Gartner: By 2028, at least 15% of routine work decisions will be made autonomously by AI agents
![]() 10/29 2024
10/29 2024
![]() 673
673
The pace of artificial intelligence development continues to accelerate, and capabilities that were previously unimaginable are now becoming a reality. Especially AI agents—or virtual colleagues, if you will—will work alongside us in the future and may eventually be able to execute tasks independently.
In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2028, at least 15% of routine work decisions will be made autonomously by AI agents (this figure was 0% in 2024).
To further emphasize the potential of AI technology, Gartner has listed it as a top strategic technology trend for 2025. "This is happening very, very quickly," said Gene Alvarez, distinguished vice president analyst at Gartner.
"No one can finish all their work before going to bed at night, and companies also need to spend a lot of time monitoring things. Creating AI agents can not only replace some work and assist companies in detection, but also improve work efficiency and save time," Alvarez said.
What other predictions does Gartner have for future strategic technology? Here are some trends discussed by the company at the Gartner IT Symposium/Xpo 2024 conference.
"The primary role of AI agents is to solve tedious tasks that consume human time and energy. The next level is AI agents that can autonomously monitor and manage systems," Alvarez explained.
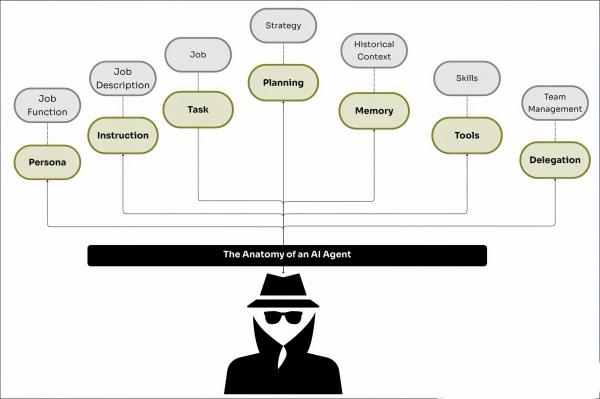
"AI agents have the ability to plan, perceive, and take action, allowing them to analyze, repair, and report on what has happened, rather than simply existing as a monitoring system," Alvarez said.
"In more complex scenarios, agents may one day help enhance employees' skills. For example, instead of new hires having to learn from human colleagues, they can now be guided by AI colleagues," Alvarez added.
Alvarez acknowledged that while all of this is exciting, it also raises concerns, and fears of job losses persist.
"But if an AI agent can actually teach me a new set of skills, I can move from a job that's about to be lost to one that's in demand," Alvarez said.
Alvarez then pointed to the next major trend: "We have a whole new workforce now. How do we manage them?"
This management topic will give rise to a series of AI governance platforms, enabling companies to manage the legal, ethical, and operational performance of their AI systems.
These new tools will create, manage, and enforce policies to ensure AI transparency. They can also check for bias in AI assistants and provide information on model building.
Alvarez predicts that these tools will eventually become an integral part of the AI creation process, ensuring that ethics and governance are embedded in the model from the start.
"We can create trust through transparency. If people lose trust in AI, they won't use it," Alvarez said.
Alvarez noted that there are currently seven computing models in use: CPU, GPU, edge computing, application-specific integrated circuits, neuromorphic systems, classical quantum computing, and optical computing.
"We've always had a mindset of adapting to change, but the future of hybrid computing will combine different computing, storage, and network mechanisms to operate. Orchestration software will shift computations from one to another based on the task and the most suitable method," Alvarez said.
"Meanwhile, new, more specialized computing technologies will significantly reduce energy consumption. This is crucial given the increasing pressure to reduce consumption and carbon footprints. However, AI's demand for IT computing power is also growing at an astonishing rate," Alvarez added.
"Incremental improvements are not enough; businesses need long-term solutions. They also need new technologies, such as green cloud providers or more efficient algorithms, that have the potential to increase efficiency by thousands, tens of thousands, or even hundreds of thousands of times," Alvarez said.
AI has empowered some "threat actors" to spread disinformation faster and easier. They can push deepfakes, create phishing emails, exploit vulnerabilities in collaboration tools, eavesdrop with malware, launch account takeover attacks, and more.
Therefore, it has become crucial to combat disinformation and protect information security by actively assessing authenticity, tracking the spread of harmful information, and preventing the emergence of fake information.
Its elements include brand impersonation scanning, third-party content assessment, claims and authentication, phishing mitigation, account takeover prevention, social/mass media and dark web monitoring, and sentiment manipulation.
Alvarez explained that deepfake detection will also be able to identify synthetic media, while watermarking tools will help ensure that users are interacting with real people.
According to Gartner's prediction, by 2028, half of all enterprises will begin adopting products, services, or features specifically designed for disinformation security, up from less than 5% currently.
"Disinformation security won't be a single technology; it will be a collection of technologies," Alvarez said.
Currently, the internet uses public key cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography, to ensure secure communication between two points.
"This type of encryption is difficult to crack because it takes a long time to do so. However, quantum technology is rapidly developing and will eventually play a role due to its mathematical ability to crack encryption in real-time," Alvarez explained.
Gartner predicts that by 2029, advances in quantum computing will render most traditional asymmetric cryptography techniques insecure.
"Organizations must prepare for post-quantum cryptography now to ensure their data remains protected against decryption. Transitioning encryption methods is not easy, and it's 'not just a simple patch,'" Alvarez added.
The established standards of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are a good starting point. Alvarez noted that the agency will release the second edition of its post-quantum cryptography guidelines in spring 2025.
"When all the locks are broken, what do you do? You need new locks. We need to ensure that we update our security before quantum technology becomes a reality," Alvarez said.
Gartner takes a further leap into the realm of science fiction, predicting an increase in the use of bidirectional brain-machine interfaces (BBMI), which can read and decode brain activity to enhance human cognitive abilities.
Alvarez explained that these devices can be integrated directly into our brains or implemented through wearable devices such as glasses or headbands.
Gartner predicts that by 2030, 30% of knowledge workers will use technologies such as BBMI to remain competitive in an AI-driven work environment (up from less than 1% in 2024).
"I see the potential for enhancing human skills and next-generation marketing. For example, brands will be able to understand what consumers are thinking and feeling, allowing them to gauge consumer sentiment," Alvarez said.
Alvarez ultimately compared it to the 2011 film "Limitless" and the Apple TV+ series "Severance."
Alvarez said, "To be fair, neither of these portrayals of the technology is entirely positive, but it does enhance human cognitive abilities by tapping into the human brain."