Changan Energy Storage Research Institute: Global clean energy investment will reach US$2 trillion in 2024
![]() 06/14 2024
06/14 2024
![]() 614
614
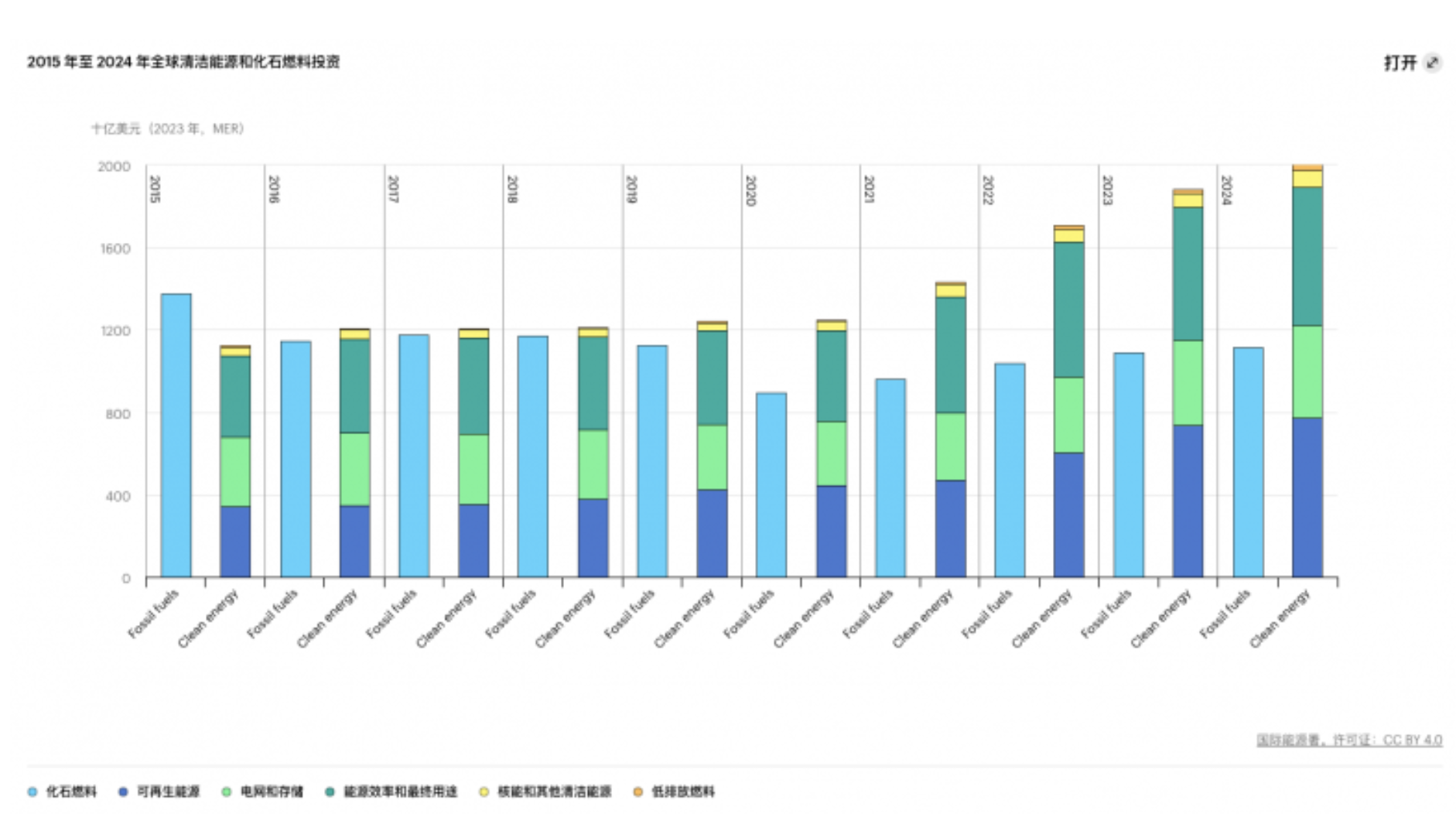
Recently, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released the "World Energy Investment 2024" report, which predicts that global energy investment will exceed US$3 trillion for the first time in 2024, of which US$2 trillion will be used for clean energy technologies and infrastructure. Since 2020, clean energy investment has accelerated, and expenditures on renewable energy, power grids, and energy storage have now surpassed total expenditures on oil, natural gas, and coal.
