Leapmotor, a Rising Star in Auto Industry, Surprises with Profitability Amidst Over RMB 20 Billion in Funding
![]() 01/23 2025
01/23 2025
![]() 789
789
In 2025, Leapmotor, a budding automaker, made a "surprising" announcement – a profit warning that revealed a positive net profit in Q4 2024.
According to the announcement, Leapmotor achieved a positive net profit in Q4 2024, accomplishing its quarterly profitability goal a year ahead of schedule.
While this accomplishment spans just one quarter, it places Leapmotor significantly ahead of most other emerging automakers. How did Leapmotor achieve this feat? Can it sustain this performance in the future? And what challenges lie ahead?
Over RMB 20 Billion in Funding
Founded in 2015 by Zhu Jiangming, Leapmotor aimed to become a leading domestic smart electric vehicle company. However, compared to peers like NIO, Xpeng, and Li Auto, Leapmotor remained relatively under the radar.
Nonetheless, Zhu Jiangming and Fu Liquan, also the founders of security surveillance giant Dahua Technology, brought strong endorsement to the venture. Coupled with the burgeoning interest in the new energy vehicle industry, Leapmotor, among other new automakers, attracted significant capital.
Initially, Leapmotor's capital flow primarily originated from the "Dahua System," including Dahua Technology, Zhu Jiangming, Fu Liquan, and others. By 2018, the company had completed eight rounds of funding before its IPO, with frequent market reports on its funding activities.
Specifically, Leapmotor raised RMB 365 million in Pre-A1 and A2 funding rounds in 2018, RMB 1.121 billion in A-1 and A2 rounds from 2018 to 2019, RMB 4.3 billion in B-1 and B-2 rounds in 2021, and RMB 6.081 billion in C-1 and C-2 rounds in August and November 2021.
In total, these eight funding rounds amounted to approximately RMB 11.866 billion, nearing RMB 12 billion. Investors included Sequoia Capital China, Sequoia Capital China Growth, Shanghai Electric Hong Kong, Jinhua Yuxuan, Changsha Nuofeng, Hangzhou Hanzhi, Zhoushan Haohai, Huzhou Jingxin, Guoshun Lingpao, Green Lingpao, CICC Binchuang, and CICC Chuangyu.
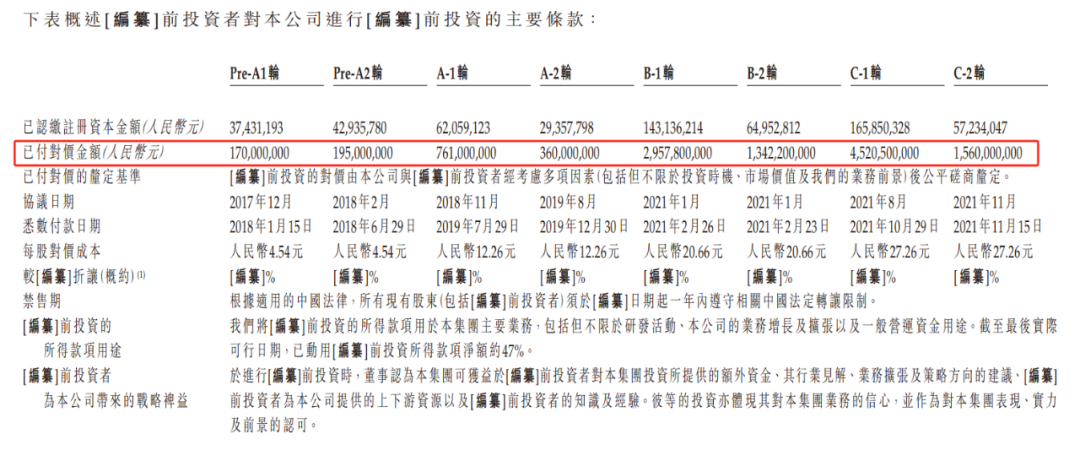
On September 29, 2022, Leapmotor successfully listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange with an issue price of HKD 48 per share. The global offering netted approximately RMB 6.169 billion, allocated to R&D (40%), production (25%), sales (25%), and supplementary operating funds (10%).
