Passenger Vehicle Market Sees First Drop in Average Price; New Energy Vehicles Witness Three Consecutive Declines
![]() 01/14 2026
01/14 2026
![]() 400
400
Automakers find themselves at a crossroads, grappling with the impossible trinity of sales volume, pricing, and profitability.
The automobile market ushers in a new era with the 'trade-in' policy update, yet challenges loom large.
As automakers unveil their sales figures, the hardships of 2025 seem to fade into the background amid celebrations of record-breaking sales.
The release of luxury car rankings, in particular, hints at a new chapter for domestic automakers. However, as more statistical data comes to light, the flip side of their growth becomes apparent.
According to the China Passenger Car Association (CPCA), the average transaction price in the passenger vehicle market in 2025 stood at 170,000 yuan, marking a 14,000-yuan decrease from 2024. With a transaction volume of 23.74 million units, this translates to a profit loss of nearly 340 billion yuan.
More notably, the average transaction price of 170,000 yuan put an end to six consecutive years of increases, propelled by the dual forces of a new energy penetration rate surpassing 50% and three consecutive declines.
The Pressured Automotive Manufacturing Industry
From a macro perspective, the automobile market in 2025 indeed flourishes, with passenger vehicle retail sales reaching 12.74 million units, a significant 4% year-on-year increase. This is a rare surge for a mature market.
More significantly, in 2025, the penetration rate of new energy vehicles finally crossed the 50% threshold, becoming a bona fide mainstream in the domestic automobile market. Annual sales exceeded 12.81 million units, outpacing those of fuel-powered vehicles by nearly 2 million units.
The accelerated expansion of new energy vehicles has led to a severe supply-demand imbalance in the market. Over the past three years, the burgeoning new energy vehicle industry has spurred massive capacity expansions.
According to data from the National Bureau of Statistics, the overall capacity utilization rate of the automotive manufacturing industry in 2024 was 72.2%, within a reasonable range but below the 75.0% average benchmark for industries of a certain scale.
Data compiled by multiple agencies reveals that the passenger vehicle manufacturing industry faces even greater challenges. Except for a few automakers like BYD and Chery Automobile, which boast capacity utilization rates above 80%, nearly half of the automakers have utilization rates below 30%.
In particular, the declining capacity utilization rate for fuel-powered vehicles averages only 58%, indicating severe overcapacity.
Overcapacity has led to increased downstream inventory levels. By the end of 2024, the national passenger vehicle inventory reached 3.05 million units. By April 2025, this figure had risen to 3.5 million units, with the inventory digestion period extending to 57 days, far exceeding the healthy level of 45 days.
It wasn't until August that, spurred by a significant 12.6% increase in sales, the inventory level barely decreased to 2.6 million units. Inventory pressures have compelled automakers to accelerate inventory clearance through price reductions and promotions, reducing capital occupation and financial pressure.

In the terminal market, overcapacity in passenger vehicles has directly triggered a price war. In 2025, over 70 models nationwide saw price reductions, with 14 major manufacturers, including BMW, FAW-Volkswagen, Volvo, Kia, Nissan, and Mazda, fully participating. BMW offered discounts exceeding 300,000 yuan, while the FAW-Volkswagen mid-size car special edition was priced at 129,900 yuan, just 60% of its previous price.
Competition in the new energy market is even fiercer. At the beginning of the year, BYD once again sparked a price war, rapidly spreading this trend from high-end models to the mid- and low-end markets. Prices for models like the BYD Qin PLUS DM-i dropped to the 100,000 yuan range.
Under the dual pressures of inventory clearance and competition, the continuous expansion of price reduction amplitudes has led to nearly the entire industry participating in the price war. Automakers appear to be engaged in a 'zero-sum game,' only to discover in the end that it is a 'negative-sum game' with no true winners.

The decline in transaction prices has directly led to a decrease in profit margins. Although this pressure is transmitted upstream from automakers to every component manufacturer, automakers themselves ultimately experience the most significant profit declines.
