Exclusive | Xiaomi’s 2nd-Gen AI Glasses May Feature a 50MP Camera
![]() 02/06 2026
02/06 2026
![]() 508
508
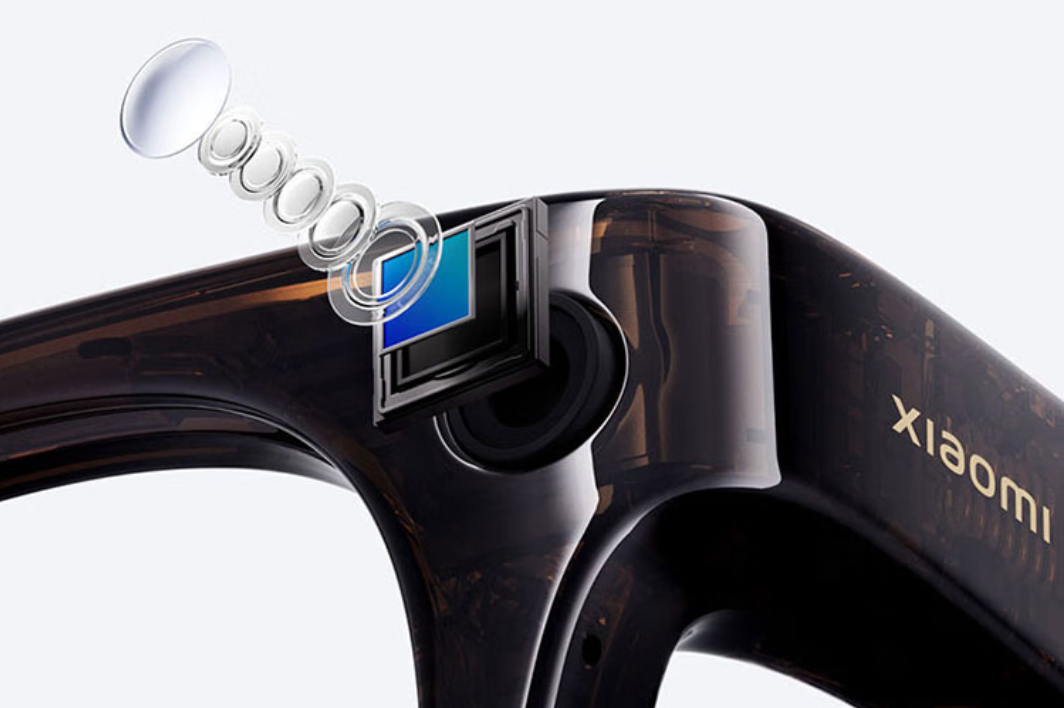

According to XR Vision Studio, the upcoming 2nd generation of Xiaomi AI Glasses may abandon the Sony IMX681 image sensor, a popular choice in many AI glasses, in favor of a 50MP camera equipped with an OmniVision CMOS sensor. This upgrade is aimed at significantly boosting the glasses' photographic capabilities. It is speculated that the OmniVision OV50M image sensor will be used. According to OmniVision’s official website, this sensor, launched in August 2024, incorporates cutting-edge technologies from smartphone front, wide-angle, ultra-wide-angle, and telephoto cameras. It is a versatile 0.61-micron pixel size CMOS image sensor capable of 50MP output and boasts features like single-exposure dual analog gain (DAG) video HDR and a low-power always-on mode. OmniVision states: "The OV50M40 supports staggered HDR and DAG HDR technologies. Staggered HDR expands the dynamic range and enhances the quality of both video and still image capture; the built-in DAG provides single-exposure HDR support, minimizing motion artifacts in challenging lighting conditions." HDR, or High Dynamic Range, is known as "高动态范围成像" (High Dynamic Range Imaging) in