2024 Fortune Global 500 List: 133 Chinese Companies Included (List Attached)
![]() 01/13 2025
01/13 2025
![]() 675
675
The 2024 Fortune Global 500 list boasts a combined revenue of approximately $41 trillion, equivalent to one-third of global GDP, marking a slight increase of about 0.1% over last year. The minimum revenue threshold for inclusion on the list has risen from $30.9 billion to $32.1 billion. The total net profit of all listed companies increased by 2.3% year-on-year to roughly $2.97 trillion. With the exception of total profits, which are slightly lower than those on the 2022 list, all other indicators, including total assets, total net assets, and total employees, have reached their highest levels since the inception of the Fortune Global 500 list.
Reply "Fortune Global 500" in the official account's backend to access the complete list.
(Unit: millions of USD)
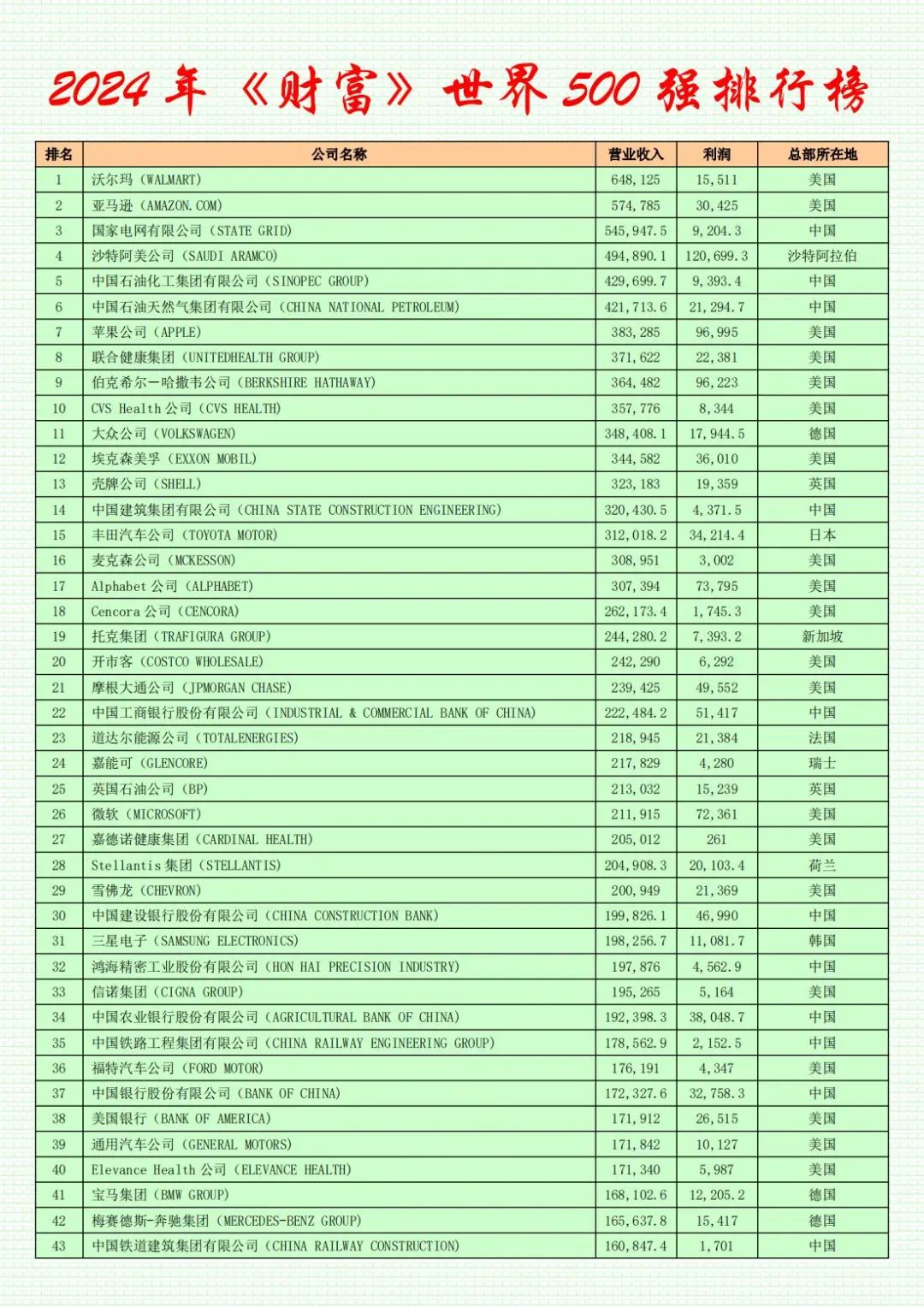
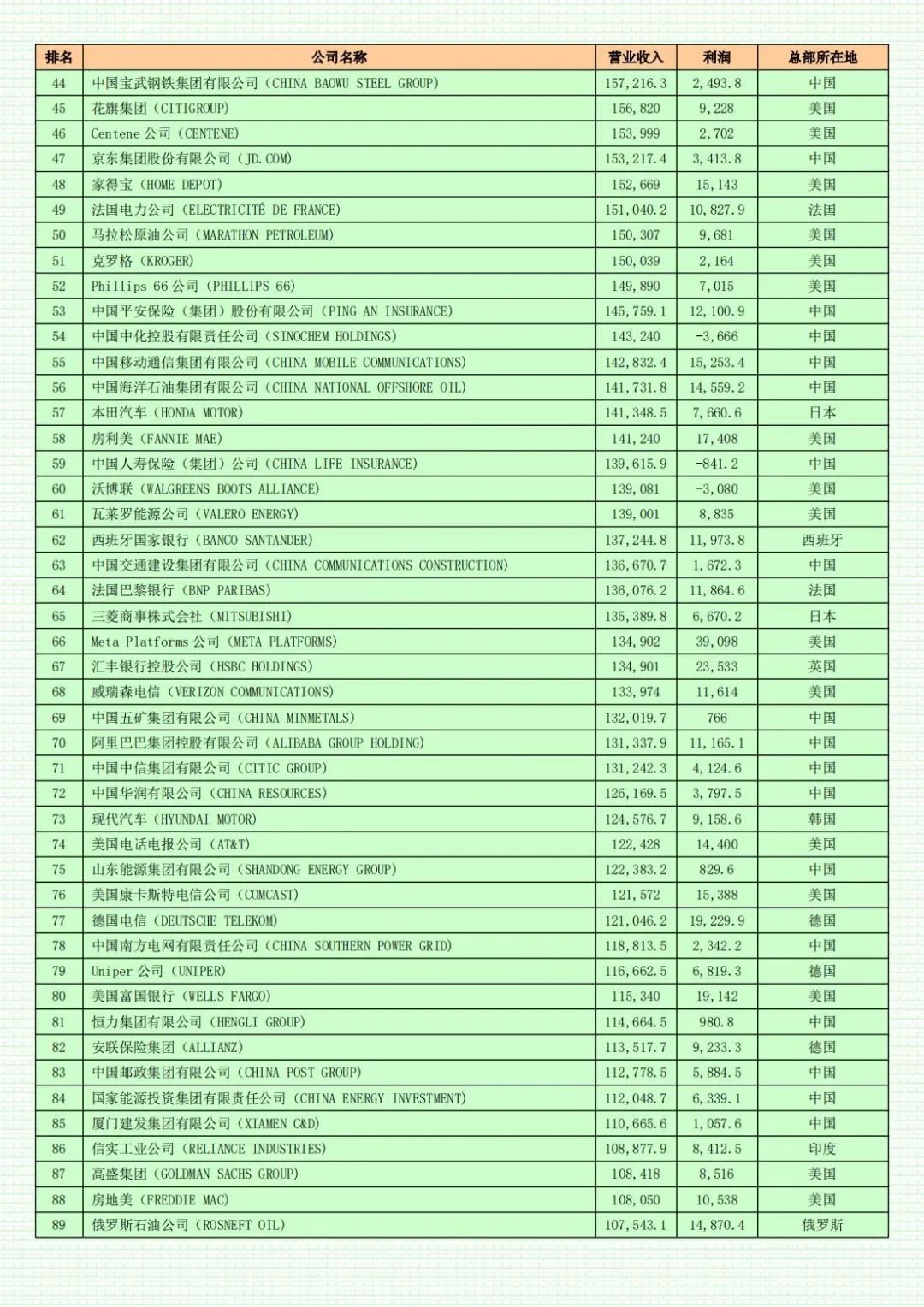
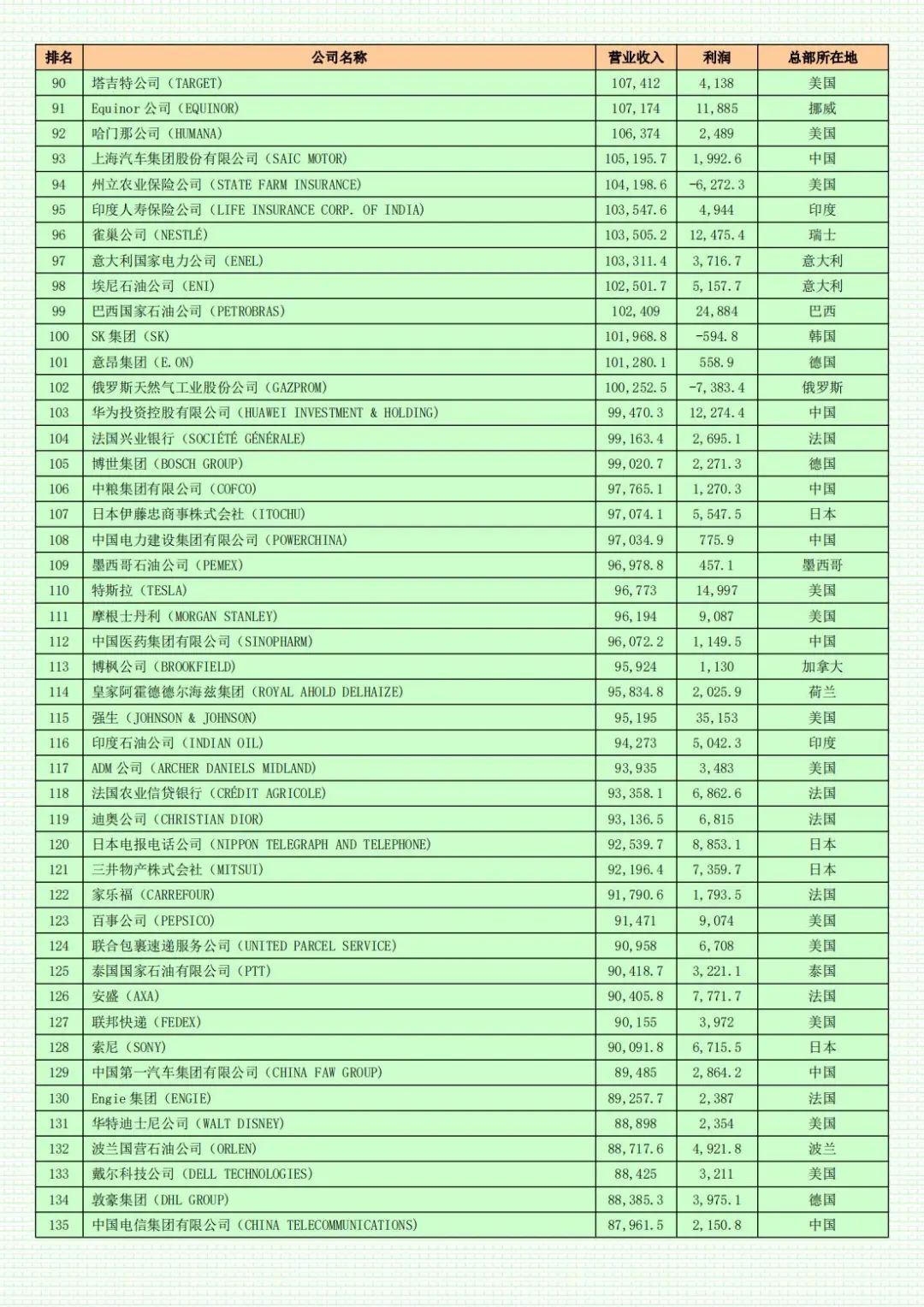
For the eleventh consecutive year, Walmart remains the world's largest company. Amazon has reclaimed the second spot. China's State Grid Corporation maintains its third-place ranking. Saudi Aramco and Sinopec occupy the fourth and fifth positions, respectively.
