SAIC Motor Falls into a Dilemma
![]() 08/20 2024
08/20 2024
![]() 578
578
Writer | Duoke
Source | Beiduo Finance

Recently, Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation Limited (hereinafter referred to as "SAIC Motor" or "SAIC") released its latest production and sales report. The report shows that SAIC's automobile production and sales in July 2024 have declined to varying degrees, with double-digit declines in cumulative sales since the beginning of the year.
Extending the timeline further, it can be seen that after SAIC's "golden era" in 2018, its performance and sales have continued to decline. The trajectory of its declining business indicators, akin to the prophecy of Ragnarök in Norse mythology, signals the end of its glory and prosperity.
However, SAIC is clearly not willing to settle for mediocrity. Following a shakeup in its senior management, the "new leader" Wang Xiaoqiu has led SAIC to initiate measures to improve efficiency and reduce costs, actively promoting changes in its marketing system to stimulate innovation and vitality. Can SAIC, standing at the crossroads of reform, embark on a new world, much like a myth?
I. Outpaced by BYD, Production and Sales Hit a Bottleneck Since the Beginning of the Year
According to SAIC's announcement, the company's total vehicle production for the year to date has been 2,050,800 units, a year-on-year decrease of 18.64%; total vehicle sales have been 2,078,400 units, a year-on-year decrease of 15.92%. However, the company claims that its cumulative terminal deliveries have reached 2,452,000 units, with a month-on-month increase of 5.1% in July.
It should be noted, however, that SAIC's monthly vehicle production in July 2024 was approximately 237,500 units, a decrease of 42.57% from 413,600 units in the same period in 2023; vehicle sales were 251,500 units, also a decrease of 37.16% from 400,200 units in the same period in 2023, with production and sales volumes shrinking by nearly half year-on-year.
Data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers shows that China's automobile industry produced and sold 2,286,000 and 2,262,000 vehicles in July, respectively, with year-on-year declines of 4.8% and 5.2%; however, overall production and sales for the year to date have increased by 3.4% and 4.4%, respectively, year-on-year. From this perspective, SAIC's operating performance is clearly below average.
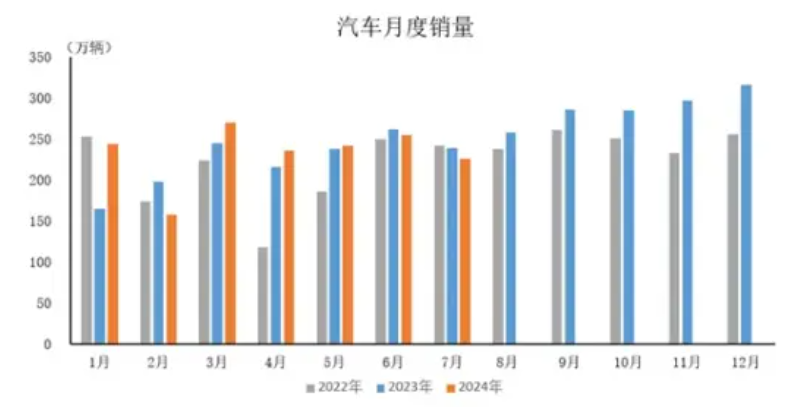
Among SAIC's many brands, Shanghai GM has experienced the most significant decline in sales, with monthly sales plummeting from 85,300 units in July 2023 to 15,000 units, a year-on-year decrease of 82.42%. In addition, sales of SAIC Volkswagen, SAIC-GM-Wuling, and SAIC MAXUS declined by 18.18%, 31.72%, and 23.34%, respectively.
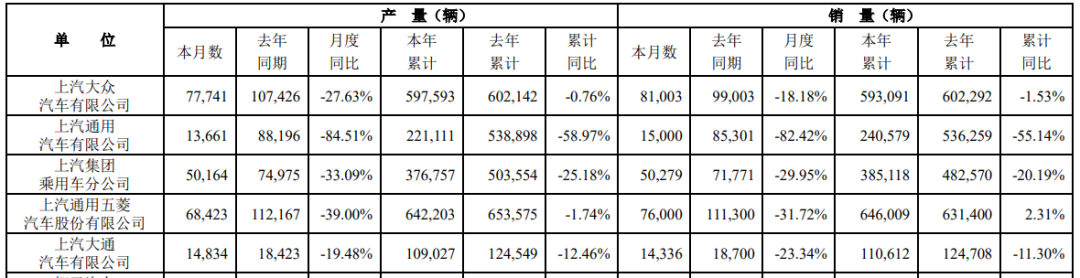
In contrast, BYD, SAIC's largest competitor, sold 342,300 vehicles in July, an increase of 30.60% year-on-year. In June, BYD surpassed SAIC's sales of 300,500 vehicles with sales of 341,600, meaning that SAIC has lost the monthly sales crown twice in a row.
Although BYD's current total sales volume of 1,955,300 units is still below that of SAIC, the sales gap between the two has narrowed from 214,000 units at the end of the first half to 123,100 units at the end of July. Some in the industry have even boldly speculated that BYD's sales this year may surpass SAIC, which has been the domestic sales champion for 18 consecutive years.
According to data from the China Passenger Car Association, 878,000 new energy passenger vehicles were sold in July, an increase of 36.9% year-on-year and 2.8% month-on-month. In the field of new energy vehicles, SAIC produced 69,200 units in July, a year-on-year decrease of 21.10%; sales were 71,100 units, a year-on-year decrease of 21.85%.

