Why Has Qingdao Emerged as the Global Pioneer for Autonomous Vehicles?
![]() 11/21 2025
11/21 2025
![]() 498
498
Highly debated high-level autonomous driving has, for the first time, achieved a commercial closed loop within the express logistics sector.
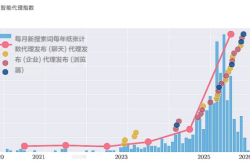
Recently, China Post unveiled the world's largest centralized procurement initiative for autonomous freight vehicles, with plans to acquire 7,000 autonomous vehicles to construct the globe's most extensive autonomous freight network.
The 'national team' placing substantial orders will undoubtedly expedite the commercialization of autonomous vehicles and broaden the industry's scope.
Capital is also keeping a close eye on the autonomous delivery vehicle sector, with its financing enthusiasm even eclipsing that of 'intelligent driving democratization.'
Leading autonomous delivery vehicle firms such as Neolix, White Rhino, and 9Z Robotics have collectively raised approximately 8.6 billion yuan in funding this year.
Among them, Neolix has successfully secured a 1 billion yuan Series C+ round and a $600 million Series D round this year. Presently, Neolix has deployed over 7,500 autonomous vehicles across more than 280 cities and regions in China, with cumulative deliveries of over 10,000 L4 autonomous vehicles as of September, marking it as the world's first L4 fleet to surpass 10,000 units.
Notably, Qingdao stands out as a pivotal city for Neolix, a premier domestic autonomous vehicle enterprise.
Currently, Neolix has stationed over 1,200 autonomous vehicles in Qingdao, directly propelling the city to overtake Waymo's headquarters in San Francisco and claim the title of the city with the highest number of autonomous vehicles globally.
Shenzhen, a frontrunner in domestic deployment, witnessed its total operational vehicle count rise to 851 by the end of October, with 484 being logistics autonomous vehicles.
It's crucial to acknowledge that autonomous delivery vehicles boast significant technological sophistication, featuring L4 autonomous driving capabilities and stringent road network operation requirements.
The sudden large-scale emergence of such a novel phenomenon in Qingdao is largely attributed to a more 'pragmatic' decision after the city missed the prime opportunity in the intelligent connected new energy vehicle sector.
Moreover, influenced by Xiaomi's autonomous driving mishaps this year, domestic regulations for autonomous driving on roads have become increasingly stringent. However, L4 autonomous driving technology for 'cargo-carrying' scenarios has matured, emerging as the most viable application scenario to achieve a commercial closed loop for autonomous driving technology.
Recognizing the commercialization potential of autonomous vehicles, Qingdao proactively granted road access, permitting autonomous vehicles on roads and offering policy support for large-scale applications.
In fact, as early as March last year, Qingdao issued the 'Implementation Rules for Road Testing and Commercial Demonstration Management of Low-Speed Autonomous Vehicles in Qingdao (Trial),' explicitly allowing low-speed autonomous vehicles on roads, signaling Qingdao's willingness to grant road access to autonomous delivery vehicles.
On August 1 last year, Qingdao's autonomous express delivery vehicles officially commenced bulk operations, with 40 vehicles initially deployed by express companies such as SF Express and YTO Express. In July this year, Didi Freight and Neolix launched a pilot program for autonomous delivery vehicle services in Qingdao. As of now, Qingdao has achieved 'two full coverages' of autonomous delivery vehicles for county-level administrative regions and major express delivery brands.
In the long term, autonomous vehicles can indeed represent Qingdao's best opportunity to 'overtake on a curve' in the automotive manufacturing sector.
For Qingdao, future planning around autonomous vehicles necessitates further efforts in scenario development, extending to the entire market of autonomous commercial and special-purpose vehicles such as autonomous buses and sanitation vehicles.
Simultaneously, on the industrial front, it requires increased investment in the full industrial chain, encompassing upstream key technologies like LiDAR, in-vehicle chips, cameras, and vehicle manufacturing.
In this endeavor, leveraging the investment resources previously made by Qingdao's state-owned assets in the intelligent driving and intelligent connected vehicle sectors is a major focus.
