Robotaxi on the eve of explosion, domestic autonomous driving enterprises rush to IPO
![]() 11/13 2024
11/13 2024
![]() 565
565

Looking back years later, 2024 may be remembered as the first year of Robotaxi.
Recently, autonomous driving companies Horizon Robotics and WeRide have gone public successively, once again drawing attention from the outside world to the autonomous driving industry.
Preceding them were lidar enterprise RoboSense and autonomous driving chip company Black Sesame Technology, and following them are Pony.ai, Momenta, Zongmu Technology, Youjia Innovation, and other companies rushing to go public.
This year has seen remarkable enthusiasm in the field of autonomous driving. In the first half of the year, Baidu's RoboTaxi service Luobo Kunpao went viral online, bringing Robotaxi into the public eye. In October, Tesla unveiled its driverless Robotaxi, sparking heated discussions worldwide.
Robotaxi represents the most promising application of Level 4 autonomous driving. After years of development, autonomous driving enterprises have finally entered a new stage of commercialization.
However, due to high initial investment, long return periods, and technical difficulties, these enterprises are still struggling with losses.
The rush to IPO reflects both a desperate need for funds and an imperative to further accelerate commercialization. "Bleeding IPO" is not the end but the beginning of a new phase.
01
Time Waits for No One
This year has seen unprecedented enthusiasm for Robotaxi, perhaps making it the best time for autonomous driving enterprises to go public.
Although Level 4 autonomous driving encompasses various scenarios such as driverless trucks, delivery robots, and driverless buses, considering market demand and prospects, Robotaxi is the best choice for the commercialization of Level 4 autonomous driving. Current views suggest that 2026 will be the first year of large-scale production of Robotaxi.
The dawn is beckoning, and autonomous driving enterprises focused on Level 4 technology have been sprinting for seven to eight years. Now, in the final stretch, everyone wants to be the first to cross the finish line. Going public means securing more funds and attention.
Following the IPOs of Hesai Technology and Zhixing Auto in 2013, several autonomous driving enterprises have initiated their IPO processes this year. During this period, RoboSense, Ruqi Chuxing, Black Sesame Technology, Horizon Robotics, and WeRide have successfully gone public, with companies like Pony.ai, Zongmu Technology, and Mushroom Auto waiting for the right moment.
Behind this wave of IPOs lies a sense of urgency – the autonomous driving industry has developed for seven to eight years, and it's now or never to go public.

Autonomous driving has experienced a funding journey marked by initial enthusiasm followed by a cooldown. Nowadays, with financing in the primary market cooling down and hot money inflow decreasing, domestic unicorns have reached a critical juncture for commercialization and capitalization.
According to Tianyancha APP, financing for autonomous driving commercialization is difficult to achieve short-term returns, and financing is becoming increasingly challenging. Capital is becoming more rational, and projects with uncertain commercialization prospects are hard to attract investment. Most autonomous driving enterprises' last round of intensive financing was in 2021-2022.
From 2015 to 2022, Zongmu Technology completed 10 rounds of financing, with the most recent round in March 2022. Black Sesame Technology, which has successfully gone public, completed 9 rounds of financing from 2016 to 2022, with the most recent in December 2022. WeRide and Pony.ai both completed new financing this year, likely due to their upcoming IPOs.
IPO is the key to solving these issues – successful listing allows investors to exit with profits, relieves startups of the pressure of high share repurchases, and provides new development funds.
However, even after a successful IPO, companies must be prepared for a possible share price drop, as evidenced by the performance of predecessors who entered the capital market in recent years.
In August this year, Black Sesame Technology listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange as an unprofitable "Specialist Technology" company, and its share price plunged by 32.9% after opening. As of November 12, Black Sesame Technology's market value was HK$14.5 billion, lower than the previous valuation of HK$17 billion. Hesai Technology's share price has also been declining since its listing, currently standing at $4.5 per share, below its issue price.
Clearly, IPO marks the end of one development stage and the beginning of a new journey. The trajectory a company takes ultimately depends on its commercialization capabilities.
