Perspective on Baidu's Q3 Report: Core Business Declines, AI Commercialization Faces Long Road
![]() 12/01 2024
12/01 2024
![]() 519
519
On November 21, Baidu released its third-quarter financial report. The search engine giant is now facing significant challenges. In the third quarter of this year, Baidu achieved revenue of 33.56 billion yuan, a year-on-year decline of 3%, marking the largest drop in more than two years. Net profit attributable to shareholders was 7.63 billion yuan, up 14% year-on-year; however, under Non-GAAP, net profit fell 19% year-on-year to 5.89 billion yuan.
Behind the decline in revenue lies the decline of Baidu's core business and the lengthy commercialization journey of its shift to AI. Accelerating the commercialization of new businesses while maintaining business stability has become Baidu's top priority. Its success or failure will also have a profound impact on the entire Chinese Internet industry.
01
Core Search Business Hit, iQIYI Drags Down Performance
Since its inception, Baidu has been committed to becoming an important platform connecting people and information. With its powerful search engine technology and extensive network coverage, it has accumulated a huge user base in China and globally. However, with the advent of the mobile internet era and rapid technological development, Baidu gradually realized the intensifying industry competition and limitations of its original business growth, prompting it to actively seek new positioning and development directions. In areas such as artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing, Baidu has undertaken a new strategic layout, striving to occupy a favorable position in the competitive landscape of the new era through technological innovation.
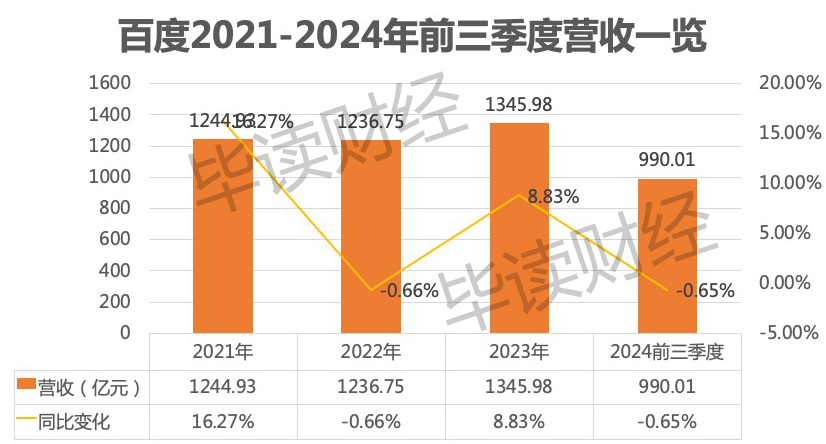
However, Baidu's performance has been volatile in recent years. Looking back at the past three years, in addition to fluctuating revenue, Baidu's profitability has also been unstable.
Specifically, from 2021 to 2023, Baidu achieved revenue of 124.493 billion yuan, 123.675 billion yuan, and 134.598 billion yuan, respectively. It achieved double-digit growth in 2021, with revenue declining 0.66% year-on-year in 2022.
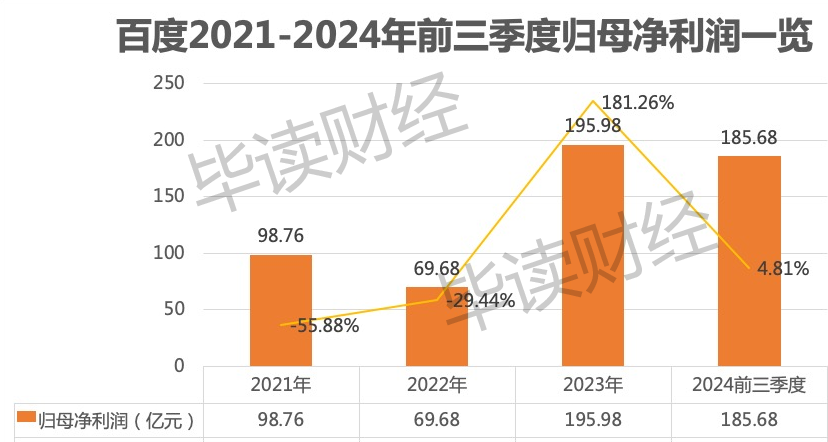
Over the same period, Baidu's net profit attributable to shareholders was 9.876 billion yuan, 6.968 billion yuan, and 19.598 billion yuan, respectively. After a 50% drop in net profit in 2021, net profit continued to decline by 29.44% in 2022. Although net profit rebounded significantly in 2023, this growth momentum has not been sustained, as evidenced by Baidu's performance in the first three quarters of 2024. In the first three quarters of 2024, Baidu achieved revenue of 99.001 billion yuan, down 0.65% year-on-year; net profit attributable to shareholders was 18.568 billion yuan, a slight increase of 4.81% year-on-year.