According to statistics, the profit margin of the passenger vehicle industry in 2025 has dropped to 4.4%, nearly halving from the 7.8% in 2017.
Consumption Transformation
In addition to automakers' proactive price reductions driven by multiple factors, changes in consumption structure are also a major factor contributing to the decline in the average transaction price of passenger vehicles.
In the new energy sales rankings, several models priced under 100,000 yuan rank at the top. The Geely Xingyuan leads with an annual sales volume of 460,000 units, followed by the once-popular Wuling Hongguang MINIEV, which also exceeded 400,000 units in sales.
This also reflects the 2025 automobile market's preference for models priced under 100,000 yuan. According to statistics, the market share of models priced below 100,000 yuan jumped from 18.1% in 2023 to 27.2% in the first five months of 2025.
As consumers flock to the market for vehicles priced under 100,000 yuan, the high-end market experiences severe contraction. According to statistics, the market share of models priced over 400,000 yuan declined from 6.3% to 5.2%, while the market share of models priced between 300,000 and 400,000 yuan also fell from 9.0% to 8.4%.
This change in consumer demand is largely influenced by policies. Driven by the two-year trade-in policy, subsidies are distributed in a fixed amount. For example, scrapping an old vehicle and purchasing a new energy vehicle entitles the consumer to a 20,000 yuan subsidy.
For instance, the Geely Xingyuan Youth Edition, with a guide price of 68,800 yuan, costs only 48,800 yuan after the scrapping subsidy. If the old vehicle has a high residual value, it may even be possible to exchange vehicles at zero cost, only needing to pay for insurance and licensing fees.
Under the policy's impetus, the scale of vehicle trade-ins in 2025 reached 11.5 million units, accounting for half of the passenger vehicle market, but it also indirectly drove changes in automobile consumption structure.
Consumers hope to exchange vehicles at a lower cost, making low-priced new energy models the preferred choice. Especially with the continuous decline in used car prices, considering cost, 100,000 yuan-level new energy models have also become a good option.
Especially against the backdrop of massive price reductions by automakers, the features offered by 100,000 yuan-level new energy models far exceed those of previously 200,000 yuan-level products. This advantage brought by technological progress is further amplified.
Of course, this policy-driven change was also revised in 2026. According to the latest automobile trade-in policy, the previous fixed subsidy method has been replaced with a proportional subsidy method, where subsidies will be provided proportionally based on the price of the new vehicle.
Under the new policy, scrapping an old vehicle and purchasing a new energy vehicle priced over 166,700 yuan or a fuel-powered vehicle priced over 150,000 yuan is required to receive the full subsidy. For trade-ins, purchasing a new energy vehicle priced over 187,500 yuan or a fuel-powered vehicle priced over 216,700 yuan is necessary to obtain the full subsidy.

The policy change also directly addresses the core contradiction in the passenger vehicle industry. While the scale of new vehicle sales continues to grow, the domestic automotive manufacturing industry has long been in a low-profit margin state, severely restricting the industry's healthy development.
In the second half of 2025, the national level began to correct issues such as low-price competition, significantly cooling down the heated price war.
The new policy will also shift the main battlefield of the 2026 automobile market to the 150,000-200,000 yuan range, which will become the most fiercely competitive 'main battlefield.' New energy vehicles, fuel-powered vehicles, and hybrid vehicles will engage in all-around competition.