However, IM Motor, SAIC's high-end new energy brand, has performed remarkably well in the market, with monthly production of 3,046 units, an increase of 120.25% year-on-year; sales of 4,180 units, an increase of 142.74% year-on-year. Since the beginning of the year, IM Motor has sold a cumulative total of 26,600 units, an increase of 131.34% year-on-year.

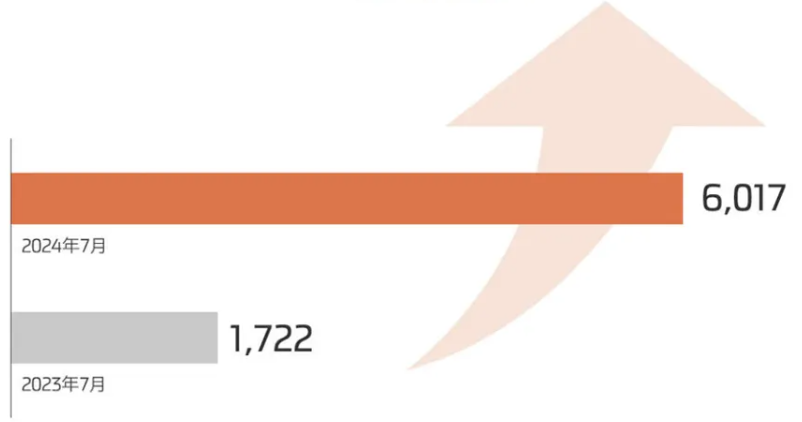
SAIC revealed that IM Motor delivered 6,017 vehicles across its entire lineup in July, a year-on-year increase of 249%, achieving leapfrog growth. The IM L6 regained the sales crown in the "mid-to-large pure electric SUV" segment, while the IM L6 solidified its position in the top three sales of "mid-to-large pure electric sedans" in the 200,000 yuan price range.
According to Beiduo Finance, IM Motor recently posted a blurred car poster on social media with the caption "Confirmed, Launch in August," hinting at the imminent release of a new model. Many netizens speculate that the new model may be an extended-range version of the IM L6.

II. Unrelenting Leadership Changes: A Wave of Executive Shuffles
Shortly after releasing its unimpressive July production and sales report, SAIC accelerated the pace of executive personnel changes, with several underperforming divisions announcing new leaders.
On August 14, SAIC announced that Yu Jingmin, the former party secretary and executive vice president of sales and marketing at SAIC Volkswagen, would become the executive vice president of SAIC Passenger Vehicles; Zhu Yong, the former executive director of the Power Drive Platform of the Business Planning and Project Management Department of SAIC Passenger Vehicles, would become its vice president.

Meanwhile, SAIC Volkswagen announced that Tao Hailong, the general manager of SAIC Volkswagen, would concurrently serve as the party secretary; Fu Qiang, the former executive director of SAIC Volkswagen's brand marketing business, would succeed Yu Jingmin as the executive vice president of sales and marketing and general manager of SAIC Volkswagen Sales Co., Ltd.
SAIC General Motors has also undergone executive changes. Upon the decision of the SAIC Party Committee, Lu Xiao, the former executive deputy general manager of Pan Asia Technical Automotive Center, succeeded Zhuang Jingxiong as general manager of SAIC General Motors; Xue Haitao, the former vice president of SAIC-GM-Wuling, succeeded Lu Yi as vice president of the company, responsible for marketing-related work.