Numerous intelligent driving enterprises have ventured into this sector this year. For instance, leading automotive electronics companies such as Desay SV and Minieye have recently launched autonomous logistics vehicle brands, with Minieye being an investment target of Qingdao's state-owned assets.
Furthermore, actively meeting the needs of enterprises to expand globally, such as Neolix and 9Z Robotics planning overseas markets, Qingdao's open advantages precisely align with the requirements of many enterprises for international expansion.
Delving deeper, utilizing the diverse data generated from the expansion of autonomous urban delivery scenarios and mining its value to lay the foundation for the construction and operation of a city-wide vehicle-road-cloud integration system also requires Qingdao to focus on strategic planning.
(Welcome to follow the Qingji Think Tank video account and participate in the discussion on 'Qingdao's Large-Scale Deployment of Autonomous Vehicles')
1
The rapid development of autonomous delivery vehicles is underpinned by the broader context of cost reduction and efficiency enhancement in the logistics industry, coupled with robust national support for autonomous vehicle applications.
By the end of 2024, the State Council issued the 'Action Plan for Effectively Reducing Logistics Costs Across Society,' explicitly advocating for the promotion of autonomous vehicle technology. Subsequently, in May this year, eight departments including the Ministry of Commerce jointly issued a document, reiterating the promotion of intelligent equipment such as autonomous delivery vehicles to reduce logistics costs and enhance supply chain efficiency.
From practical results, autonomous delivery vehicles have indeed yielded immediate benefits in cost reduction and efficiency improvement for the logistics industry. In the express delivery sector, it is estimated that the transportation cost per parcel for manned vehicles is 0.16 yuan, which can be reduced to 0.05 yuan using autonomous vehicles, representing a 69% cost reduction potential.
Beyond the express delivery industry, as giants engage in instant retail battles, demanding higher delivery efficiency, the demand for autonomous vehicles in urban delivery is also surging. Alibaba, Meituan, and JD.com are all developing their own autonomous vehicles.
At the urban application level, such as in Qingdao this year during the 'Double 11' period, thousands of autonomous vehicles were on the roads, contributing to a 20% year-on-year increase in overall transportation volume.
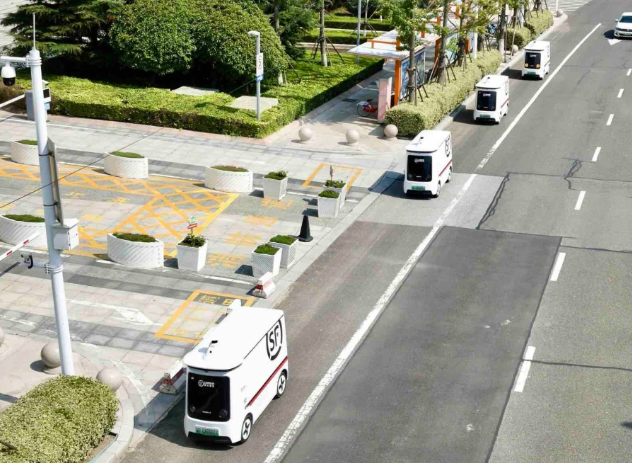

Overall, the autonomous delivery vehicle sector has witnessed a landscape dominated by autonomous vehicle startups such as Neolix, 9Z Robotics, and White Rhino, with e-commerce and logistics giants like Meituan, JD.com, Alibaba, and SF Express, as well as intelligent driving enterprises like Desay SV and Minieye, vying to enter the market.
With the explosion in market demand, Neolix, 9Z Robotics, and White Rhino have experienced a comprehensive surge in orders this year. For instance, Neolix anticipates its annual delivery volume to exceed 15,000 units, tenfold last year's volume. 9Z Robotics emerged as the largest bid winner for China Post's 7,000 autonomous vehicles, undertaking at least 50% of China Post's core transportation capacity.
While orders are surging, corporate financing scales are also rapidly expanding. For instance, Neolix completed a 1 billion yuan Series C+ round and a over $600 million Series D round this year, White Rhino secured a 500 million yuan Series B round, and 9Z Robotics raised $400 million in a Series B round.
Among these, many investors are downstream partners of the companies.
For example, Neolix received investment from Didi in August, with many analysts suggesting this will accelerate Neolix's cooperation with Didi Freight to expand national autonomous delivery services.
