The auto industry seems prosperous, but profits have plummeted to record lows
![]() 10/31 2024
10/31 2024
![]() 477
477

Introduction
Introduction
The auto industry is becoming more competitive, making it harder to make money from car sales! The traditionally prosperous "Golden September" has turned into a "Copper September".
According to historical trends, September has always been the most vibrant and prosperous month for the auto industry. New car models emerge like mushrooms after rain, auto shows are held back-to-back, and sales figures soar. Therefore, this month is affectionately referred to as "Golden September" by industry insiders.
However, this year's situation is vastly different, with the auto industry seemingly hit by a chill.
As competition in China's auto market intensifies, major brands have resorted to price cuts and added features to compete for market share. While this has somewhat stimulated consumer demand, it has also squeezed automakers' profit margins. Data shows that the total profit of the auto industry this year is only 32.4 billion yuan, a staggering 28.5% drop from the same period last year.
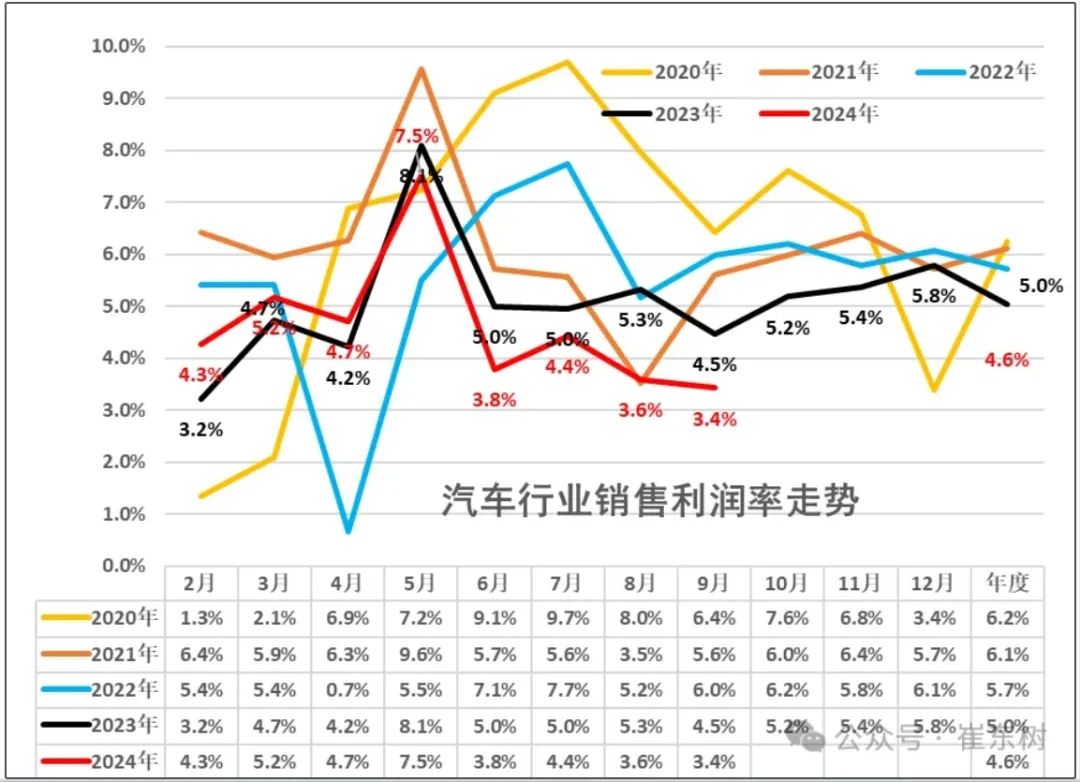
Even more concerning is that the profit margin in September this year was just 3.4%, the lowest for the year and the second-lowest in the past four years. This means that despite seemingly strong sales, automakers are finding it increasingly difficult to make money. This "thin profit, high volume" model is clearly not a good sign for the long-term development of automakers.
From an annual perspective, the profit margin of the auto industry has been declining year by year. In 2020, the industry's profit margin was still at 6.2%, but it dropped to 6.1% in 2021. In 2022, it further declined to 5.7%, and for the first nine months of this year, the average profit margin was only 4.6%, far below previous years' levels.
This continuous decline in profits and profit margins has undoubtedly sounded the alarm for the entire industry and cast a shadow over its future development.
It can be said that while the auto industry appears bustling on the surface, it is actually fraught with many hidden crises. Intensifying competition, shrinking profit margins, and declining profit rates are all realities that the industry must confront.

In fact, the auto industry's record-low profits could trigger a series of significant consequences, profoundly affecting not only the survival and future development of enterprises but also socioeconomic stability and employee welfare. These implications cannot be ignored.
The sharp decline in auto industry profits will first and foremost impact companies' investments in research and development (R&D) and innovation. In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the auto industry stands at a crossroads of electrification and intelligent transformation, where new technology development and application are paramount.
Breakthroughs in battery technology, autonomous driving, and connected vehicles all require substantial R&D funding. However, with profit margins plummeting, companies may face the embarrassing situation of having their R&D budgets slashed. This reduction in funding will directly impact the pace and quality of technological innovation, ultimately weakening their market competitiveness.
In an era where new technologies emerge continuously, lagging behind in R&D can lead to losing market opportunities and even being left far behind by competitors.

