Toyota has reversed course, and its secret plan for new energy vehicles has finally been exposed!
![]() 10/09 2024
10/09 2024
![]() 622
622
After BYD became the world's first new energy vehicle company and one of the top ten global automakers as the only automaker globally with in-house R&D capabilities for batteries, motors, and electric control systems, the era of new energy vehicles has arrived globally.
Among the leading multinational automakers, Volkswagen has ambitious plans in the new energy vehicle market. After partnering with LG Energy Solution and CATL for battery development, Volkswagen strategically invested in XPeng Motors to develop new electric smart vehicles. Meanwhile, General Motors has collaborated with Honda and Hyundai Motor globally on new energy vehicles.
On October 1, Toyota announced that its battery joint venture, PEVE (Primearth EV Energy), had officially become a wholly-owned subsidiary, rebranded as TOYOTA BATTERY. Has Toyota finally shed its disguise?

TOYOTA BATTERY's predecessor was Panasonic EV Energy, founded in 1996. In 1997, it began producing the first-generation Prius's cylindrical nickel-metal hydride hybrid battery. In 2009, it was renamed Primearth EV Energy and officially mass-produced the fourth-generation ternary lithium-ion battery for hybrid vehicles in 2023, accumulating over 25 million battery sets produced.
In 2013 and 2014, Primearth EV Energy established two battery joint ventures in Changzhou, China—STAES and CPAB—marking Toyota's comprehensive promotion of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) in the Chinese market.
TOYOTA BATTERY is located in Kozushi, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. Its first plant began producing batteries for HEVs in February 2024, with the second and third plants scheduled to commence operations within the year. The site will eventually produce Toyota's full range of batteries, including solid-state batteries.

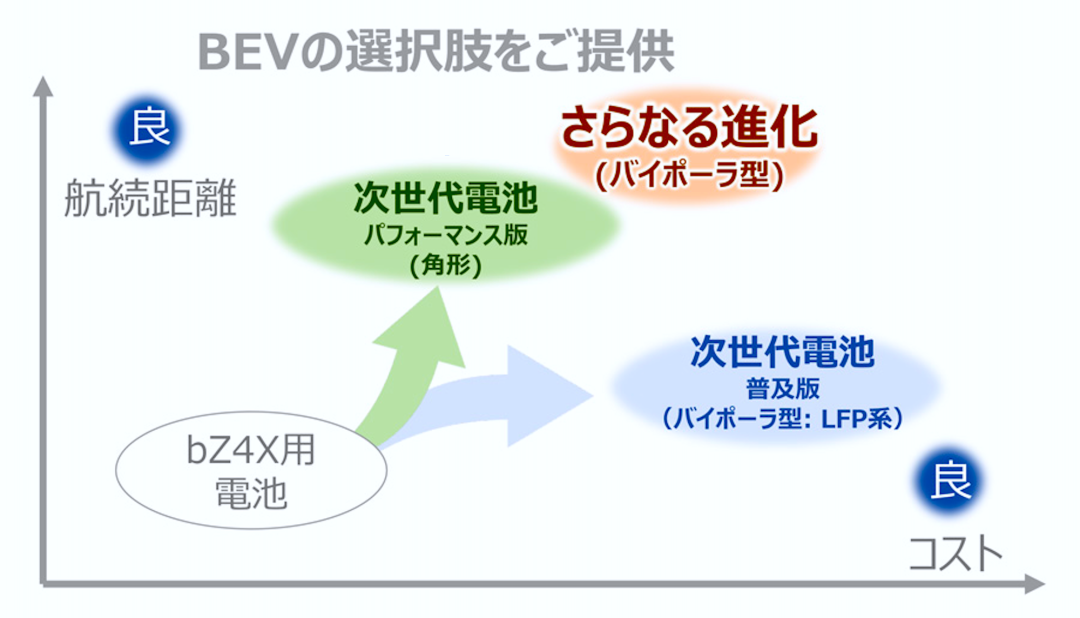
Toyota and Panasonic jointly established Prime Planet Energy Solutions (PPES) in 2020, a battery joint venture with a maximum annual production capacity of 30GWh. PPES primarily produces prismatic ternary lithium-ion batteries for Toyota's battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). Toyota's upcoming "Next-Generation Performance Battery," set for release in 2026, will also be produced here.
PPES's subsidiary in Dalian, China, PPEDL, supplies ternary lithium-ion batteries to Toyota's hybrid vehicles in China and will become one of Toyota's major production bases for new energy vehicles in the country.
While global automakers are accelerating their push for BEVs, Toyota has been dismissive of this trend, focusing instead on rapidly developing HEVs to compete with new energy vehicles globally.