Despite this, Leapmotor continued fundraising post-IPO due to its lack of self-sufficiency.
On October 26, 2023, Leapmotor signed a subscription agreement with the Stellantis Group, which subscribed for 194 million shares at HKD 43.8 per share, totaling approximately HKD 8.509 billion. Additionally, Stellantis acquired all 90 million shares held by Dahua Technology for HKD 3.493 billion, making Dahua Technology no longer a shareholder.
Through these transactions, Stellantis became a significant shareholder of Leapmotor, obtaining two board seats with a 21.26% shareholding ratio, playing a pivotal role in operational decision-making.
These funding rounds provided Leapmotor with ample "ammunition" to maintain operations, reduce losses annually, and gradually achieve profitability.
Sales Soar
Expanding automaker operations can enhance a company's supply chain influence, exemplified by BYD. This benefits automakers by reducing costs and increasing profits, rooted in car models and sales volume.
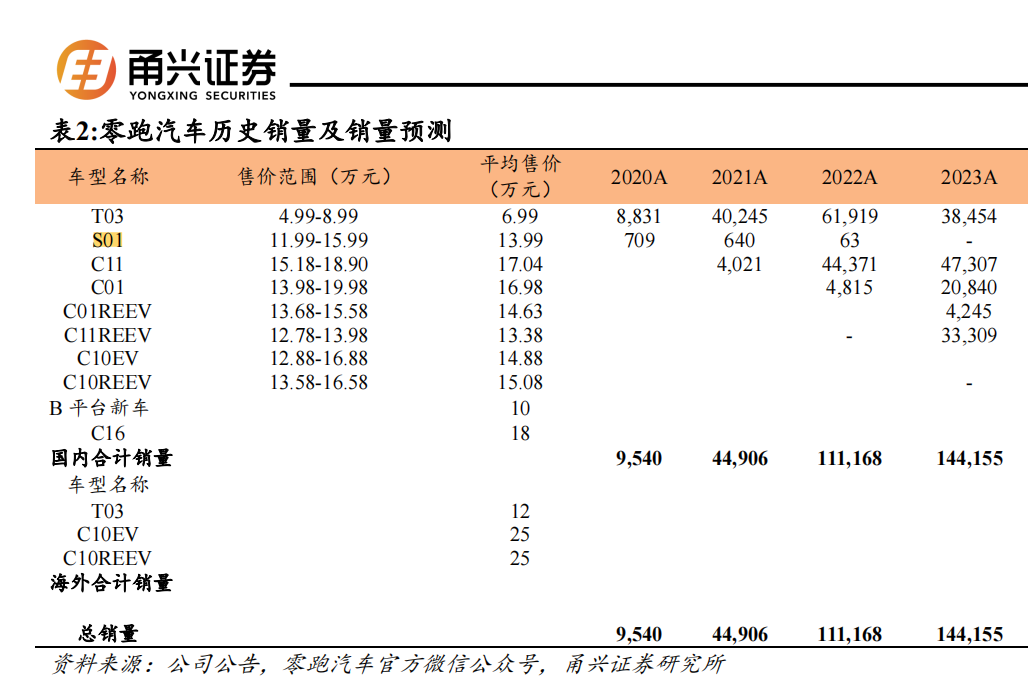
From 2020 to 2024, Leapmotor's sales volumes surged from 9,540 to 293,724 units, with a cumulative increase of over 280,000 units and a growth rate of nearly 30 times, including a 104% increase last year.
Leapmotor's keen market observation and excellent product capabilities made its models since 2020 consumer favorites and market darlings.
In 2017, Leapmotor began constructing its Jinhua factory and delivered the smart electric sports car S01 in July 2019, priced at RMB 119,900-159,900. However, market response was mediocre, with sales volumes of 709, 640, and 63 units from 2020 to 2022, respectively, and is currently off the official website.
In May 2020, the company launched the pure electric mini car T03, priced at RMB 49,900-89,900. Upon release, it was a market hit, selling 8,831, 40,425, 61,919, and 38,454 units over the next four years.
In May 2021, the mid-size pure electric SUV C11, priced at RMB 151,800-189,000, received positive market feedback, selling 4,021, 44,371, and 47,307 units in the following three years.