Looking at individual quarters, Baidu's revenue declined 0.4% year-on-year in the second quarter of this year. Since the second quarter of 2023, Baidu's revenue growth rate has not exceeded double digits.
The volatility in Baidu's performance is closely related to the deteriorating condition of its core search advertising business. Li Yanhong has publicly stated that the current advertising business is under various external pressures, including uncertainty in the macroeconomic environment and intensifying industry competition.
According to the financial report, Baidu's revenue consists of two parts: online marketing services revenue and other revenue, with the former being Baidu's largest and most dependent source of income. In the third quarter of this year, Baidu's online marketing services revenue reached 20.1 billion yuan, accounting for 59.9% of total revenue, down 5.8% year-on-year.
It is worth mentioning that this is not the first decline in this business. In the second quarter of this year, Baidu's online marketing services revenue was 20.6 billion yuan, down 2.2% year-on-year.
Online marketing services revenue, or Baidu's advertising business, heavily relies on the traffic of Baidu's core search business. However, in recent years, this business has been under tremendous competitive pressure from the industry.
With the rapid popularization of the mobile internet, the way users access information has fundamentally changed. Especially with the rise of emerging platforms such as Xiaohongshu and Douyin, which attract a large number of young users with intuitive and easy-to-digest content formats, posing a direct threat to traditional search engines.
These platforms provide users with richer search results and enhance the authenticity and interactivity of information through user-generated content (UGC). Therefore, users prefer these emerging platforms when seeking specific types of information. According to data from the "2024 Xiaohongshu Search Promotion White Paper," 70% of Xiaohongshu's monthly active users use the search function, and 88% of search behaviors are initiated by users proactively. Obviously, Xiaohongshu has become an important channel for young users to obtain information.
This trend is not only reflected in changes in user behavior but also further reflected in changes in Baidu's market share. The latest data from Statista shows that in May 2024, Baidu's share of the Chinese search market had dropped to 55.85%, compared to 86.82% in November 2021. In just a few years, Baidu's market dominance has been severely eroded. According to media reports, insiders at Baidu have revealed that the company has long felt competitive pressure from external platforms, especially in the search business, where many emerging platforms are rapidly closing the gap with Baidu.
As a result, as users gradually turn to other platforms for information, Baidu's ad exposure and click-through rates have also declined, affecting not only Baidu's advertising revenue but also weakening its competitiveness in the online marketing market. At the same time, emerging platforms attract a large number of advertisers through precise content recommendations and personalized user experiences, further squeezing Baidu's market share. Taking Douyin Search as an example, the platform provides users with a new search experience through short videos and image-text content, making it more attractive for advertisers to place ads on these platforms to achieve higher conversion rates.
Data shows that in 2023, ByteDance's advertising revenue reached 400 billion yuan, with Douyin contributing a significant portion of this. In comparison, Baidu's online marketing revenue for the same period was 75.1 billion yuan. It can be seen that the rise of emerging platforms such as Xiaohongshu and Douyin has not only captured important market share from Baidu but is also a key factor in the gradual decline of Baidu's search business.
On the other hand, the underperformance of iQIYI's business has also dragged down Baidu's overall performance. In the third quarter, iQIYI's revenue declined by 10% year-on-year to 7.2 billion yuan. Excluding iQIYI, Baidu's core business revenue for the quarter was 26.524 billion yuan, flat year-on-year; net profit attributable to shareholders under Non-GAAP was 5.676 billion yuan, down 18% year-on-year.
It is worth mentioning that in the third quarter, despite the decline in revenue, Baidu achieved net profit growth. The reason is that through organizational restructuring, rationalizing employee size, and prudent management of R&D investments, the company reduced operating costs, with the operating profit margin increasing by 0.5 percentage points compared to the previous quarter.
Among them, Baidu optimized and streamlined its human resource management, with equity incentive expenses resulting from personnel reductions decreasing by 19% year-on-year. Additionally, Baidu conducted internal business unit integrations, such as merging the Healthcare Business Group (HCG) into Mobile Ecosystem Group (MEG), which improved operational efficiency while reducing the cost of redundant construction.
Furthermore, Baidu achieved more effective management of its R&D expenditures, with R&D expenses decreasing by 13% year-on-year, creating conditions for further improving profit margins.
02
Long Road to AI Commercialization, Personnel Turbulence Attracts Attention
Under pressure from its core business, Baidu began exploring new growth points, with artificial intelligence becoming a crucial development direction. As early as 2010, Baidu began investing continuously in the field of artificial intelligence and later boldly announced an "all-in AI" strategy, positioning itself as an AI company. Baidu can be considered one of the earliest domestic enterprises to embrace the AI concept.