The combined profits of the 500 companies have resumed a growth trajectory. In 2023, the total profits of Fortune Global 500 companies approached $3 trillion, an increase of 2.3% over the previous year. Despite a year-on-year decline of approximately 24%, Saudi Aramco retained its top spot on the profit list with earnings of roughly $120.7 billion. Three American tech giants—Apple, Alphabet (Google's parent company), and Microsoft—ranked second, fourth, and fifth among the most profitable companies, respectively. Berkshire Hathaway, which was the most loss-making company on last year's Fortune Global 500 list, climbed to third place on this year's profit list with profits exceeding $96.2 billion. Three Chinese companies entered the top ten of the profit list, all of which are commercial banks: Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank, and Agricultural Bank of China, with Industrial and Commercial Bank of China's profits exceeding $51.4 billion.
01 China, the United States, and Japan
This year, including companies from Taiwan, China has a total of 133 companies on the list, a decrease of 9 from last year. In contrast, the United States has 139 companies on the list this year, an increase of 3 from the previous year, securing the top spot in terms of the number of large companies. This marks the first time since 2018 that the number of Chinese companies on the list has fallen below that of the United States.
The number of mainland Chinese companies (including Hong Kong) on the list is 128, a decrease of 7 from last year. Japan ranks third in terms of the number of companies on the list, with a total of 40 companies, a decrease of one, continuing its downward trend. When the Fortune Global 500 debuted in 1990, Japan had as many as 149 companies on the list. Today, the United States, China, and Japan collectively contribute approximately two-thirds of the companies, revenues, and profits on the list.