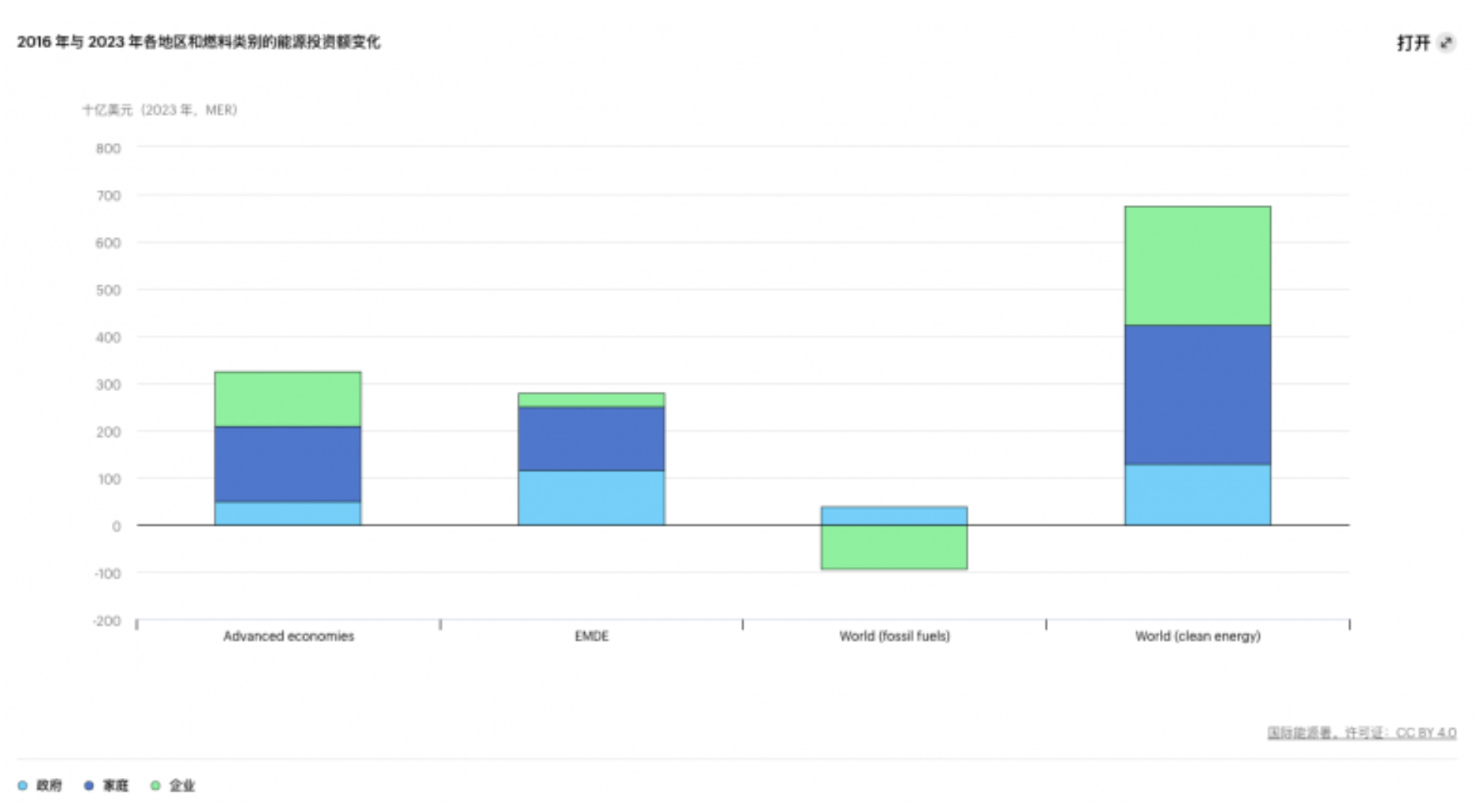
The report provides a new analysis of investment sources and financing sources. Overall, most investments in the energy sector are made by companies, which account for the largest share of investments in both fossil fuels and clean energy. However, there are significant differences among countries: half of the energy investments in emerging markets and developing economies are made by the government or state-owned enterprises, while only 15% in developed economies. State-owned enterprise investments mainly come from national oil companies, especially in the Middle East and Asia, where these companies' investments have increased significantly in recent years.
The proportion of private households in energy investment has increased from 9% in 2015 to 18% currently. This is mainly due to the growth of rooftop solar installations, building energy efficiency investments, and electric vehicle purchases. Currently, these investments mainly come from wealthier households, so it is crucial to formulate good policies to ensure that everyone has access to clean energy technologies. Data shows that since 2016, household investment in clean energy expenditures has contributed more than 40%, making it the largest contributor.
China is undoubtedly the largest contributor to global clean energy investment. The IEA pointed out that by the end of 2024, China will invest US$675 billion in the global clean energy sector, accounting for the largest share, mainly due to strong domestic demand for solar energy, lithium batteries, and electric vehicles. Europe and the United States will invest US$370 billion and US$315 billion in clean energy, ranking second and third, respectively. These three major economies account for more than two-thirds of global clean energy investment, highlighting severe imbalances and deficiencies in global clean energy investment. Opportunities and challenges coexist in the future energy market.
