Does a 'Smart Car' Need a 'Smart Road'?
![]() 11/01 2024
11/01 2024
![]() 640
640
Lead
When Tesla unveiled its self-driving taxi, the Cybertruck, it marked a new chapter in the era of autonomous vehicles. In China, autonomous driving technology is quietly evolving, with self-driving taxis operating in multiple cities and numerous automakers enhancing their Navigate on Autopilot (NOA) features to cover the entire country. Increasingly intelligent vehicles are evolving from ordinary modes of transportation into new technologies that will revolutionize future travel.
Produced by: Heyan Yueche Studio
Written by: Cai Jialun
Edited by: He Zi
Total words: 1762
Reading time: 3 minutes
Tesla's Full Self-Driving (FSD) is a representative technology for vision-based end-to-end autonomous driving. Currently, many domestic automakers are following Tesla's vision-based approach. However, the concept of vehicle-road-cloud integration is more popular in China. This year, the Chinese government has released up to four documents related to pilot applications of vehicle-road-cloud integration. Relevant institutions estimate that by 2030, the scale of the vehicle-road-cloud integration industry will reach 2 trillion yuan, and China is currently in a leading position in this field. So, the question arises: as individual smart vehicles become increasingly advanced in their autonomous driving capabilities, is vehicle-road-cloud integration still necessary?

△With Tesla's FSD becoming stronger, is vehicle-road-cloud integration still needed?
Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration is Superior
In the future, autonomous driving will take two paths. One path is represented by Tesla's autonomous vehicle intelligence, which relies on the vehicle's own perception and decision-making to navigate road conditions and achieve autonomous driving. The other path is represented by the collaborative intelligent solution of vehicle-road-cloud integration. Vehicle-road-cloud integration has higher requirements for infrastructure, while autonomous vehicle intelligence has higher requirements for vehicle software and hardware, with significant costs associated with high-end sensors and high-performance chips. For consumers, vehicle-road-cloud integration is the most economically viable option. Unlike smart vehicles that blindly stack sensing components and increase chip computing power to enhance individual vehicle intelligence, vehicle-road-cloud integration favors a collaborative approach, utilizing road smart infrastructure, cloud computing, satellite internet, and dynamic high-precision maps that are constantly updated, providing a more reliable and intelligent solution.
Currently, from the development of autonomous driving technology among domestic automakers, it is evident that to achieve L4 autonomous driving technology, vehicles cannot operate as independent entities. Connecting drivers, vehicles, and roads is the ultimate goal. Meanwhile, vehicle-road-cloud integration will effectively achieve refined urban traffic management, which is the vision China aims to realize. Taking the Xiong'an New Area as an example, as a demonstration site for 5G-based vehicle-road collaboration and the Internet of Vehicles, this smart city aims to create digital roads, and currently has integrated traffic lights, cameras, radars, and various sensing facilities on both sides of the digital roads.