02
Differences within the Same Race
High investment and low returns characterize the current state of autonomous driving enterprises.
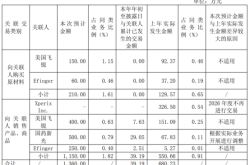
From 2021 to the first half of 2024, WeRide's revenue was RMB 138 million, 528 million, 402 million, and 150 million, respectively, with corresponding net losses of RMB 1.007 billion, 1.298 billion, 1.982 billion, and 882 million. Cumulatively, it has lost more than RMB 5 billion in three and a half years.
Its revenue peaked in 2022 and has since declined, with a particularly sharp drop in the first half of this year. Net losses have continued to widen and have not narrowed in the first half of this year.
Pony.ai is also under profit pressure. According to its prospectus, its adjusted net losses for the past two and a half years were $148 million, $125 million, and $51.78 million, respectively, totaling $325 million, or approximately RMB 2.307 billion.
Horizon Robotics, a highly anticipated smart driving chip technology company, has accumulated losses exceeding RMB 22 billion in the three and a half years since 2021.
From autonomous driving technology to chips to RoboTaxi operations, losses have been the main theme across the entire industry chain due to high initial investment and long return periods.
For instance, from 2021 to 2023, WeRide's cumulative R&D expenditure was RMB 2.26 billion, more than twice its revenue. The prospectus predicts that R&D expenditure will continue to increase as the company tests, trials, and commercializes its autonomous driving technology. In other words, if revenue does not increase significantly, losses will continue to expand.
Despite the common challenges, each enterprise faces unique circumstances.
WeRide primarily relies on two types of businesses: sales-focused, involving L4 autonomous vehicles such as robot buses, robot taxis, and various robotic vehicles and sensor kits; and service-focused, providing L4 autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance system services, including operations, technical support, and ADAS research and development.
Pony.ai's main businesses include autonomous ride-hailing services, autonomous trucking, and technology licensing and application services.

Both companies' businesses cover Robotaxi but cannot rely on it as their primary revenue source due to complex deployment scenarios and technological limitations.
In 2022 and 2023, Pony.ai's technology licensing and application services accounted for 54.2% and 54.5% of total revenue, respectively, followed by autonomous trucking, which accounted for over 32%. In the first half of this year, autonomous trucking (Robotruck) became the primary revenue source, accounting for 73% of total revenue.
Robotaxi's revenue contribution peaked at 13.1% in 2022 and fell to 4.7% in the first half of this year. WeRide's Robotaxi revenue is categorized under services and not disclosed in detail.
While Robotaxi represents the aspiration of autonomous driving enterprises due to its open scenarios and vast imagination, the reality is focused on Robotruck, a closed scenario with limited growth potential. The story of Level 4 autonomous driving has become less sexy in the short term.
Business differences also fuel the ongoing debate over which company deserves to be the "first Robotaxi stock." Currently, Pony.ai appears more focused on Robotaxi and is progressing faster than WeRide.
Pony.ai has over 250 Robotaxi vehicles with over 33.5 million kilometers of autonomous road tests, including 3.9 million kilometers of driverless tests, and each vehicle averages over 15 orders per day. In comparison, Baidu's Luobo Kunpao, which has gained widespread attention, peaks at around 20 orders per vehicle per day.
WeRide has made no significant progress in its Robotaxi business, disclosing limited information. Due to unsatisfactory sales of autonomous taxis and driverless shuttles, its operational focus has shifted from product sales to services. This shift has raised questions about the value of being the "first Robotaxi stock."
Regardless, companies like Pony.ai, WeRide, and Luobo Kunpao are forging ahead toward the long-term goal of Robotaxi. Who will make the first qualitative breakthrough remains to be seen, subject to various tests in technology, products, and operations.
03
The Key to Scalability
Everyone recognizes the vast potential of Robotaxi, but crossing the chasm to realize this potential is challenging.
