Three AI PCs torn down: what chips are used?
![]() 11/27 2024
11/27 2024
![]() 456
456

Compiled by Semiconductor Industry Review (ID: ICVIEWS) from eetimes
2024 marks the gradual release of AI PCs, which can even be called the "First Year of Edge Device AI".
In 2024, the semiconductor industry is expected to be comprehensively led by AI technology. Chips with AI processing capabilities, high-capacity dynamic random access memories compatible with AI technology (including high-bandwidth memory and low-power double data rate type 5X), and power integrated circuits capable of segmented power management are being integrated into the mobile device field on an unprecedented scale.
With the rapid development of generative AI technology, AI functions have become standard in personal computers, smartphones, augmented reality/virtual reality devices, drones, in-vehicle systems, and other devices. Some AI systems are combined with cameras and sensors, while others run in the background to optimize wireless communication environments, among other functions.
Given the imminent launch of numerous processors and products, 2024 can undoubtedly be considered the "First Year of Edge Device AI Applications." Therefore, this article will focus specifically on personal computers and processors equipped with AI technology introduced in the second half of 2024.
Three major changes brought about by mobile AI
Mobile AI devices are leading three significant transformations.
Firstly, processors have integrated specialized hardware computing units called NPUs (Neural Processing Units), responsible for executing specific integer, floating-point, and multiply-accumulate operations, leading to a corresponding increase in chip area.
Secondly, the mounting height of parallel high-capacity DRAM matched with computing units has increased, and companies have increased DRAM capacity in 2023 models. For example, the "Google Pixel 8" is equipped with 12GB of DRAM (similar examples include the 2024 "Google Pixel 9" with 16GB of DRAM).
Thirdly, processors are paired with a large number of power ICs to achieve fine control over power consumption. As the number of NPU cores in processors and the capacity of DRAM increase, power ICs are also subdivided and increased accordingly. Mobile AI devices are gradually increasing semiconductor usage.
In the PC field, models compatible with the "Copilot+ PC" (over 40TOPS NPU) function will be released as AI PCs from June 2024.
ASUS AI PC with Qualcomm Snapdragon X
Figure 1 shows the "Vivobook S 15 S5507QA" launched in September 2024, which is compatible with ASUS Copilot+ PC. It is powered by the Qualcomm "Snapdragon X Plus 8-CORE," an economical alternative to "Snapdragon X Elite" with compromised performance.
The device is equipped with 16GB of DRAM. Given that high-end laptops typically cost more than 200,000 yen in the market, this product is priced at around 100,000 yen. Although it supports Copilot+ PC, its CPU and GPU performance are downgraded.

Figure 1: ASUS "Vivobook S 15 S5507QA" released in September 2024
Table 1 reveals the power system and processor configurations of the Qualcomm Snapdragon X Elite (top row) introduced in June 2024 and the Snapdragon X Plus 8-CORE (bottom row) introduced in September. Qualcomm not only provides chipsets for smartphone power and communication systems but also offers a diverse range of battery charging, battery management, and power IC products for the personal computer market that are compatible with processors.
Among these products, a total of 8 power ICs and 4 battery ICs are equipped. Both the high-end Snapdragon X Elite and the more affordable X Plus 8-CORE use the same power ICs and battery ICs. This standardized power supply system is also widely used in the smartphone field.