Chinese. Ordinary image sensors have a limited dynamic range, leading to two common issues in scenes with extreme contrasts (such as shooting people against backlight, shooting indoors by a window, or shooting sunsets): bright areas (sky, lights) are overexposed and lack detail; dark areas (shadows, indoor corners) are excessively dark and unclear.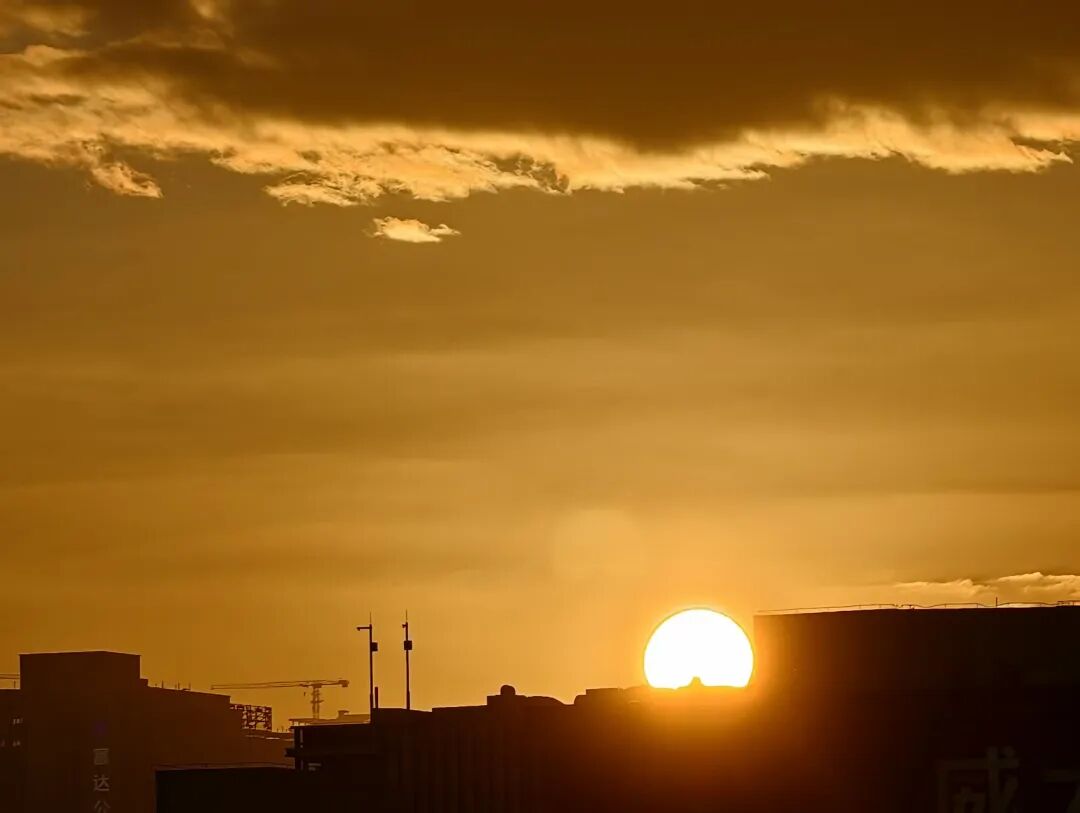 
▲ The image above illustrates overexposure in bright areas and a lack of detail in dark areas.
Some products utilizing the Sony IMX681, such as the Meta Rayban AI Smart Glasses and Thunderbird V3 AI Smart Glasses, also support HDR effects, typically achieved through software and algorithmic "multi-frame fusion." In simple terms, "multi-frame fusion HDR" means that during shooting, the device continuously captures multiple frames with varying exposures. Leveraging the sensor's rapid readout speed and the processor's robust computing power, it selects the optimal bright and dark details from each frame and combines them algorithmically to produce the final HDR image. Currently, if the HDR algorithm is integrated into the glasses' AR1 chip, it increases power consumption on the glasses' end. If processed by the App, it requires transmitting the "multi-frame" data to the smartphone for processing.

