US Food Delivery Behemoth Unveils Robot – DoorDash’s Autonomous Delivery Sidekick: Meituan’s US Counterpart ‘Adorable Delivery Companion’ Hits the Streets! Will the ‘Charming Robot Dog’ Dot Snatch Job
![]() 10/10 2025
10/10 2025
![]() 474
474
Introduction
As Meituan is vigorously rolling out drones and autonomous vehicles across China, the US food delivery titan DoorDash has opted to embark on its automation journey with land - based robots. These contrasting strategies from the East and the West are reshaping the future landscape of global logistics.
On Tuesday (local time), DoorDash, the largest food delivery platform in the US, proudly introduced its self - developed delivery robot, Dot.
This compact robot is capable of autonomously navigating roads, bike lanes, and sidewalks at speeds up to 32 km/h, delivering meals and small parcels. With a cartoon - like appearance, Dot sports a bright red body, large LED eyes, and a mouth that opens to store food.
Let's delve into this topic with “Autonomous Vehicles Are Here” (WeChat Official Account: wrclyj)!
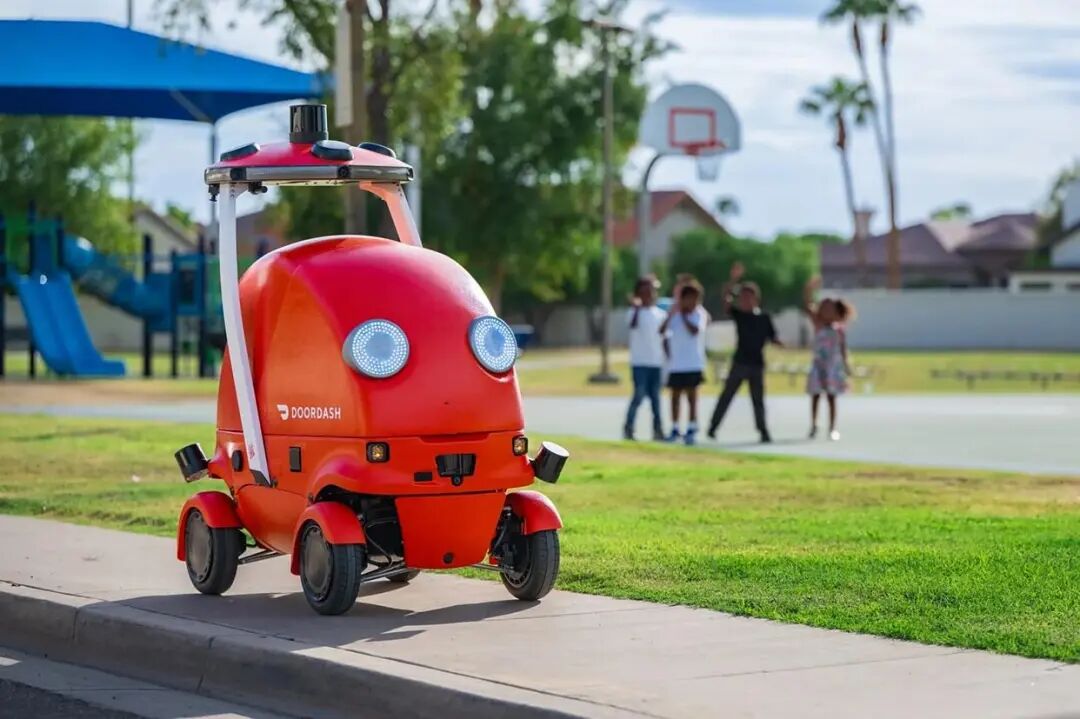

I. Dot’s Grand Vision: Not a Tech Gadget, but the Community’s ‘Delivery Champ’
DoorDash's vision for Dot is crystal clear: it's not about flaunting technology in labs but becoming a well - known presence in daily community life.
This practical approach is evident in every design detail:
1. Perfectly Sized
Dot is just one - tenth the size of a car. This size is meticulously calculated to enable it to carry 16 kg of food (which covers 95% of delivery orders) while being able to maneuver flexibly through sidewalks and bike lanes.
In comparison, Amazon’s Scout robot can only carry 5 kg, which means Dot has three times its load - carrying capacity.
DoorDash co - founder Stanley Tang said, “Delivering a tube of toothpaste or a pack of diapers doesn't require a full - sized vehicle. Dot is specifically designed for millions of daily deliveries. It's small enough to pass through doorways and driveways, fast enough to keep food fresh, and smart enough to choose the best routes.”
2. Sophisticated Sensing System
Equipped with a multi - modal sensor array, Dot can simultaneously detect potential hazards on sidewalks, such as sudden dashes by children, haphazardly parked bikes, and even falling branches.
Testing data reveals a 99.2% success rate in autonomous obstacle avoidance in San Francisco’s Mission District.
3. Emotion - Driven Design for Acceptance
The LED “eyes” of Dot change expressions based on different scenarios. For example, it has “smiling eyes” when interacting with pedestrians and “patient eyes” at red lights. This anthropomorphic interaction has increased resident acceptance by 40%.