Table 1: Internal configuration of Qualcomm "Snapdragon X" series
Figure 2 shows the Qualcomm Snapdragon X Elite (left) and Snapdragon X Plus 8-CORE (right) chips produced using TSMC's 4nm process technology. The X Elite on the left, as a high-end model, features a 12-core ORYON CPU and a 12-core Qualcomm self-developed GPU Adreno, with a maximum CPU operating frequency of 4.3GHz.
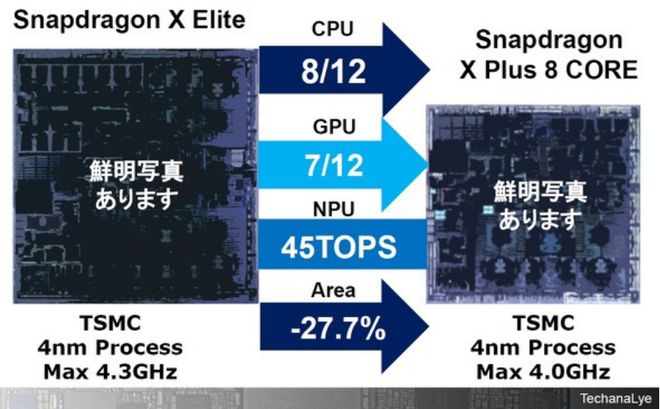
Figure 2: Snapdragon X series chips
The economical CPU configuration of the X Plus 8-CORE on the right is an eight-core setup, reduced by four cores compared to the standard version, with a seven-core graphics processing unit (GPU), a reduction of five cores. By streamlining features, the chip's silicon area is reduced by approximately 28%, and the maximum operating frequency is adjusted to 4.0GHz.
To meet the performance requirements of Copilot+ PC, the economical version of the neural network processing unit (NPU) maintains the same performance as the high-end version, at 45TOPS. By reducing the silicon area by approximately 30%, it not only increases the amount of data obtained from the wafer but also enables the reuse of multiple test patterns, significantly reducing production costs and ensuring compatibility with AI PC processors priced in the 100,000 yen range.
HP AI PC with AMD Ryzen
Figure 3 shows the HP OmniBook Ultra 14-fd0005AU, a Copilot+ PC-compatible device launched in July 2024. It is powered by AMD's APU (Accelerated Processing Unit, a combination of CPU and GPU), the "Ryzen AI 300" series specifically designed for Copilot+ PC compatibility.
Compared to the 2023 "Ryzen 8000" series APU, which already integrated AI functionality but fell short of the 16TOPS performance required for Copilot+ PC, the Ryzen AI 300 series processors offer up to 50TOPS of performance, more than tripling the NPU (Neural Network Processing Unit) performance of its predecessor. Since July 2024, this series of processors has been integrated into AI personal computers.

Figure 3: "HP OmniBook Ultra 14-fd0005AU"
Table 2 presents a comparative analysis of the "Ryzen 9 8945HS" processor from the AMD Ryzen APU 8000 series and the "Ryzen AI 9 365" processor from the Ryzen AI 300 series. It should be noted that AMD does not provide chipset support, and both processors are equipped with MPS (Monolithic Power Systems) power system integrated circuits.
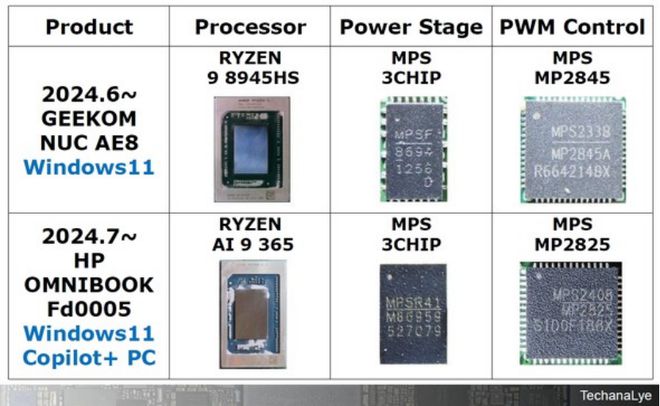
Table 2: Comparison between "Ryzen 9 8945HS" and "Ryzen AI 9 365"
Figure 4 shows a comparative analysis of the Ryzen 9 8945HS and Ryzen AI 300 chips. Both chips include a CPU, GPU, and NPU and are manufactured using TSMC's 4nm process technology. Both chips have upgraded CPU and GPU architectures, with the CPU architecture upgraded from Zen 4 to Zen 5 and the GPU architecture from RDNA3 to RDNA3.5, while the core count increases from 12 to 16.
In terms of CPU configuration, a 4-core Zen 5 architecture and an 8-core Zen 5C (compact) architecture are adopted, with streamlined performance. Due to the use of the same TSMC 4nm process technology, the chip's functionality is enhanced, resulting in an approximate 28% increase in silicon area.
It is certain that the next generation of products after 2025 will adopt a 3nm process technology, so the 4nm process technology may be used for the last time and has an expanded size.
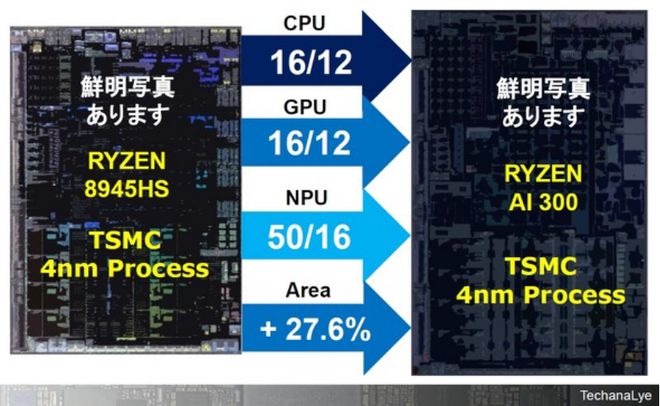
Figure 4: Chip comparison between Ryzen 9 8945HS and Ryzen AI 300
ASUS AI PC with Intel Ultra
Figure 5 shows the "Zenbook S 14" (model UX5406) from ASUS's Copilot+ PC series, launched in October 2024. It is powered by Intel's 200V Lunar Lake processor, the second generation of the "CORE Ultra" series. In comparison, the Meteor Lake, introduced in January 2024 as the first-generation product of the CORE Ultra series, had an NPU performance of 36TOPS but fell short of the performance requirements for Copilot+ PC. The second-generation Lunar Lake processor boasts an enhanced NPU performance of 48TOPS, compatible with the performance requirements of Copilot+ PC.