Subsequently, in 2012, Li Yanhong encouraged all product managers within the company to keep up with the latest trends in AI technology through an internal email; in 2013, Baidu established a Deep Learning Lab, fully entering the AI exploration phase. Over the past decade, Baidu has consistently focused on cutting-edge technology areas such as artificial intelligence, autonomous driving, and intelligent cloud, with cumulative investments exceeding 170 billion yuan.
Despite significant investments, Baidu has lagged behind in finding commercialization paths for AI, with its achievements falling far behind those of its peers.
For example, in the smart assistant market, according to public data, as of October 2024, Douyin's Doubao had 51.3 million monthly active users, while Baidu's "Wen Xiaoyan" only recorded 12.57 million monthly active users, less than one-third of Doubao's. Meanwhile, "Moon's Dark Side's" Kimi smart assistant also reached 10.06 million monthly active users, almost equaling Baidu's "Wen Xiaoyan." Clearly, in this fierce competition, even as an early entrant, Baidu's products have not only been surpassed by latecomers in terms of user base but are also under pressure from being further caught up.
Turning to the field of autonomous driving. Since 2015, Baidu has established a dedicated business unit and collaborated with multiple automakers, hoping to promote its Apollo advanced intelligent driving solutions. However, most of these collaborative projects have failed to achieve the expected results, with only a handful of models, such as Geely's Jiyue and LanTu FREE, equipped with Baidu's technology. Currently, Jiyue sells only about 400-500 vehicles per month, while LanTu FREE does not exceed 1,000 vehicles. Judging by the "life-or-death line" of monthly sales of 10,000 vehicles for measuring the survival of new forces, neither brand has met the standard.
Moreover, in recent years, Baidu's autonomous driving department has experienced brain drain. For example, Yu Kai, the former executive vice president of Baidu Research Institute, founded Horizon Robotics, while Peng Jun and Lou Tiancheng, the former chief architects of Baidu's autonomous driving department, co-founded Pony.ai. Guo Yang, the former chief product architect of IDG, joined Geely Automobile's autonomous driving team. The departure of multiple core members to establish their businesses or join competitors poses a significant threat and challenge to Baidu's maintenance of technological leadership.
Additionally, Luobo Kuaipao, which Baidu holds high hopes for in the intelligent driving service field, has also seen a noticeable slowdown in order growth. From the first to the third quarters of 2024, Baidu's autonomous driving service Luobo Kuaipao provided 826,000, 899,000, and 988,000 autonomous driving orders, respectively, with year-on-year growth rates of 25%, 26%, and 20%. In contrast, the year-on-year growth rate of Luobo Kuaipao's orders was as high as 49% in the fourth quarter of 2023. This is mainly due to Luobo Kuaipao's limited business scope to specific areas of a few cities, restricting order volume growth.
Although Baidu's intelligent cloud business performed well, achieving a 12% increase to 7.7 billion yuan in the third quarter, bringing a certain degree of balance to the overall revenue structure, it has not fully resolved the fundamental challenges faced by the company on the AI commercialization path. Facing competitive pressures from multiple sources and its development bottleneck, how to effectively convert huge R&D investments into practical commercial value has become one of the critical issues Baidu urgently needs to address.
At the same time, Baidu has also undergone a series of significant personnel changes internally, further increasing development uncertainty.
On October 18 of this year, Baidu announced adjustments to the positions of three senior vice presidents and above: Luo Rong, the executive vice president and former Chief Financial Officer, was rotated to lead the Mobile Ecosystem Group (MEG); the Healthcare Business Group (HCG) was integrated into MEG, and He Mingke, the former president of HCG, is no longer responsible for specific work; meanwhile, He Junjie, the former head of MEG, was appointed as the acting Chief Financial Officer. During the integration process in key business areas, new leaders need time to familiarize themselves with the business, adjust strategies, and gain the trust of the team. For Baidu, the challenge has only just begun.
It is worth noting that these three executives are relatively new faces who joined Baidu within the past two years and are not seasoned veterans of the company. Additionally, Baidu's Core Business Group has recently experienced deeper personnel turbulence, including the departure of two senior vice presidents, Xiao Yang and Wang Fengyang. Xiao Yang was once the CTO of MEG, while Wang Fengyang was responsible for the mobile ecosystem business system, which has had a significant impact on Baidu, which is undergoing a transformation period and urgently needs both stability and innovation.
Conclusion
For Baidu, from the PC era to the mobile internet era and now to the intelligent agent era, it has been striving to adapt to the changes of each era. However, under the influence of multiple factors such as fluctuating performance, frequent personnel changes, and unsuccessful searches for new growth points, Baidu's development path has become increasingly difficult. It will not be easy for Baidu to rediscover its position in this wave of intelligent transformation.