A DoorDash product manager revealed, “We want grandmas to see it as harmless as a neighbor's dog.”
II. SmartScale Revolution: Taking the Accuracy Battle to the Kitchen
While the industry is mainly focused on the delivery process, DoorDash has quietly shifted automation to merchant kitchens. The SmartScale delivery scale may seem ordinary at first glance, but it's actually the cornerstone of a data - driven empire:
1. Impressive Error Correction
Installed during the packing process, SmartScale can detect the weight of items and match them with orders in just 0.3 seconds.
Pilot data indicates a 62% drop in order complaints at restaurants using the device, especially resolving issues like “missing utensils” or “forgotten drinks.”
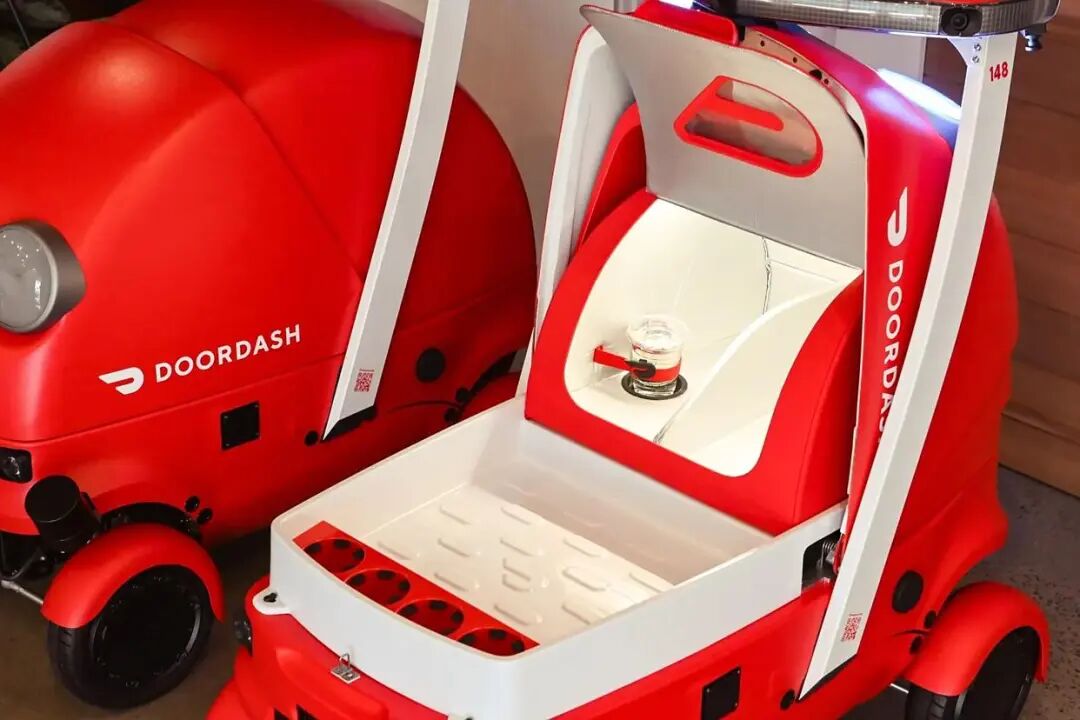

2. Real - Time Data Empowerment
The packed order data is instantly uploaded to the cloud and deeply integrated with delivery robots and scheduling systems.
When Dot receives an order, it already knows the number of containers, the estimated weight, and even the markers for fragile items, enabling truly “smart delivery.”
3. Master of Cost Control
For merchants, SmartScale reduces verification labor costs by 80%.
A pizza shop owner calculated that previously, they needed two full - time staff for order checks. Now, only occasional spot checks are required, saving $4,000 per month.
III. Hybrid Model: The Optimal Ratio of Human - Machine Collaboration
DoorDash is not replacing humans with robots but is exploring the best balance between cost and efficiency:
1. Innovative Human - Machine Collaboration
In Phoenix tests, Dot is responsible for short - range deliveries (less than 3 km), while human riders focus on medium and long - distance orders.
This division has boosted overall fulfillment efficiency by 35%, and riders' daily income has increased by 15% as they are freed from handling small orders.
2. Dynamic Scheduling System
The platform's algorithms dynamically allocate human and robot resources based on real - time traffic, weather, and order density.
Robot deployment automatically decreases in rainy or snowy weather, while both humans and robots operate at full capacity during holidays.
3. Gradual Replacement Strategy
DoorDash predicts that robots will handle 30% of deliveries by 2027, mainly in standardized communities with fixed routes.
This phased approach helps avoid labor conflicts and allows time for technological refinement.
IV. US - China Clash: Two Distinct Automation Paths
As DoorDash is betting on ground robots, US and Chinese platforms are pursuing different tech routes:
1. US Pragmatism
Dot is targeting the “last mile” delivery, aiming to cut costs.
US delivery fees range from $0.5 - 3, and robots have the potential to reduce them to below $0.5, which is a concrete advantage highly valued by the US market.
