Huang Renxun Unveils OpenAI and AMD's Recurring Deceptive Tactics
![]() 10/09 2025
10/09 2025
![]() 509
509

Source: Byte
The 'closed-loop AI economy' in Silicon Valley is escalating in intensity.
On October 6th, OpenAI and AMD announced a groundbreaking collaboration in AI infrastructure, aiming to establish a long-term strategic synergy through a deeply intertwined 'technology + equity' model.
Specifically, OpenAI plans to deploy a staggering 6 billion watts of AMD GPU computing power over the next few years. To further solidify their strategic alignment, AMD will directly issue up to 160 million ordinary shares to OpenAI, enabling OpenAI to hold up to approximately 10% of AMD's equity.
AMD's Chairman and CEO, Dr. Lisa Su, expressed enthusiasm: 'We are thrilled to collaborate with OpenAI to enable large-scale AI computing. This partnership leverages the strengths of both AMD and OpenAI, creating a true win-win scenario and propelling the development of the entire AI ecosystem.'
Over the past two months, Silicon Valley has orchestrated a series of impressive capital maneuvers, binding together AI ecosystem giants such as OpenAI, NVIDIA, Intel, Oracle, and Arm.
With OpenAI and AMD's equity-for-computing-power deal, the 'closed-loop AI economy' has become firmly entrenched. From OpenAI's current trajectory, there appears to be no sign of slowing down in the near future.
It's astonishing to witness that in the AI arena, brimming with creativity and intellectual strategic maneuvering, Silicon Valley's elite have concocted a new tactic: 'AI conglomerates'.
01
AMD Finally Enters the Arena
As a leader in large language models, OpenAI is clearly not content to be constrained by computing power limitations.
On September 22nd, NVIDIA announced a staggering $100 billion deal with OpenAI, whereby NVIDIA will invest in OpenAI and construct a 10 billion-watt AI data center for its use.
Now, OpenAI has partnered with AMD to build computing infrastructure. While AMD's 6 billion watts of computing power may seem modest compared to NVIDIA's 10 billion watts, it significantly reduces OpenAI's reliance on NVIDIA.
Media calculations reveal that a single GPU server can consume several kilowatts, with a 100 MW data center consuming 100,000 kWh per hour. A total capacity of 7 GW (7 billion watts) implies 7 million kWh per hour, or 61 billion kWh annually—equivalent to half a year's output from the Three Gorges Dam, a colossal feat.
With NVIDIA on one side and AMD on the other, OpenAI's strategy does not come as a surprise to outsiders, given its prior 'gentleman's agreement' with AMD.
On June 13th, at the highly anticipated Advancing AI 2025 conference, AMD and OpenAI announced a strategic partnership. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman personally endorsed AMD's new chips, explicitly stating that OpenAI would utilize AMD's AI chips in the future.
Thus, AMD's absence during OpenAI's recent public demands for computing power surprised onlookers.
While AMD still trails behind NVIDIA, its momentum is undeniable. According to financial reports, AMD's revenue reached $7.685 billion in Q2 2025, up 32% year-on-year from $5.835 billion and 3% sequentially from $7.438 billion.
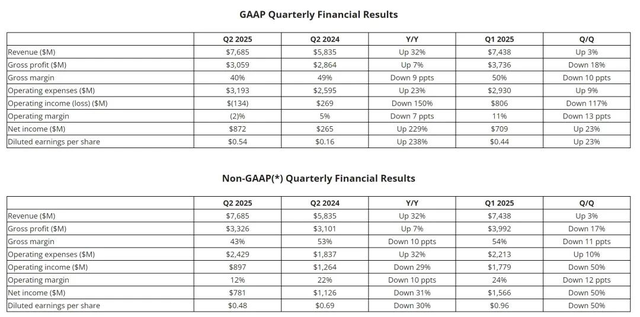
Screenshot from company financial report
For AMD, deepening collaboration with OpenAI represents a critical step in leveraging external forces to break through and expand market share in high-performance computing and AI—a strategic high ground. The star product at the time, the Instinct MI400/MI350 series, showcased potential to rival NVIDIA's B200 in hardware specifications, thanks to TSMC's advanced processes and AMD's design optimizations.
This collaboration with OpenAI will utilize GPUs from the Instinct MI400 series. By partnering with a heavyweight like OpenAI, AMD not only directly boosts chip sales but also gains a powerful endorsement for the technical prowess and commercial viability of its Instinct MI400 series, significantly enhancing AMD's brand influence and market confidence in high-performance computing and AI.
02
Bootstrapping Growth Through Strategic Alliances
OpenAI's collaboration models with two chip giants highlight its shrewd transactional design. The core of these arrangements lies in leveraging OpenAI's massive computing power demands as a bargaining chip to secure deep-binding partnerships and financial support from chip suppliers.