Figure 5: ASUS Copilot+ PC "Zenbook S 14" (UX5406)
Table 3 reveals the PC chip configurations equipped with the first-generation Meteor Lake of CORE Ultra (top row) and the second-generation Lunar Lake (bottom row). Lunar Lake minimizes chip area and shortens signal transmission distance by integrating DRAM within the package.
This technology has been adopted since Apple introduced the "M1" chip in 2020, with Apple officially adopting it since the "A12X" chip in 2018. For Meteor Lake, the combined power IC is provided by Alpha & Omega in the United States, while for Lunar Lake, the combined power IC is provided by Renesas Electronics in Japan, totaling four chips.

Table 3: PC chip configurations with Meteor Lake and Lunar Lake
Table 4 showcases the silicon structures of the first-generation Meteor Lake and second-generation Lunar Lake in the CORE Ultra series. Both are composed of multiple chiplets. Meteor Lake consists of five different silicon materials, including a silicon interposer that connects various chips and provides power.
In contrast, Lunar Lake is composed of four silicon materials. Meteor Lake's CPU is manufactured using Intel 7nm process technology (codename INTEL 4), while its GPU and NPU are outsourced to TSMC. In Lunar Lake, the CPU, GPU, and NPU are all manufactured using TSMC's 3nm process technology.
Almost simultaneously, Intel also began introducing the Arrow Lake processor for desktops, which also uses TSMC's 3nm process and features a chiplet architecture. It is expected that Copilot+ processors compatible with PCs will be introduced in the second half of 2024, but it is worth noting that companies differ in the power ICs used in chip manufacturing.
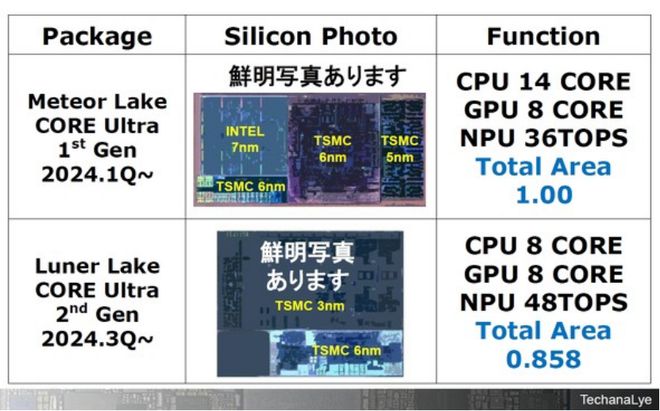
Table 4: Silicon status of Meteor Lake and Lunar Lake
By 2025, the alliance between MediaTek and NVIDIA is expected to further expand into the Copilot+ PC market. Simultaneously, Qualcomm, AMD, and Intel also intend to launch their next-generation processor products. We will continue to monitor the smartphone market and provide corresponding observations and reports.
*Disclaimer: This article is created by the original author. The content represents their personal views. Our republication is solely for sharing and discussion purposes and does not imply our endorsement or agreement. For any objections, please contact us.







