Unraveling Leadshine's Valuation: Why 300+ Times?
![]() 01/15 2025
01/15 2025
![]() 673
673
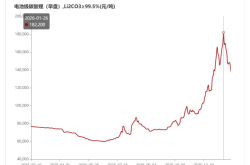
The humanoid robot sector stands poised to become a long-term, formidable race track that cannot be ignored. If one were to pinpoint the most promising enterprise within this sphere, Leadshine would undoubtedly be among the frontrunners. From January 8th to 14th, the company's stock surged by nearly 50% within five trading days, underscoring its remarkable explosive potential.
Historically, Leadshine's P/E ratio has consistently hovered at over 100 times, even reaching 200 times in recent years. This signifies that the company is not merely a fleeting concept hype but is supported by solid, underlying value.
[Vast Market Potential]
The reducer industry in which Leadshine operates is reaping the benefits of two major trends: the resurgence of the industrial robot market and the ascendancy of humanoid robots.
Data indicates that domestic industrial robot production briefly declined in 2023 but swiftly stabilized. Commencing from April and May 2024, production turned positive. From June to October, industrial robot production increased by 12.4%, 19.7%, 20.0%, 22.8%, and 33.4% year-on-year, with growth rates continually rising month-on-month. According to statistics from the China Industry Information Research Institute, industrial robot production from January to November 2024 reached 487,900 units, a year-on-year increase of 11.1%, surpassing any previous year and setting a new historic high.

Reducers are classified into three types: harmonic reducers, planetary reducers, and RV reducers. Planetary reducers are suited for heavy-load scenarios, such as heavy machinery and cranes. RV reducers are predominantly used in the industrial robot industry. Harmonic reducers, due to their compact size, lightweight nature, and high precision, are primarily utilized in humanoid robots. Leadshine primarily focuses on harmonic reducers (accounting for over 80% of its revenue), thus the company's primary growth potential lies in the mass production of humanoid robots.
In 2024, the global humanoid robot industry achieved significant strides. Renowned domestic and international manufacturers, including Tesla, 1-X, Figure, Zhiyuan, and Fourier, have all completed small-batch production, with the threshold for large-scale industrialization fast approaching.
Recently, Northeast Securities provided a development guideline, predicting that global humanoid robot production could reach 10,000 units in 2025, 100,000 units in 2026, and 500,000 units in 2027. Assuming global robot production reaches 1 million units by 2030, the new demand for harmonic reducers will surge to 14 billion.
In hindsight, this data appears notably conservative.
On January 8, U.S. time, Musk stated in a recent interview that if everything proceeds smoothly, Tesla aims to produce 50,000 to 100,000 humanoid robots in 2025 and then escalate production tenfold to 500,000 units in 2026.
At this pace, Tesla alone is poised to achieve shipments of 1 million units within three years.
The actuators of a humanoid robot primarily comprise three parts: rotary joints, linear joints, and dexterous hands. Reducers are the quintessential core of rotary joints. Guosen Securities previously analyzed the cost structure of Tesla's Optimus and found that after mass production, reducers account for approximately 15%-20% of the cost of a single Optimus.
As the production of humanoid robots escalates, harmonic reducers are poised to capture a substantial market share.
Another noteworthy trend is that vertical integration within the industry will also usher in new growth opportunities for related enterprises.
Internationally leading reducer companies are currently promoting mechatronics by integrating harmonic reducers with motors, encoders, brakes, and sensors. By offering comprehensive motion control solutions, they enhance product added value and retain greater profits on their balance sheets.
[Favorable Industry Landscape]
The reducer industry boasts a promising future, but not everyone can capitalize on it. This is an industry with high barriers, encompassing thresholds in materials, processes, production, assembly, and other facets.
Taking equipment as an example, the high-precision characteristics of reducers impose stringent demands on gear grinding machines, gear shaving machines, hobbing machines, and grinding machines. Much of the processing equipment for core components needs to be imported from Europe and the United States, with delivery times spanning at least one year.