The success of these two models bolstered Leapmotor's confidence to go public. Recognizing the potential of C-segment models, the company launched the large electric sedan C01 in May 2022, priced at RMB 139,800-199,800, selling 4,815 and 20,840 units in the subsequent two years.
In 2024, Leapmotor introduced the B-segment SUV C10 and the C-segment six-seat SUV C16, both available in pure electric and extended-range versions. According to China Passenger Car Association data, sales volumes within the year were 72,529 and 43,528 units, respectively (narrow-sense passenger car wholesale sales data).
Additionally, the company updated the C11 and C01, both adding extended-range versions.
Leapmotor plans to launch multiple models in 2025, including the SUV B10 and the sedan B01. Moreover, B05 will commence pre-sales, and the D-series models will be unveiled by year-end. Will these new models maintain excellent performance? Only time will tell.
Direct Sales Combined with Dealerships Aid Expansion. Leapmotor's sales success is intertwined with its sales model. Unlike other new automakers emulating Tesla's direct sales model, Leapmotor opted for a "direct sales + dealership" model. This strategy not only reduces expansion costs but also better reaches consumers, crucial for the company's catch-up and profitability.
From 2020 to the first half of 2024, Leapmotor had 95, 291, 582, 560, and 802 stores (sales + service), covering 187 cities. In 2023, the company introduced an innovative "1+N" model, where one regional center store with 4S service functions supports several "N" showroom channel models within the region.
More importantly, Leapmotor strategically partnered with the Stellantis Group to establish Leapmotor International, leveraging the latter's distribution channels to accelerate globalization. By last October, Leapmotor International had opened 339 stores in Europe, signaling great potential in overseas markets.
Why Leapmotor
With increasing car sales, Leapmotor's business scale expanded rapidly, and operating revenue hit new highs. From 2020 to 2023, operating revenue was RMB 631 million, RMB 3.123 billion, RMB 12.385 billion, and RMB 16.747 billion, respectively, with a cumulative increase of over RMB 16.1 billion and a growth rate of 25.5 times. In 2023, it increased by 35% year-on-year.
Simultaneously, the company's losses followed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing, with net profits attributable to shareholders of the parent company losing RMB 1.1 billion, RMB 2.846 billion, RMB 5.109 billion, and RMB 4.216 billion, respectively. In 2023, losses narrowed.
In the current profit warning, Leapmotor estimated 2024 operating revenue to be not less than RMB 30.5 billion, a year-on-year increase of not less than 80%. Sustaining such growth amidst yearly scale expansion is commendable.
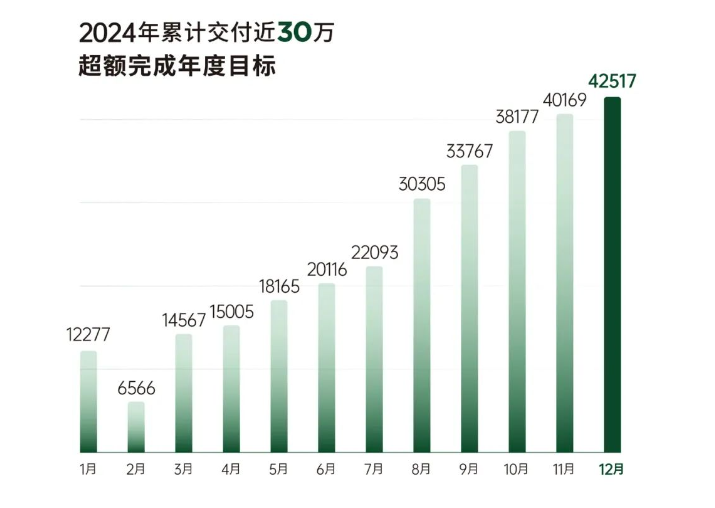
Leapmotor achieved a positive profit in Q4 2024 due to continuous sales growth, optimized product mix (C-series models accounting for over 77%), effective cost control, and operational efficiency.
Since February 2024, monthly sales volumes have repeatedly set new highs, with an average of over 40,000 units in Q4, crucial for the company's quarterly profitability.