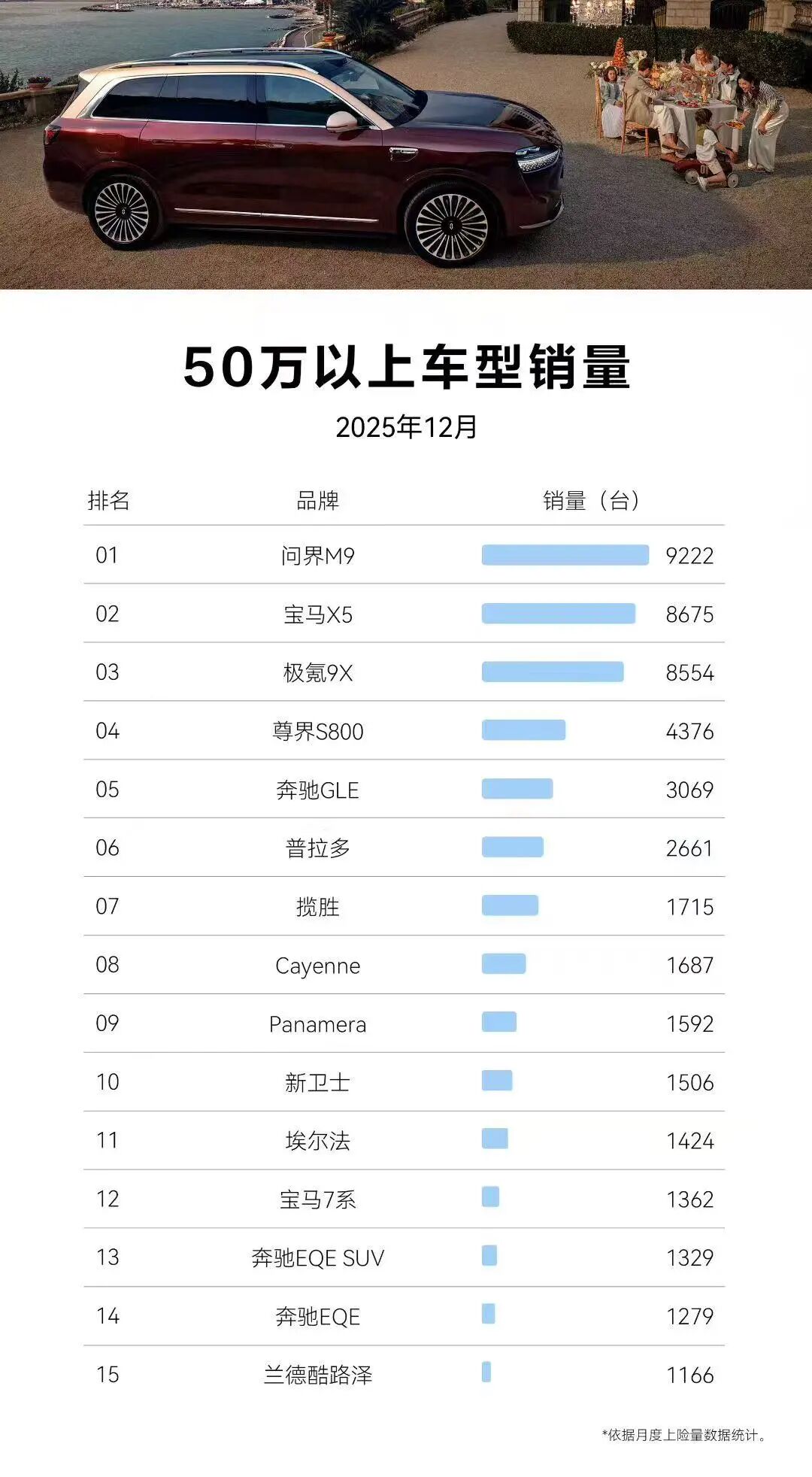
The high-end market priced over 300,000 yuan will become the core market for automakers' profitability goals. New energy vehicles will dominate, with prices remaining basically stable and technological premiums becoming prominent. High-end new energy models like the Li L Series and AITO M9 will maintain their existing price systems, enhancing product competitiveness through technological iteration and service upgrades.
At the same time, more automakers will enter this segment, as seen with the cluster of 9-series large vehicles, all targeting high-profit models in hopes of maintaining profitability through the high-end market.
In 2026, the automobile industry will begin to transition from a 'price-for-volume' model to a new stage of 'value competition,' which will also drive further industrial upgrading.
Note: Some images are sourced from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.
-END-