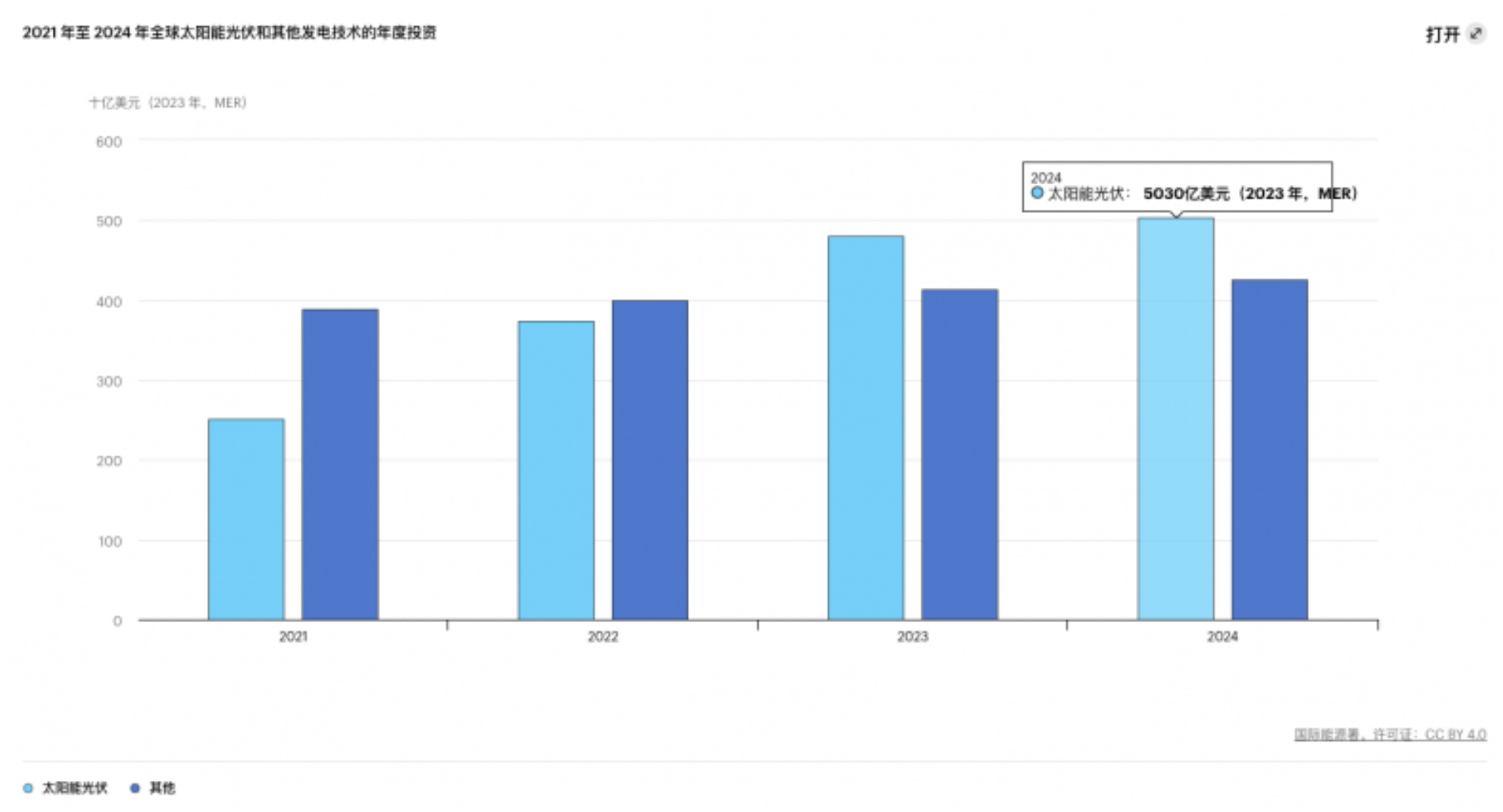
The report points out that investment in solar photovoltaic (PV) technology in the power industry will exceed US$500 billion by 2024, surpassing the sum of all other power generation sources. Although growth may slow slightly due to declining PV module prices, solar energy remains at the core of the power industry transformation. Every dollar invested in wind energy and solar photovoltaics in 2023 produced 2.5 times more energy output than investments in the same technologies a decade ago.
As the cost of photovoltaic power generation has dropped significantly, the power grid has become a bottleneck in the energy transition. Global grid investment has stagnated at around US$300 billion annually since 2015 and is expected to reach US$400 billion by 2024, thanks to new policies and funds in Europe, the United States, China, and parts of Latin America. Developed economies and China account for 80% of global grid expenditures.
Changan Energy Storage Research Institute is fully funded by Changan Green Power Technology Co., Ltd. and jointly established with several professors and scientists from Xi'an Jiaotong University's National Energy Storage Research Platform. As a new energy storage research platform, the institute focuses on cutting-edge technology research and market insights in the field of energy storage, committed to promoting the transition from theory to practical application of industry-university-research collaboration.
Data source: IEA official website