Staggered HDR involves an internal sensor process where adjacent pixels alternate between long and short exposure times to capture information within a single frame, achieving "short exposure for bright areas and long exposure for dark areas," and then merging them into a high dynamic range image. Its advantage lies in significantly expanding the dynamic range of still images and regular videos, providing more comprehensive details in high-contrast scenes. It is ideal for backlit portraits, sunrise/sunset landscapes, mixed indoor-outdoor lighting, and slow-motion videos.
DAG HDR (Dual Analog Gain HDR) involves a single exposure but employs two sets of analog gains (high and low) simultaneously when reading the signal, directly outputting a high dynamic range image in a single frame without the need for capturing and merging multiple frames as in traditional multi-frame HDR. This method thoroughly reduces motion artifacts/ghosting (multi-frame HDR tends to blur moving objects) and can still capture clear dynamic images under harsh lighting conditions such as strong light or backlight, making it suitable for real-time shooting in high-frame-rate 4K@60fps HDR videos, sports photography, and fast-moving scenes.
The OV50M40 image sensor achieves HDR effects at the hardware level. For shooting photos, HDR can be implemented through hardware or algorithms, but for shooting videos, algorithms have limited capabilities, and hardware implementation is primarily relied upon. 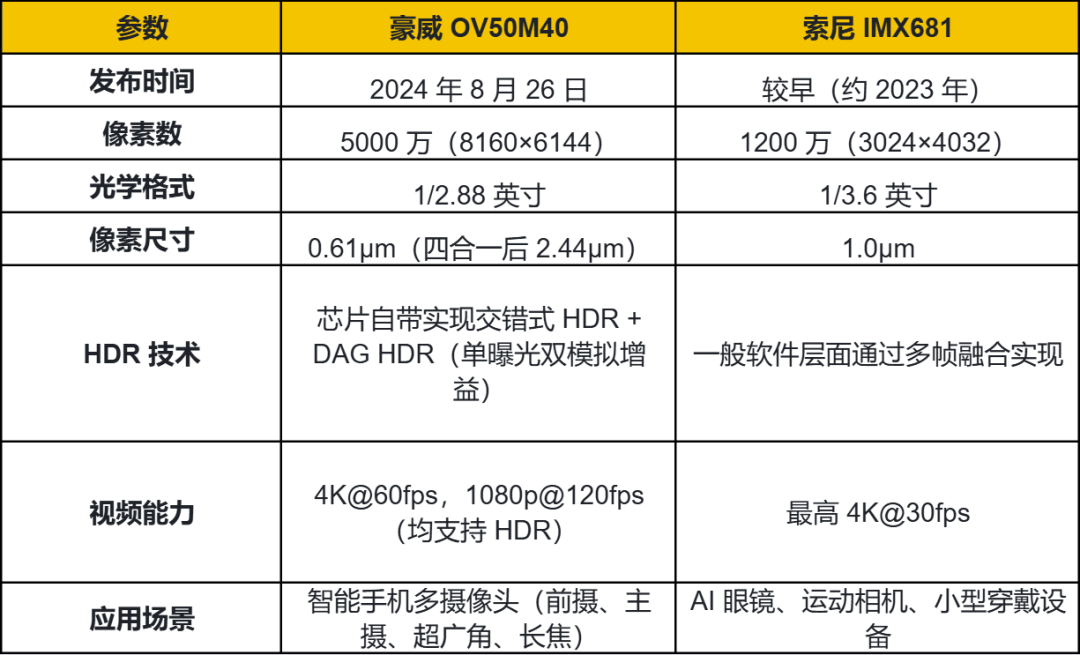
The OmniVision OV50M40 features a 1/2.88-inch sensor size, with a photosensitive area 56% larger than that of the Sony IMX681. A larger physical photosensitive area of the sensor forms the hardware foundation for imaging and determines a higher upper limit for underlying image quality, but it also results in a larger camera module size, which may impact the appearance of AI glasses and increase power consumption. Additionally, the 2nd generation of Xiaomi AI Glasses will offer more model options for users. Note: Imaging expert Li Long also contributed to this article.