In Toyota's lexicon, new energy vehicles encompass HEVs and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). Facing increasingly stringent fuel consumption and emission regulations in major automotive markets like Europe and China, Toyota is poised to mass-produce dedicated small-displacement and compact engine powertrains for PHEVs, along with next-generation batteries.
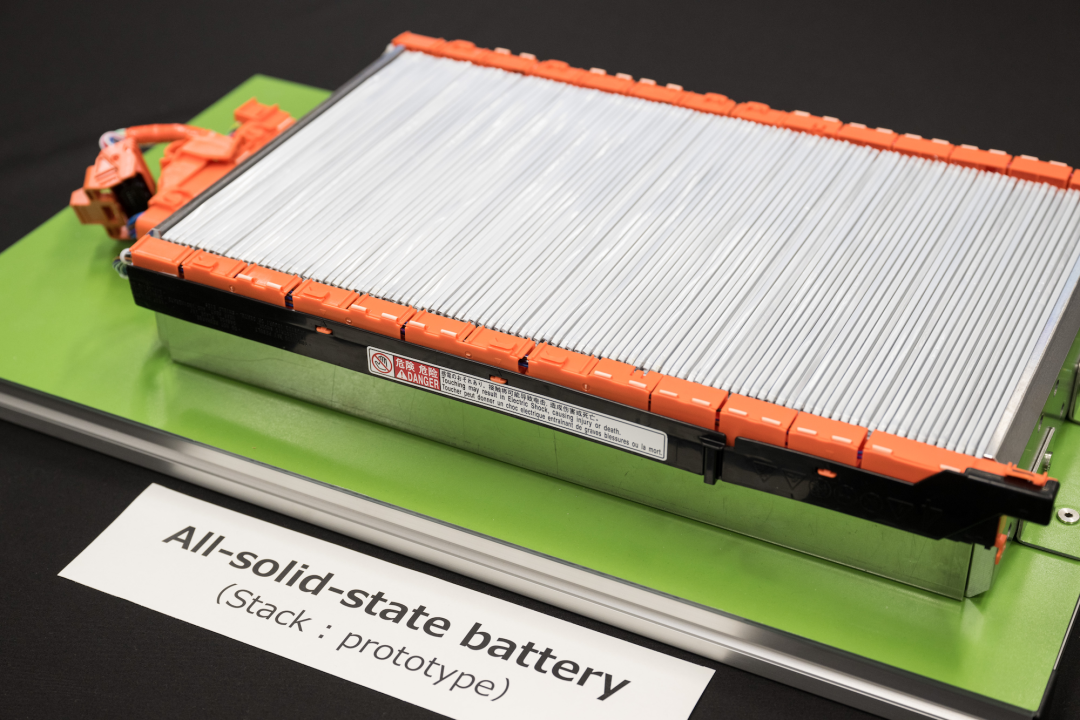
Toyota boasts a comprehensive range of batteries, including HEV-exclusive batteries, low-cost and long-range performance batteries, ultra-high-performance batteries, and solid-state batteries. It's only a matter of time before Toyota surpasses CATL and BYD in production capacity, making it the only automaker globally with such a diverse battery portfolio.
The official establishment of TOYOTA BATTERY signifies Toyota's ample preparation for the upcoming era of comprehensive new energy vehicles.

In addition to battery joint ventures, Toyota has collaborated with BYD on ternary lithium-ion batteries for HEVs, with the first vehicles equipped being the Corolla Hybrid and Levin Hybrid. Toyota has also partnered with CATL for ternary lithium-ion batteries for BEVs, with the first vehicle being the bZ4X.
North America is Toyota's largest overseas market, and the automaker continues to invest heavily in battery production. Toyota Battery Manufacturing North Carolina (TBMNC) has a cumulative investment of approximately $13.9 billion and employs over 5,100 people. The first production line is expected to commence operations in 2025, with long-term plans for an annual capacity exceeding 30GWh.
TBMNC will establish a total of 14 ternary lithium-ion battery production lines, four dedicated to HEV batteries and ten for PHEV and BEV batteries.

CATL, the world's largest battery technology company, installed a total of 259.7GWh of new energy vehicle and energy storage batteries in 2023.
BYD, the world's largest new energy vehicle manufacturer, installed approximately 150.909GWh of new energy vehicle and energy storage batteries in 2023, with a cumulative installation of 127.720GWh from January to September 2024.
From Japan to North America and China, with the official commissioning of Toyota's battery plants, the automaker's annual global battery production capacity is expected to reach 200GWh by 2030. This capacity supports Toyota's ambition to sell millions of HEVs annually, potentially leading to the largest number of battery installations globally.
While other global automakers tend to collaborate with leading component suppliers in the "three electrics" sector, Toyota prioritizes maintaining absolute dominance and control in its electric vehicle plans. This is one reason for Toyota's relatively slow and lagging progress in new energy vehicles.
With the establishment of TOYOTA BATTERY, outsiders perceive that Toyota has reversed course and is finally entering the new energy vehicle market.
However, the truth is that Toyota has long been secretly preparing and is now fully equipped to secure an absolute leadership position in the new energy vehicle market, rather than working for battery manufacturers and having its future development throttled.
Whether it's the official launch of the fifth-generation HEV system or the cumulative sales of over 27 million HEVs, Toyota is poised to begin popularizing PHEVs globally in 2025, following the widespread adoption of HEVs.
Under the TNGA architecture, HEVs can seamlessly upgrade to PHEVs. The timing of large-scale promotion will depend on global market demand and policy changes.
It is certain that, following its world-leading HEV technology, Toyota is poised to become the only multinational automaker fully promoting PHEVs.

In China, the world's fastest-growing and largest new energy vehicle market, batteries have achieved leapfrog improvements in range and safety. Current development focuses on enhancing energy efficiency and charging speeds.
Toyota's massive in-house battery factories and comprehensive battery range, including cost-effective batteries 20% cheaper than existing models with over 1,000 km of range and ultra-fast-charging solid-state batteries, cater to the needs of various global market segments.
As battery technology continues to advance and approach the level of industry leaders, Toyota's long-standing commitment to product safety, stability, and durability will enable it to outpace competitors in the new energy vehicle market.
BYD is poised to reach a peak annual sales volume of 4 million vehicles in 2024, but 2025 remains uncertain. However, this marks the beginning of Toyota's new energy vehicle era, with the automaker set to unify the global new energy vehicle market by 2026.