Analysts widely view NVIDIA's $100 billion collaboration with OpenAI as suspiciously circular, with NVIDIA providing Altman $100 billion, only for OpenAI to spend it on NVIDIA chips. Combined with OpenAI's agreement with Oracle in the Stargate project, a bubble-like scenario of 'bootstrapping growth' naturally comes to mind.
Also last month, NVIDIA and Intel announced a partnership to jointly develop multiple generations of custom data center and PC products, accelerating applications and workloads across hyperscale, enterprise, and consumer markets. NVIDIA will invest $5 billion in Intel ordinary shares at $23.28 per share.

Screenshot from Intel China's official website
In essence, Silicon Valley is forming a 'closed-loop AI economy' where capital, equity, and computing power circulate among a few leading companies: OpenAI anchors massive computing demand, while NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel supply chips, and Oracle helps build data centers.
Current secondary market feedback strongly favors this 'closed-loop AI economy' model, with nearly every related move boosting corresponding stock prices. Even lagging players like Intel have experienced sharp stock price surges.
However, analysts worry that if any link in this system fails, the entire ecosystem could face severe pressure.
In this deal, AMD agreed to provide OpenAI with a substantial number of stock warrants, totaling up to 10% of the company's shares. These warrants will vest gradually over several years based on factors like stock price appreciation. In exchange, OpenAI will use and assist in developing AMD's next-generation AI graphics processor chips.
UBS analyst Timothy Arcuri noted in a research report that if AMD's stock price reaches specific milestones, OpenAI's equity stake could be worth up to $100 billion—enough to cover most of its GPU procurement bills.
However, NVIDIA founder Jensen Huang offered a different perspective, stating that NVIDIA's investment in OpenAI differs fundamentally from AMD's partnership because NVIDIA's model allows direct product sales to ChatGPT's developer (OpenAI).
Huang's assertion holds merit, as AMD's promised Instinct MI400 series chips have not yet fully entered the market and remain 'futures.'
Thus, the pressure falls entirely on AMD. If the Instinct MI400 series underperforms, the entire ecosystem could collapse.
03
Lisa Su's New Challenge
Technically grounded Lisa Su remains undeterred by technical challenges.
In 2014, when Su took over AMD, the company was burdened with $2.2 billion in debt, with its stock price languishing below $2, struggling in Intel's shadow. Her doctoral advisor questioned her decision: 'Lisa, are you serious? Taking on Intel?'
At the time, AMD had been overshadowed by Intel for over a decade. Critics remarked, 'This isn't firefighting—it's jumping into a fire pit.'
Su's response reflected a technologist's confidence: 'Why not?'
Her subsequent tenure became Silicon Valley legend. She announced a 7% global layoff, raised over $600 million through technology licensing and equity monetization, and bet everything on the revolutionary Zen architecture.
In 2017, the Zen architecture debuted, boosting performance by 52%. AMD survived.
In June 2017, AMD officially launched the EPYC processor, re-entering the data center processor market after years of absence.
Meanwhile, rival Intel lingered in 'incrementalism,' allowing AMD to dominate the market.
After technological iterations, AMD EPYC quickly penetrated the Intel-dominated data center market, winning support from giants like Amazon, Microsoft, and Meta. In 2018, AMD launched a 7nm EPYC processor, leveraging TSMC's manufacturing capabilities, while Intel only achieved 7nm chip mass production in 2022.
This data center success emboldened Su to venture into AI, where key buyers include Silicon Valley giants like Amazon, Microsoft, and Meta.
At CES 2023 in Las Vegas, Su declared AI AMD's top strategic priority: 'We're actively collaborating with all customers to bring joint solutions to market. The Instinct MI300 accelerator, expected to ship in Q4 this year, will help AMD capture market share.'
However, AMD's challenges extend beyond technology.
As the AI chip market's near-monopolist, NVIDIA's strength lies not just in GPU hardware performance but in its decades-built, continuously reinforced CUDA unified computing architecture and the robust software ecosystem around it.
CUDA provides AI developers with rich libraries, toolkits, and development platforms, significantly simplifying parallel computing and AI model development, training, and deployment. Millions of developers worldwide innovate using CUDA, with mainstream deep learning frameworks (e.g., PyTorch, TensorFlow) offering native, optimal support for it.
AMD Senior Vice President of AI Vamsi Boppana admitted, 'Developers writing kernels are accustomed to CUDA and have accumulated substantial CUDA code over the years. We believe we're the only viable alternative to facilitate smooth migration, as we provide HIPIFY to compile HIPC++ code.'
In other words, while AMD narrows the hardware gap with NVIDIA—even surpassing it in some metrics—it still lags in software ecosystems.
Under the current ecosystem, only OpenAI supports AMD's computing power procurement demands. While OpenAI's endorsement helps, it's not entirely reliable.
Beyond technical breakthroughs, OpenAI and AMD must persuade more large model and cloud computing giants to allocate part of their procurement budgets to AMD.
Some images sourced from the internet. Please notify us for removal if any infringement occurs.