With product mix optimization, Leapmotor's gross profit margin improved annually, from -50.63% in 2020 to 0.48% in 2023. Last year's first three quarters showed a 4.8% gross profit margin, with Q2 and Q3 at 2.8% and 8.1%, respectively.
However, Leapmotor also has shortcomings.
R&D Investment Continues to Increase but Still Lags Behind Peers. High R&D expenses are a significant loss factor for new automakers. Leapmotor's R&D expenses from 2020 to the first half of 2024 were RMB 289 million, RMB 740 million, RMB 1.411 billion, RMB 1.92 billion, and RMB 1.221 billion, respectively. The first half of last year saw a 48.4% year-on-year increase, with an R&D expense ratio of 13.81%.
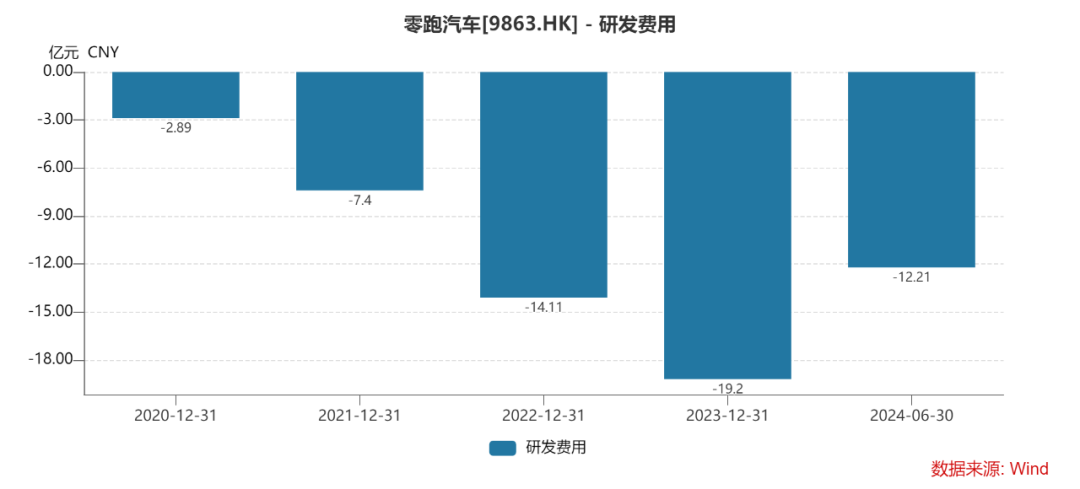
Nonetheless, Leapmotor's R&D investment significantly lags behind NIO, Xpeng, and Li Auto. In the first half of 2024, these three automakers' R&D expenses were RMB 6.076 billion, RMB 6.083 billion, and RMB 2.817 billion, respectively, all surpassing Leapmotor.
Regarding the R&D expense ratio, the ratios of NIO, Xpeng, and Li Auto were 10.6%, 22.24%, and 19.22%, respectively. Leapmotor's ratio was only slightly higher than Li Auto but behind the other two.
In terms of R&D personnel, NIO, Xpeng (2023), and Li Auto had 5,373, 11,222, and 5,619 personnel, respectively, while Leapmotor had 3,823, trailing behind.
According to Gao Gong Intelligent Automobile, from January to November 2024, Leapmotor delivered a cumulative total of 37,000 high-level intelligent driving models equipped with lidar, accounting for only 16.01% of the brand's total new vehicle deliveries during the same period.
With both R&D scale and personnel falling short of its peers, it's evident that Leapmotor needs to make breakthroughs in this area. After all, in the long run, R&D is the key and core competitiveness in the smart car race.
Of course, the premise for all this is survival!
Li Auto was the first new automaker to achieve profitability, and now Leapmotor has also reached the goal of single-quarter profitability. A common thread between them is their relatively low R&D expense ratio. Perhaps automakers yet to achieve profitability can take this as a reference and strengthen cost control.
Which automaker will be the next to achieve profitability?
(Quick analysis - original work, please do not reprint without permission! PS: If the manuscript infringes or the data is incorrect, please contact us for correction in a timely manner)