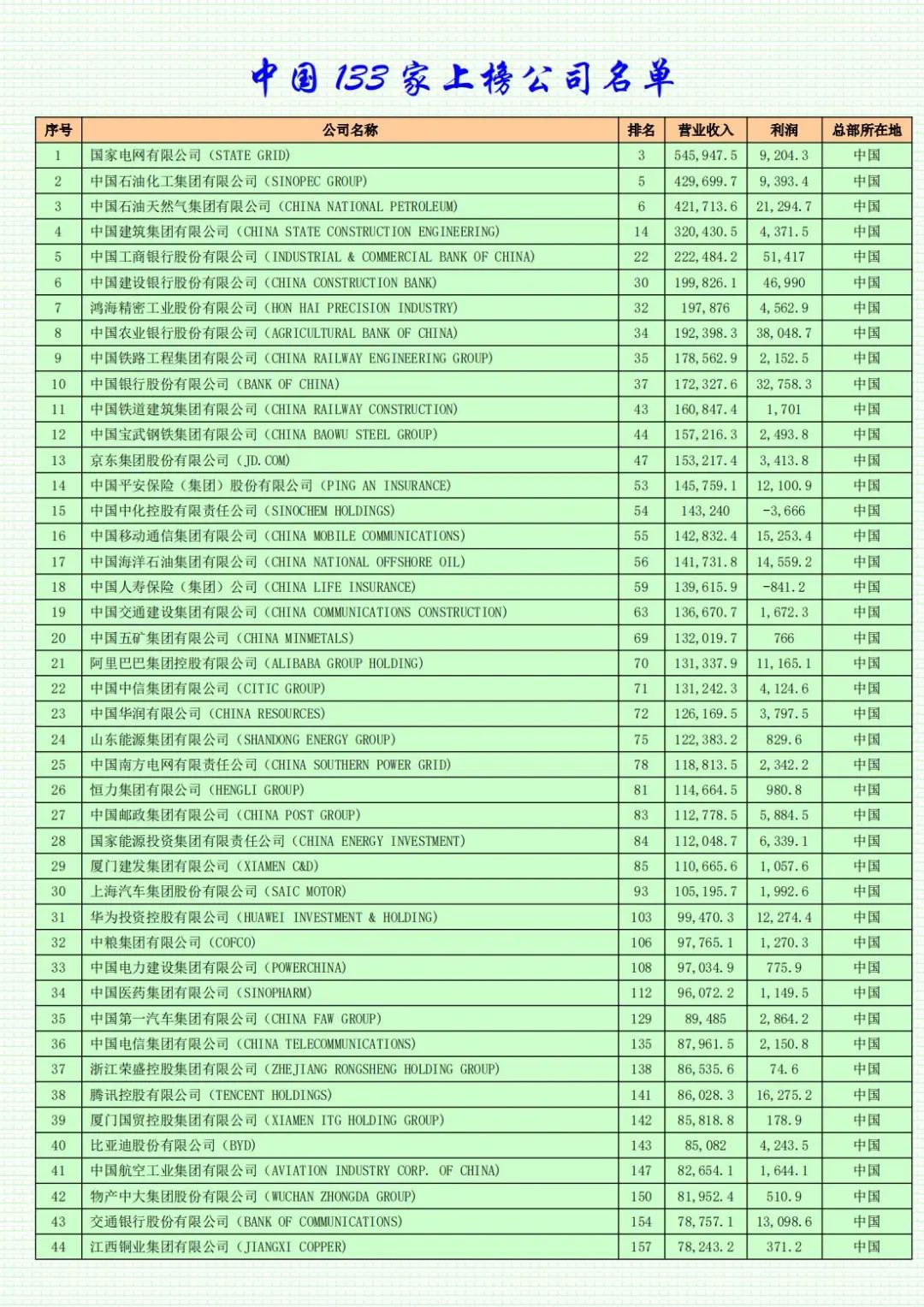
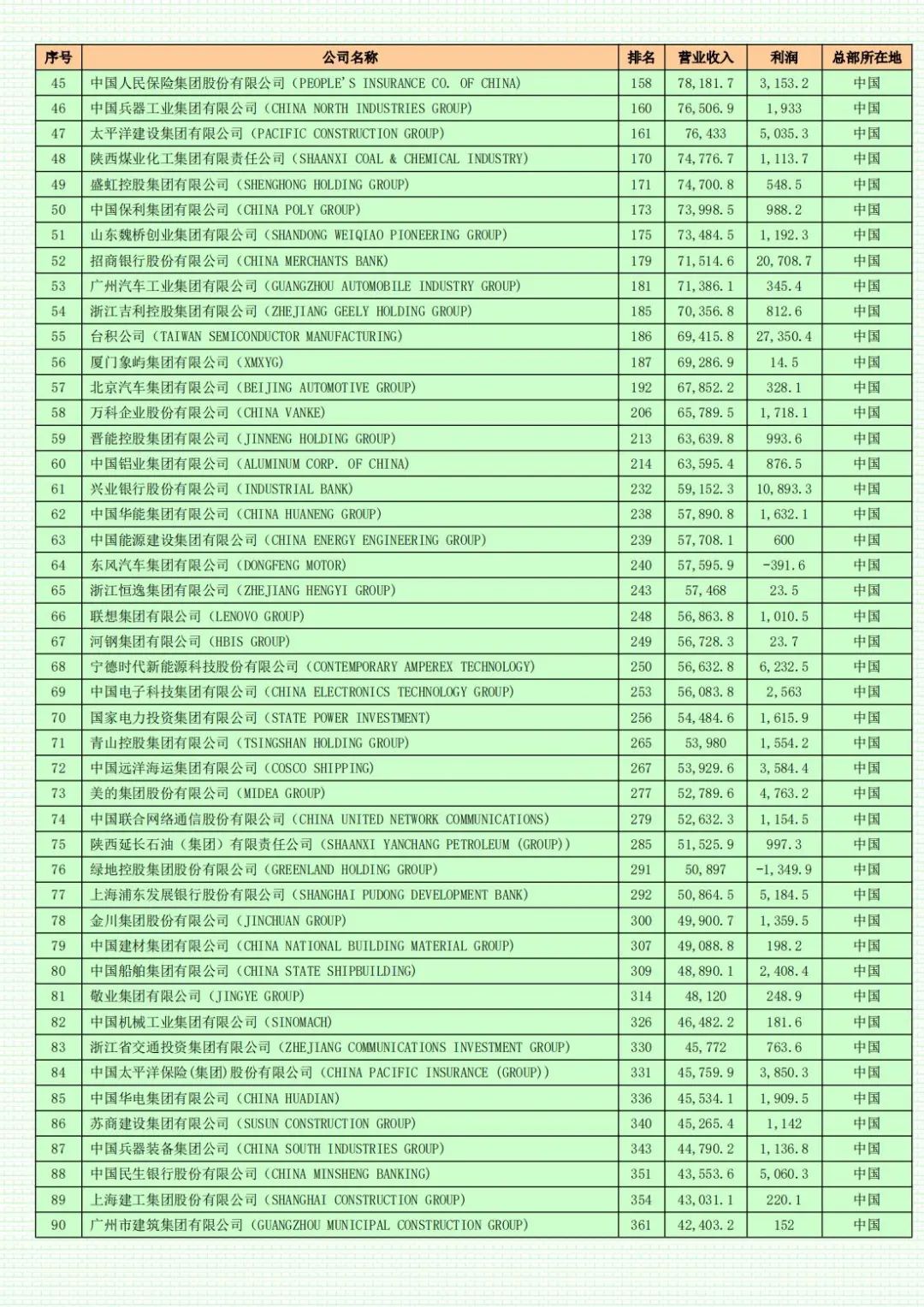
This year, the total revenue of China's 133 listed companies in 2023 is approximately $11 trillion, a decrease of roughly 6% compared to last year's total revenue of 142 listed companies. The average sales revenue stands at approximately $83 billion, lower than the average revenue of $99 billion for listed American companies but slightly higher than the average for all 500 companies on the list. However, operating profits are significantly lower than the average for American companies. The average profit of American companies is $8.8 billion, whereas the average for listed mainland Chinese (including Hong Kong) companies is $3.9 billion, less than half of that of listed American companies and also failing to meet the average profit of $5.9 billion for all 500 companies on the list. The total profits of 139 American companies amount to $1.2236 trillion, accounting for 41% of the total profits of all Fortune Global 500 companies.
Contributed author Wang Zhile points out that the 2024 Fortune Global 500 list reflects a stagnation or even decline in the quantitative growth of Chinese companies on the list, with their operating quality falling below the global average. Currently, the combined effects of issues within Chinese companies' own management and the domestic business environment (such as insufficient support for private enterprises and the promotion of foreign-invested enterprises) along with the restructuring of international industrial chains pose unprecedented challenges to the development of Chinese companies.
02 Rise of the Automotive Industry, Internet Rebound
While acknowledging the developmental challenges faced by Chinese companies, we can also identify groups of Chinese companies that have achieved new breakthroughs. Among the 15 sectors in which listed Chinese companies operate, the "automotive and parts" sector stands out:
A total of 10 Chinese automotive and auto parts companies have made it onto the 2024 Fortune Global 500 list. Among these 10 companies, Chery appears on the list for the first time, ranking 385th with revenues of $39.1 billion. Most of the other nine companies have seen their rankings rise year-on-year. Last year, BYD recorded the largest increase in ranking among Chinese companies. This year, the company's revenue increased from $63 billion last year to $85.1 billion, and its ranking improved by 69 places compared to the previous year. Additionally, CATL's revenue increased from $48.8 billion last year to $56.6 billion after making the list for the first time last year. Geely's revenue also increased by 40 places, from $60.4 billion to $70.4 billion. These companies have propelled Chinese automobiles, particularly electric vehicles, into the global market. Wang Zhile believes that Chinese companies such as Huawei, BYD, and CATL are already highly competitive world-class enterprises.
Among the 128 mainland Chinese (including Hong Kong) companies, excluding 5 newly listed and relisted companies, as well as 6 companies whose positions remained unchanged, 46 companies saw their positions rise, while 71 saw their positions fall. Notably, large companies in the internet sector rose overall. Among the five internet giants, except for Alibaba, which fell by 2 places, JD.com, Tencent, and Meituan all witnessed improvements in their rankings, while Pinduoduo made the list for the first time. Benefiting from the rebound of China's internet industry, Meituan became the Chinese company with the largest increase in ranking on the list, jumping 83 places to 384th. JD.com Group, ranked 47th, re-entered the top 50, replacing Ping An Insurance as the largest private company in mainland China.