△Driverless buses appear on the streets of Xiong'an
China prefers the vehicle-road-cloud integration solution and is actively promoting it. In July this year, five ministries, including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the Ministry of Transport, released a list of pilot cities for the integrated application of intelligent and connected vehicles, vehicle roads, and clouds. Currently, many places in China have established closed testing areas for intelligent and connected vehicles, and plan to establish a unified and shared vehicle-road-cloud integration standard system by 2026, promoting its application in multiple scenarios such as smart cities and intelligent transportation. Driven by strong policies, the construction of vehicle-road-cloud integration in China is accelerating, potentially becoming another major transportation project after highways and high-speed rail networks.
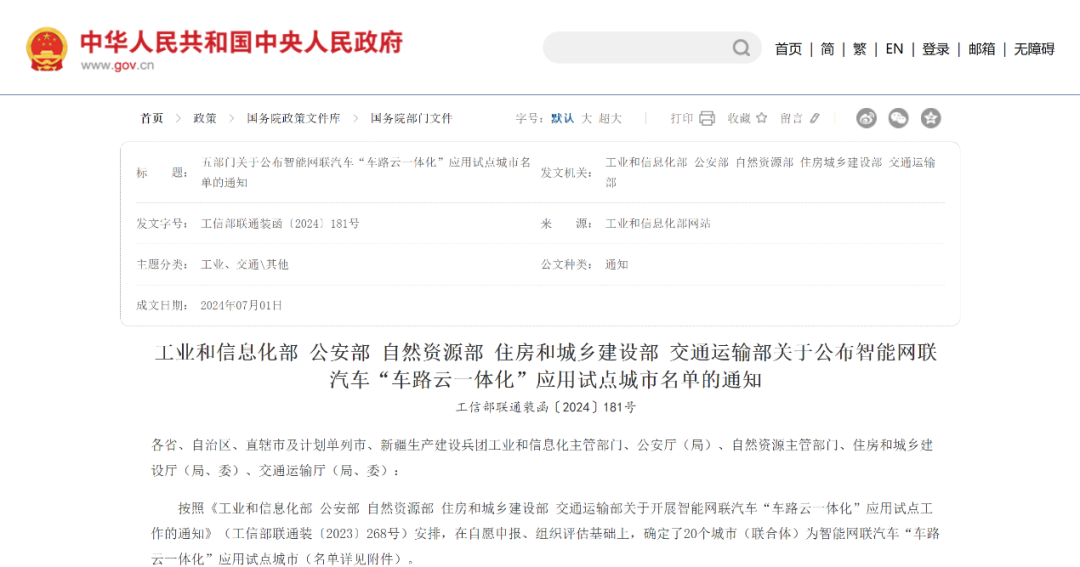
△Relevant policies are accelerating the construction of vehicle-road-cloud integration
How Far is Vehicle-Road-Cloud Integration?
Vehicle-road-cloud integration has broad development prospects and a vision for building smart cities, but there is still a long way to go before nationwide implementation. Currently, a complete system architecture for vehicle-road-cloud integration has not yet been established, and infrastructure construction in some pilot areas is still inadequate. Academician Li Keqiang of the Chinese Academy of Engineering has stated that most current vehicle-road-cloud integration systems are trapped in a "stovepipe" architectural platform, resulting in fragmented data and isolated resource islands. Vehicle-road-cloud standards tend to be regional and cannot be unified. Some demonstration areas have inevitably become mere "bonsai" for viewing, with practical applications yet to be improved. Judging from the current state of vehicle-road-cloud integration development, many challenges remain to be solved before mass production and large-scale commercial operations can be achieved in the future.
As a massive infrastructure project, vehicle-road-cloud integration must consider regional differences in China, making it difficult to achieve nationwide standardization. Even current autonomous vehicle intelligence is divided into two approaches: pure vision and LiDAR, which raises another issue. The solutions adopted by various automakers for intelligent and connected vehicles vary greatly. How to adapt different brands and types of intelligent and connected vehicles to vehicle-road-cloud integration facilities remains to be explored. Meanwhile, vehicle-road-cloud integration involves various industries such as automotive information, transportation, and energy, and building such a vast ecosystem can only be achieved through collaboration.
The realization of vehicle-road-cloud integration cannot rely solely on the unilateral efforts of automakers but requires collaboration among automakers, the internet industry, and government services. Automakers should enhance vehicle intelligence and accelerate computing power and sensing hardware where possible. Internet companies should explore new business models to provide data support for the vehicle-road-cloud ecosystem. Government departments should accelerate infrastructure construction and jointly implement effective policies with transportation and urban construction departments.
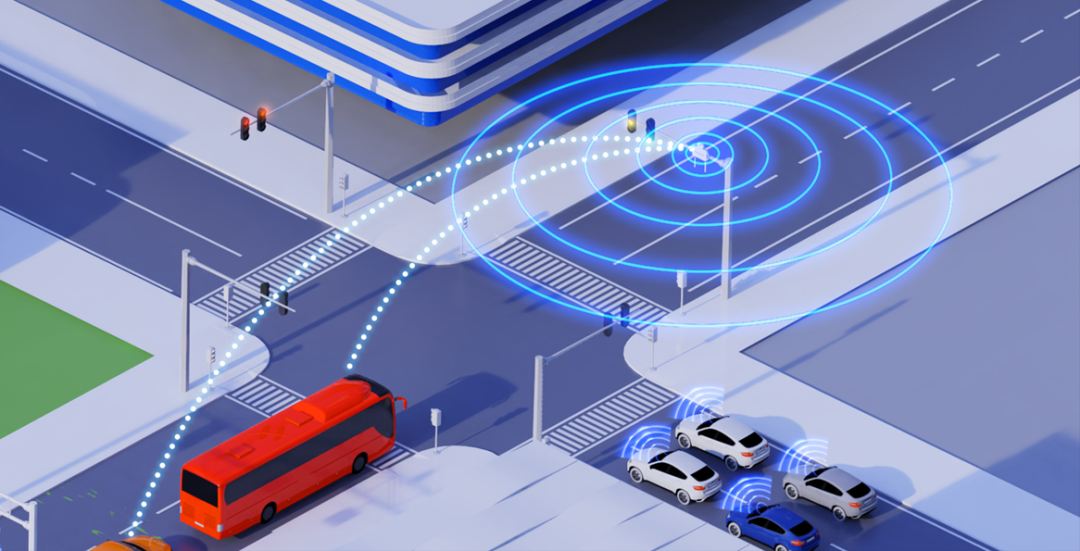

△Vehicle-road-cloud integration requires collaboration among multiple parties
Commentary
Although the cost of current intelligent driving solutions is gradually decreasing, and many automakers have extended intelligent driving technology to the 150,000-yuan home vehicle market, breaking through autonomous driving relies on more than just autonomous vehicle intelligence. Vehicle-road-cloud integration is a necessity. In the future, vehicle-road-cloud integration will combine 'smart cars' with 'smart roads' to provide us with a sci-fi movie-like travel experience.
(This article is originally created by Heyan Yueche Studio and may not be reproduced without authorization)