White Rhino has received three investments from SF Express since August last year. It is reported that the daily active operational fleet of autonomous vehicles within the SF Express system has reached several hundred units and continues to grow rapidly.
2
In contrast to the large-scale deployment of autonomous delivery vehicles, the opening of road rights and license issuance in various cities still face uncertainties.
According to industry insiders, the primary obstacle currently confronting the autonomous delivery industry is the absence of unified national access thresholds and road rights management rules. This has led to divergent development of autonomous delivery across cities.
For instance, Shenzhen, a leader in road rights opening, had opened 1,257 road rights routes totaling 3,581 kilometers for functional autonomous vehicles as of September, with 19 new routes and 396 kilometers added in September alone.
With the accelerated deployment of autonomous vehicles, Shenzhen completed 1.02 million autonomous deliveries in September, including 845,000 express deliveries and 175,000 fresh produce deliveries, generating approximately 8.7 million yuan in commercial value, a 14.5% month-on-month increase.
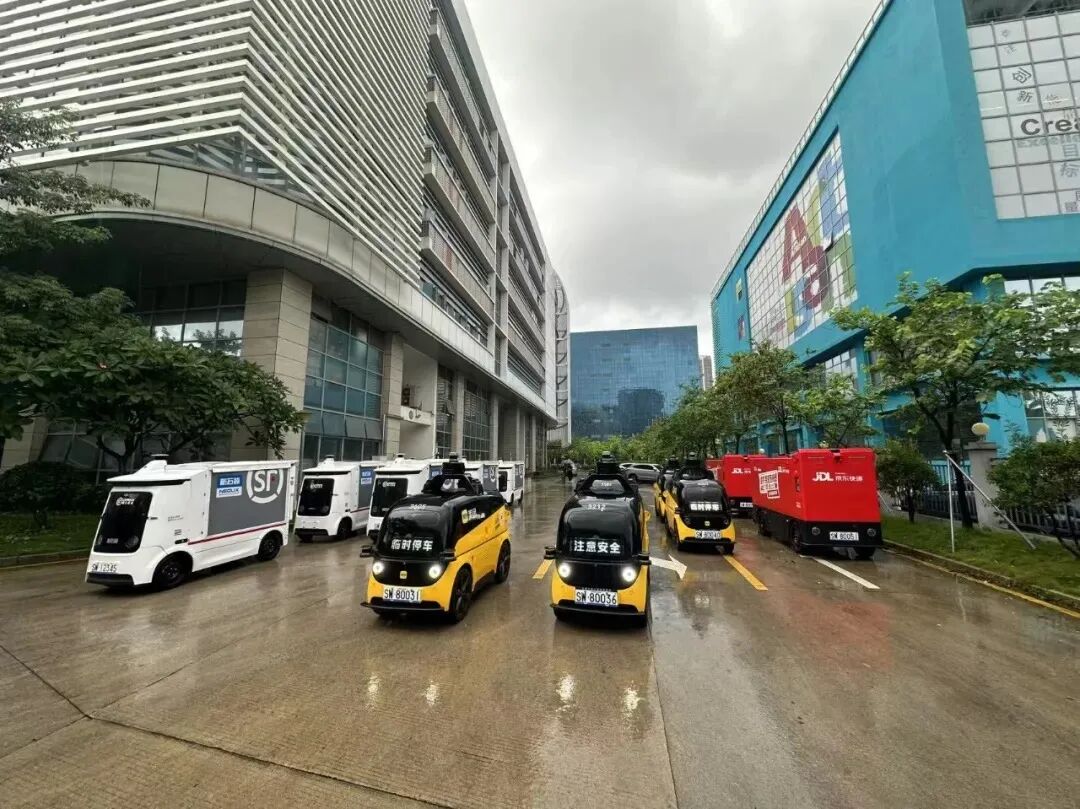

Nationwide, as of the first half of the year, 103 cities have opened road rights for autonomous delivery vehicles, covering over 80% of major logistics node cities. However, since most autonomous delivery vehicles currently on the roads are still in the testing phase, the number of licenses issued by each city remains limited.
In reality, the 'mismatch' between industry development needs and road rights and license restrictions has also led to management challenges such as illegal road use by autonomous vehicles.