03 Insights into Business Sectors
The Fortune Global 500 list classifies all companies by their business sectors. The so-called business sector encompasses several sub-industries. The 128 mainland Chinese (including Hong Kong) companies on the list belong to 15 business sectors. Among these 15 sectors, only 4 have an overall return on sales exceeding 5%, namely finance, retail, telecommunications, and high-tech. The high-tech sector is at the forefront of global technological development and the focus of global competition.
According to Fortune's classification, this business sector includes companies in networking, communications equipment, internet services, computers, electronic and electrical equipment, semiconductor components, computer software, artificial intelligence, and other categories. A total of 33 high-tech companies made it onto the 2024 Fortune Global 500 list, with an average operating revenue of $88.2 billion and an average profit of $14.6 billion. The operating profit rate of high-tech enterprises ranks among the best in the industry. Huawei remains the leading Chinese company in this sector, with sales of nearly $100 billion and profits of approximately $12.3 billion this year as the company emerges from difficult times. Among these 33 high-tech companies, there are 16 American high-tech enterprises with an average operating revenue of $102.6 billion and profits of $23.6 billion.
A total of 17 non-American high-tech companies made it onto the 2024 list (including 6 mainland Chinese companies), with an average operating revenue of $74.6 billion and an average profit of only $6.3 billion. Clearly, large American high-tech enterprises dominate this highly competitive sector. Their profitability is substantial: Apple, Alphabet, Microsoft, and Meta Platforms alone generated a net profit of $282.2 billion. This year's Fortune Global 500 list includes a total of 43 "newly listed and relisted" companies, of which 5 are Chinese companies: Chery Holding Group Co., Ltd., Hangzhou Industrial Investment Group Co., Ltd., Hailiang Group Co., Ltd., Pinduoduo Holding Company, and AIA Group Limited. Chery, Hangzhou Industrial Investment Group, and Pinduoduo are all making the list for the first time. Fifteen of the 43 companies come from the banking industry.
Driven by strong demand from the artificial intelligence boom, NVIDIA makes the list for the first time, ranking 222nd, the highest among the newly listed companies this year. On the Return on Equity (ROE) list, The Home Depot retains its top spot with an ROE exceeding 1,450%, while Oracle jumps to second place with an ROE exceeding 792%. Cencora Inc. and Apple rank third and fourth, respectively. Among the top 50 companies with the highest ROE, only two are Chinese companies—Chery Holding Group ranks 40th with an ROE of 35%, and Pinduoduo ranks 47th.
Among Chinese companies, the top 10 in terms of ROE are: Chery Holding Group Co., Ltd., Pinduoduo Holding Company, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited, BYD Company Limited, Quanta Computer Inc., Midea Group Co., Ltd., Zijin Mining Group Co., Ltd., Luxshare Precision Industry Co., Ltd., and Lenovo Group Limited. On the profit margin list, Visa tops the list with a net profit margin exceeding 52%. Three of the top five companies with the highest profit margins come from the semiconductor and electronic components industries, namely NVIDIA, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, and Broadcom Inc., ranking second to fourth.
In terms of changes in ranking, the company with the largest increase this year is UBS Group, which jumped 165 places to 182nd. Deutsche Bank rose 149 places to 205th, the second-largest increase in ranking. Among the top 10 companies with the largest increases in ranking, all but one insurance company are banks. This year, four Chinese companies rose by at least 50 places: Meituan, BYD Company Limited, Shenghong Holding Group Co., Ltd., and Taikang Insurance Group Co., Ltd. A total of 33 companies failed to achieve profitability this year, including six mainland Chinese companies. The top loss-making company on the list is British American Tobacco Group, with losses exceeding $17.8 billion. Impacted by the Russia-Ukraine conflict and EU sanctions, Gazprom ranks second with losses exceeding $7.3 billion. Compared to last year, the total losses of loss-making companies on this year's list have decreased significantly.