Apart from R&D investments, declining profits may also force companies to cut expenses on marketing and branding. In today's increasingly competitive market, branding and marketing are undeniably crucial. A strong brand image and marketing strategy can help companies establish a foothold in consumers' minds, thereby boosting sales and market share.
However, with profits sliding, companies may struggle to maintain their previous marketing efforts. Reduced advertising spending and scaled-back promotional activities can lead to a decline in brand awareness and influence. Over time, this will inevitably impact sales performance and market share, further exacerbating the trend of declining profits.
The impact of declining auto industry profits is not limited to vehicle manufacturers alone. In fact, this shift will ripple through the entire automotive supply chain, affecting upstream and downstream enterprises to varying degrees.
For upstream parts suppliers, they may face reduced orders and increased price pressures. As vehicle manufacturers' profits decline, they will impose stricter cost controls on parts, placing immense pressure on suppliers' operations.

As for downstream car dealers, declining profits can lead to sales difficulties and inventory backlogs. Consumers may become more cautious when purchasing cars, cooling the auto sales market. Dealers may have to resort to price cuts and promotions to maintain operations, further compressing profit margins.
Profit is a crucial indicator of a company's profitability. When profits hit record lows, it signifies a severe weakening of a company's earning power. This directly affects its financial health and solvency. In the long run, declining profitability can negatively impact a company's reputation and sustainable operations.
With deteriorating financial conditions, companies may struggle to repay debts or secure new financing. This can disrupt normal operations and potentially trigger more severe financial crises. Therefore, enhancing profitability and improving financial health are crucial tasks facing the auto industry.
Lastly but importantly, declining profits can also directly impact employee salaries and benefits. To reduce costs and address profitability pressures, companies may have to consider adjusting employee compensation and benefits, including pay cuts, layoffs, or eliminating certain benefits.
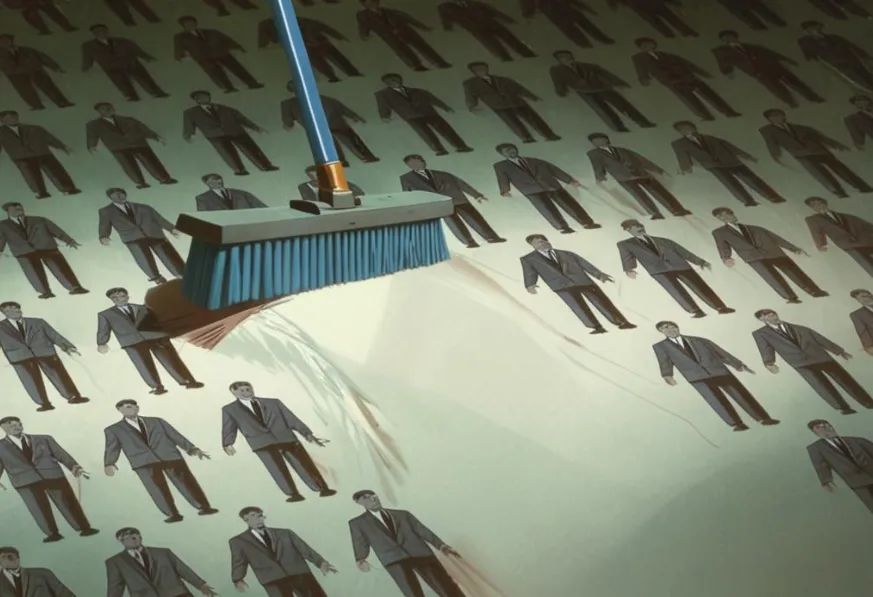

These adjustments can significantly impact employees' quality of life and work motivation. Pay cuts and layoffs can cause financial stress and hardship, affecting workers' efficiency and loyalty. Eliminating benefits may reduce employee satisfaction and sense of belonging.
This year, the auto industry appears thriving on the surface, with new car models emerging continuously and auto shows held regularly, giving the impression of robust growth. However, upon closer inspection, the severe consequences mentioned above are essentially playing out daily in the industry.
Thus, the continuous decline in profits has become an issue that cannot be ignored. It's like an invisible time bomb, constantly threatening the survival and development of companies. The primary factor contributing to declining auto industry profits lies in the intense competition within China's auto market, commonly referred to as "involution." While competition is crucial for industry progress, the key lies in how to harness it effectively.
In this highly competitive market environment, "involution" has become the norm. However, simply getting caught up in it is not a wise move. Harnessing "involution" effectively means that companies need to maintain their competitiveness while identifying unique innovation points to stand out in the market.