According to a report by Qingdao Daily in August this year, the number of autonomous express delivery vehicles on Qingdao's roads far exceeds the number of vehicles with test codes. 'Some express companies, in a rush to capture the autonomous delivery market, have deployed vehicles without test codes, which is illegal,' the report stated.
However, it cannot be denied that due to the gap between the technological maturity of autonomous vehicles and their adaptability to traffic order, common issues such as running red lights, driving against traffic, crossing lines, and low-speed driving exacerbating traffic congestion persist.
This places higher demands on urban standardized management.
In terms of specific management, Shenzhen proposed the 'Autonomous Vehicle 2.0' development plan this year, pioneering the standardized, large-scale, commercialized, and connected development of autonomous logistics nationwide.
For example, Shenzhen is exploring a tiered management system that matches vehicle performance, algorithm capabilities, and road traffic rules to balance industrial development with regulatory compliance.
Regarding road rights opening in urban central areas, such as the Futian District Lotus Hill Central Area, Shenzhen's relevant departments conducted comprehensive and strict assessments of route operational conditions and traffic impacts, while requiring operational vehicles to connect to government platforms for dynamic data supervision and scheduling.
Notably, to support the operations of autonomous vehicle companies, Shenzhen innovatively proposed a 'bus + logistics + autonomous vehicle' integration model. Leveraging the advantages of Shenzhen Bus Group's depot resources, network management system, and personnel system, it provides one-stop service solutions for autonomous vehicle operators, integrating vehicle safe parking, efficient charging and battery swapping, and localized operation and maintenance support through 'grid-based depot management.'

Hangzhou has enacted legislation for autonomous vehicles, becoming the first city outside special economic zones nationwide to explicitly define the specific procedures for autonomous vehicles to go on roads through local legislation. It is also the first city to legislate for low-speed autonomous vehicles.
It is reported that besides the regulatory framework for autonomous vehicles' road operations, the 'Regulations' also clarify the construction of supporting infrastructure for autonomous vehicles, stating that 'the inclusion of vehicle-road coordination infrastructure in the construction of new, reconstructed, and expanded road projects should be designed, constructed, accepted, and put into use simultaneously with the main road project.'
3
Besides market demand and policy support, another key driver behind the explosive growth of the autonomous delivery vehicle market is the maturation of core technologies and cost reductions, propelling the industry towards industrialization and large-scale development.
One example is that the price of an autonomous delivery vehicle has dropped from 200,000 yuan to less than 20,000 yuan.
Based on this, while ramping up scenario applications, Qingdao should also focus on the industrial front, laying out the full industrial chain of autonomous delivery vehicles, and adopting a 'unified chessboard' approach to expand the entire market of autonomous commercial and special-purpose vehicles, covering segments such as autonomous buses, sanitation vehicles, and inspection vehicles.
Currently, relying on its commercial vehicle industry foundation, Qingdao holds advantages in the autonomous vehicle manufacturing sector but lacks布局 (layout) in upstream areas such as LiDAR, cameras, and in-vehicle chips.
Looking further, deepening cooperation with Neolix could be a crucial breakthrough for Qingdao to layout the full industrial chain of autonomous vehicles.
This is because Neolix has consistently adopted a self-built factory model for vehicle manufacturing, offering stronger integration and agglomeration effects for the full industrial chain.

Neolix Factory
In the LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) industry, Neolix is strengthening its collaboration with Hesai Technology, a globally renowned enterprise specializing in LiDAR research and manufacturing. Hesai's products are extensively deployed in both passenger and commercial vehicles, supporting advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Leveraging self-developed chips that enable integrated, chip-based designs and facilitating large-scale production, Hesai Technology is driving the localization of LiDAR technology and bolstering the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles.
On the other hand, Neolix is proactively charting a course for global expansion, and Qingdao's open economic environment and strategic advantages perfectly complement Neolix's international growth ambitions.
It has been learned that Neolix has earmarked the Middle East as its initial springboard for international expansion. The company has already secured the world's first officially issued license for autonomous vehicles to operate on public roads in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Given that Neolix's latest Series D funding round was led by UAE-based Leystone Capital, this development is poised to significantly expedite Neolix's international expansion endeavors.