Mate60.
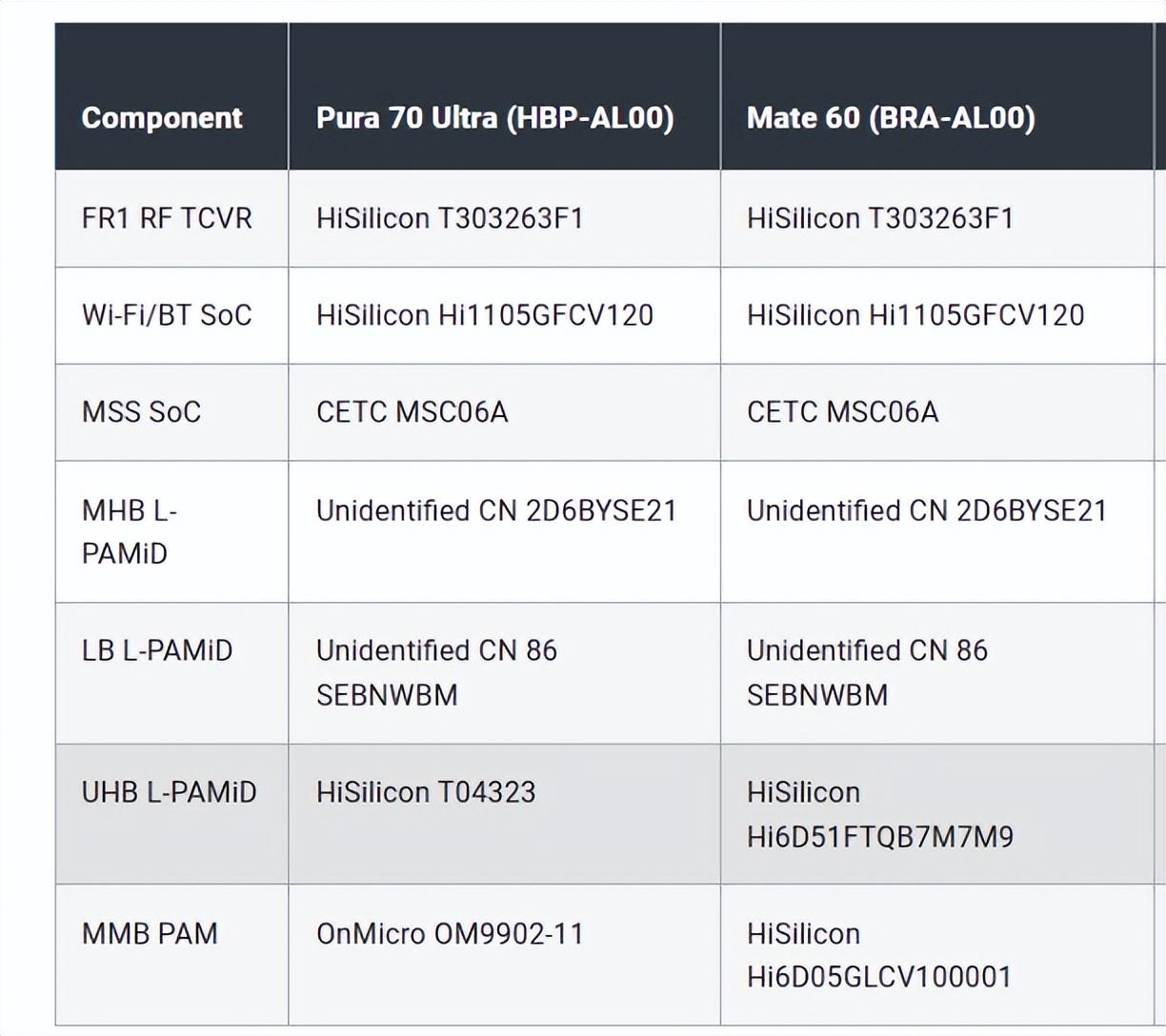
It was found that the MateXT and Pura 70 Ultra share a significant amount of mobile RF architecture with the Mate 60, with many components being essentially the same. Importantly, these RF chips are predominantly domestically produced, with no foreign chips involved.
Many of the chips come from Huawei HiSilicon itself, while others originate from companies like China Electronics Corporation and Onray Microelectronics, all 100% domestically manufactured.
This explains why Huawei has been fearless in the face of pressure and continues to launch 5G phones. With domestic supply chains capable of producing 5G chips and RF chips, Huawei no longer relies on foreign imports and can confidently introduce 5G phones.

It was once commonly believed that while domestic phones were impressive, key components like chips and RF chips still had to be imported, with RF chips almost entirely monopolized by foreign manufacturers.
However, from late 2020 to late 2023, a mere three years passed during which Huawei, in collaboration with domestic supply chains, managed to overcome the challenge of producing advanced SoC and 5G RF chips. This capability is perhaps unique to Huawei. What do you think?