2. China’s Tech Radicalism
Meituan has launched drone + autonomous vehicle delivery in cities like Beijing and Shenzhen, with 15 regularized routes.
Its goal is not just cost reduction but also overcoming terrain limitations to reach areas that were traditionally difficult to access.
3. Fundamental Model Differences
In general, US communities have spacious sidewalks, which are more suitable for ground robots.
China's dense cities, on the other hand, are better suited for a combination of “low - altitude economy + ground stations.” Both paths reflect localization.
V. Real - World Challenges: Three Major Hurdles for Robot Delivery
Despite the promising prospects, DoorDash faces three core challenges:
1. Regulatory Maze
US state regulations for robots vary widely.
California limits the speed to 10 mph, New York bans nighttime operations, while Texas has more lenient regulations.
This fragmented regulatory landscape makes it difficult to scale up operations.
2. Technical Edge Cases
Dot encountered some unforeseen scenarios during tests, such as being blocked by homeless individuals, kicked by drunkards, or chased by children who treated it as a toy.
Although these incidents are rare (accounting for 0.1% of cases), they can cause 100% operational disruption.
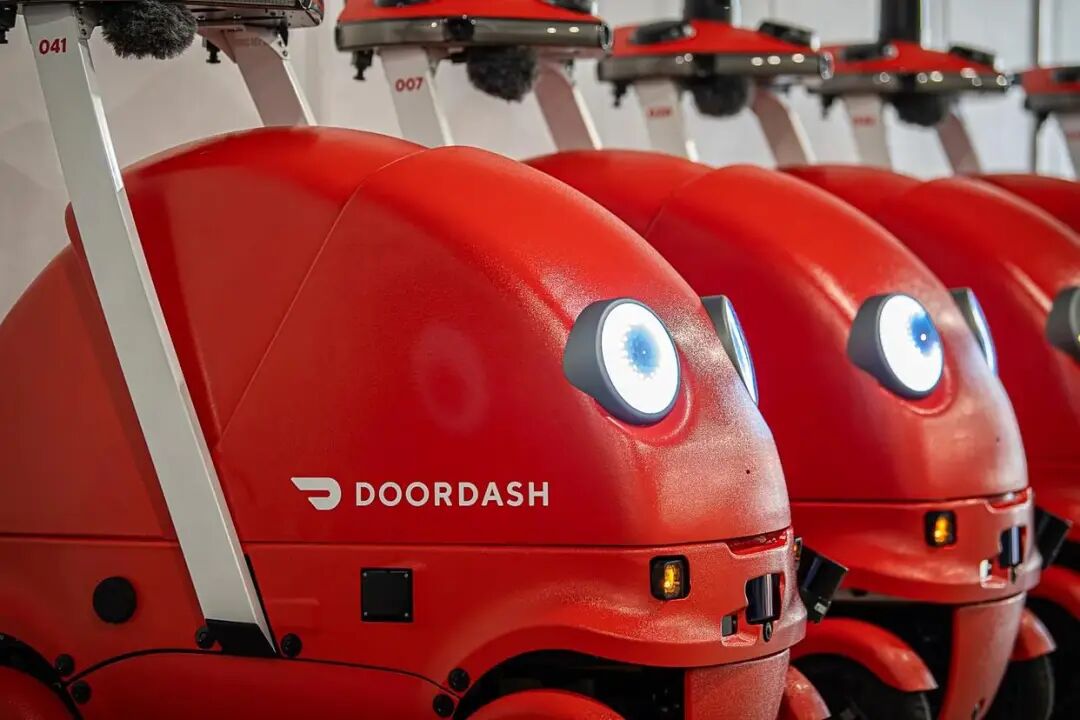

3. Social Acceptance Battle
Communities in San Francisco have protested against robots, claiming that they “occupy public space,” while unions have called it “a war on blue - collar workers.”
Whether DoorDash's “cute marketing” can overcome this resistance remains to be seen.
VI. Future Vision: Delivery in 2028
DoorDash is currently conducting tests in Phoenix's metro area and plans to serve 1.6 million residents by late 2025. The roadmap includes:
2026
Dot will be launched in 20 major US cities, handling 15% of deliveries with a 40% cost reduction per order. Smart scales will cover the Top 100 chains, boosting order accuracy to 99.5%.
2027
Human - machine collaboration will mature, creating new roles like “robot dispatchers.” Delivery personnel will transition to handling complex scenarios, such as large items and special requests.
2028
Self - driving vehicles and delivery robots will integrate for multi - tiered logistics. Suburban orders will be transported by autonomous cars to community hubs and then delivered by Dot.
In conclusion, “Autonomous Vehicles Are Here” (WeChat Official Account: wrclyj) believes:
When DoorDash's robot blinks its LED eyes to receive your delivery, it's not just being cute; it's participating in a revolutionary movement that will reshape the $800 billion delivery market. This time, the tech revolution has an adorable face.
What do you think?
#AutonomousVehiclesAreHere #AutonomousDriving #SelfDriving #AutonomousVehicles