Frost & Sullivan predicts that China is poised to become the largest Robotaxi market, with an estimated market size of $200 million in 2025 and $39 billion in 2030, accounting for approximately 58.5% of the global autonomous mobility services market in 2030.
However, according to Lou Tiancheng, CTO of Pony.ai, we are still far from the envisioned ubiquity of Level 4 autonomous driving: "Even with end-to-end technology, today's advanced intelligent driving can only reach L2.99, falling short of L4."
For autonomous driving enterprises, it's crucial to balance ambition with practicality. In other words, making big money is for the future; surviving in the present is paramount. Therefore, many companies are collaborating in the L2 field to "earn and support the family."
In January 2023, Pony.ai officially announced its intelligent driving product line for passenger vehicles and later partnered with Geely to co-develop intelligent driving solutions for mass-produced vehicles. Black Sesame Technology, which started in smart chip business, began providing intelligent driving solutions for passenger vehicles in 2022. Momenta, which is preparing for its IPO, announced a partnership with GAC Toyota in June 2024 to deploy intelligent driving solutions.
However, the relationship between autonomous driving enterprises and automakers is complex, characterized by both cooperation and competition.
Both new-energy vehicle makers and leading traditional automakers have their intelligent driving teams and even involve themselves in self-developed chips. After all, no automaker wants to hand over their "soul" to others."
Moreover, from a technical standpoint, autonomous driving enterprises do not have a clear lead.
In October, Yu Chengdong, Chairman of Huawei's Intelligent Automotive Solution BU, announced that Huawei's ADS 4.0 will be launched next year, offering commercial high-speed L3 autonomous driving and pilot projects for urban L3 autonomous driving.
The broader prospect of Robotaxi also intertwines cooperation and competition.
Ruqi Chuxing, a subsidiary of GAC Group, collaborates with Pony.ai and WeRide. SAIC Motor's Enjoy Robotaxi is based on Momenta's autonomous driving technology. Leading new-energy vehicle maker BYD has also partnered with Dongchao Technology to deploy Robotaxi in Shenzhen.
Autonomous driving companies and ride-hailing platforms procure vehicles from automakers, who can combine their operational capabilities with autonomous driving technology to jointly develop Robotaxi, forming a mutually beneficial cooperation model.

For autonomous driving enterprises, enhancing scalability is crucial to stand out in various competitions.
On one hand, increasing the number of operational vehicles and achieving economies of scale as soon as possible can help achieve break-even earlier. Vehicle procurement costs, maintenance costs, and operational management costs will decrease with scale, vital for sustainable business development.
On the other hand, scalability also enhances service quality. Robotaxi relies on extensive data training. More vehicles and longer total operating hours mean more data sources, improving autonomous driving intelligence, optimizing dispatching algorithms, and further enhancing operational efficiency.
Industry leaders have emerged. In the second quarter of this year, Luobo Kunpao provided approximately 899,000 trips, a year-on-year increase of 26%. Chen Zhuo, General Manager of Baidu's Autonomous Driving Business Unit, stated that Luobo Kunpao is expected to achieve break-even in Wuhan by the end of this year and enter a comprehensive profit period next year.
Time waits for no one. While an IPO can alleviate the financial pressure on autonomous driving enterprises, the real competition may just be beginning. Through competition and cooperation, various enterprises jointly promote the large-scale popularization of Robotaxi, enabling autonomous driving to truly transform people's mobility habits, marking a more profound significance.
04
Conclusion
After seven to eight years of challenging exploration, enterprises across the autonomous driving industry have finally gathered on the IPO stage.
With the rapid iteration of AI technology, related industries of autonomous driving are also maturing. Participants including government agencies, chip manufacturers, automakers, and technology companies are jointly driving the large-scale application of autonomous driving technology.
Today, autonomous driving has become a global industrial competition. As a promising commercial scenario, Robotaxi is a must-win territory for domestic autonomous driving enterprises.
By combining proven commercialization models with long-term strategies and addressing issues related to technology maturity, policy soundness, and business model clarity, the true turning point for the autonomous driving industry lies in the near future.