Another illustration is the process. Heat treatment determines the hardness and wear resistance of gears. Only advanced carburizing and quenching technology can ensure an optimal balance between hardness, tensile strength, and toughness. Processing accuracy must reach the micrometer level, which not only necessitates top-notch equipment but also poses a significant challenge to the operating skills and experience of personnel. Even the seemingly straightforward processes of grouping and mass production require maintaining high precision at all times.
All these are not areas where one can rapidly catch up. Leadshine's R&D expense ratio has long been maintained at 12%-14%, which has cemented its current position.
Consequently, the competitive landscape in the reducer industry, particularly in the realm of harmonic reducers, is highly favorable.
In the global market, the Japanese brand Harmonic Drive dominates 80% of the harmonic reducer market share, while Leadshine holds approximately 10%. In the domestic market, Harmonic Drive's market share is around 30-40%, while Leadshine's is approximately 25%. Following them are Japan's Shimpo and China's Laifu Harmonic, both with single-digit market shares. Leadshine is the largest and most promising local enterprise in this field, with the potential to compete with foreign companies. It is also the sole manufacturer globally that achieves independent supply of all components for precision harmonic reducers.
High industry concentration translates to low competition intensity and substantial profit margins.
In 2021, Leadshine's net profit margin reached an impressive 42.87%. In recent years, the decline in market demand coupled with the increase in depreciation due to capacity expansion has significantly reduced the company's profit margin. However, it still maintains above 20%, which is undoubtedly top-tier in the current manufacturing sector.
Looking ahead, as the industry expands overall and domestic substitution occurs in the existing market, Leadshine will enter a leapfrog development stage. The cost reduction effect stemming from large-scale production is bound to propel the company's profit margin upwards.
[Substantial Advantages]
Two factors determine that Chinese reducer companies are destined for long-term and substantial growth potential.
First, cost advantages.
For the same type of product, Harmonic Drive's selling price hovers around 3,000-4,000 yuan, whereas Leadshine's is only about 2,000 yuan. Comparing the product performance of the two companies, except for minor gaps in individual indicators such as minimum backlash and reduction ratio, other data are essentially on par.
Second, supply chain advantages.
According to MIR Data, in the first three quarters of 2024, the year-on-year growth rate of domestic industrial robot manufacturers reached 21.1%, markedly higher than the overall market growth rate, driving the market share of domestic manufacturers to increase to 51.6%, an uptick of 4.5 percentage points compared to the same period in 2023. The status and influence of domestic manufacturers in the industrial robot market have further strengthened.
This is even more pronounced in the realm of humanoid robots. Currently, China and the United States are the two largest development hubs globally, with the majority of manufacturing taking place in China. As a supporting enterprise, local companies like Leadshine possess the inherent advantage of being close to the action and can swiftly mobilize resources to respond to customer needs and penetrate the supply chain.
After going public in 2020, Leadshine invested a portion of its IPO proceeds in a project to produce 500,000 precision harmonic reducers annually. In October 2022, the company announced a private placement plan, intending to invest 2 billion yuan to add annual production capacity of 1 million harmonic reducers and 200,000 mechatronic actuators.
According to the latest news, Leadshine ultimately raised 1.413 billion yuan. Although this fell short of expectations, calculating at a 70% discount, it can still add 700,000 harmonic reducers and 140,000 mechatronic actuators to production capacity.
In 2023, Leadshine produced 206,000 harmonic reducers and 8,117 mechatronic products. Based on these figures, the company's long-term production capacity will be at least five times its current capacity.
In summation, Leadshine, with its certainty and imagination, appears almost flawless. However, it is crucial to note that before performance effectively digests valuation, a dynamic P/E ratio of over 300 times is undoubtedly not a secure position.
Of course, if subsequent developments significantly surpass expectations, it is plausible that the company will continue to thrive.
[Disclaimer]
This article involves content related to listed companies, based on the author's personal analysis and judgment derived from information (including but not limited to temporary announcements, periodic reports, and official interactive platforms) publicly disclosed by listed companies in accordance with legal requirements. The information or opinions presented in this article do not constitute any investment or other business advice. Market Value Observation assumes no responsibility for any actions taken as a result of adopting this article.
——END——