Such intensive personnel changes are rare in the industry, and this series of strategic moves can be traced back to SAIC's executive rotation in July of this year. According to Beiduo Finance, Chen Hong, the former chairman of SAIC who had served the company for 40 years, submitted his resignation on July 8 due to reaching retirement age.

According to the announcement of the 23rd meeting of the eighth board of directors of SAIC, the board elected Wang Xiaoqiu, the former president of SAIC, to succeed Chen Hong as chairman; Jia Jianxu, the former vice president, was appointed president of SAIC, with a term consistent with that of the current board of directors.
This large-scale personnel "reshuffle" is undoubtedly the handiwork of the new leadership team at SAIC, centered on Wang Xiaoqiu. After reviewing the current management team, Beiduo Finance found that most of these new executives are post-70s individuals with rich experience in brand marketing or technology research and development, and many of them have worked for the companies where they are now serving.
According to China Economic Net, SAIC's new talent layout aims to create a complementary combination of "technology + marketing." In other words, while focusing on the entire marketing chain, SAIC plans to deepen the deployment of innovation chain construction, further promoting the restructuring of its automotive industry value chain and launching a renewed challenge to the market high ground.
III. Continuously Shrinking Performance and Sales Failing to Meet Expectations for Consecutive Years
Behind SAIC's bold moves to reshuffle its senior management, its ambition and determination to break through the sales dilemma are clear. In fact, after 46 years of development, SAIC, which has now reached a turning point in the development of new energy vehicles, is at a time to explore more diverse innovation paradigms.
According to previous financial reports, SAIC achieved a total operating revenue of 744.705 billion yuan in 2023, a slight year-on-year increase of only 0.09%, similar to the revenue scale in 2022; net profit attributable to shareholders was 14.106 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 12.48%; and net profit after deducting non-recurring gains and losses was 10.045 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 11.71%.

SAIC's performance can only be described as mediocre, and the market is clearly dissatisfied with this financial report. It should be noted that during its peak period, SAIC's total operating revenue once exceeded 900 billion yuan, with a net profit of 36.009 billion yuan. However, its current profitability is close to halved and even lower than it was a decade ago.
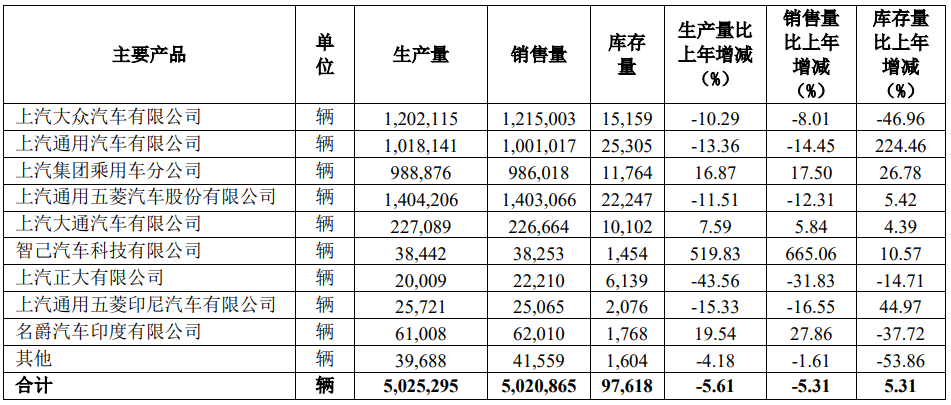
Turning to sales, SAIC sold a total of 5,020,900 vehicles in 2023, a year-on-year decrease of 5.31%, failing to meet its sales target of 6 million vehicles. According to Beiduo Finance, SAIC's business objectives have not been met for six consecutive years since 2018, with overall sales declining for five consecutive years.
Among them, "SAIC's old trio" of SAIC Volkswagen, SAIC General Motors, and SAIC-GM-Wuling saw sales declines of 8.01%, 14.45%, and 12.31%, respectively, in 2023, with cumulative sales falling short of 4 million units. In 2018, these three companies could still support SAIC's sales volume of over 7 million units with sales of 6.107 million units.
In its financial report, SAIC readjusted its business plan and strategy, focusing on enhancing cost competitiveness to achieve an increase in sales volume and stabilize cash flow. It aims to sell 5.45 million vehicles in 2024, with an expected total operating revenue of over 790 billion yuan and operating costs of around 700 billion yuan.
At SAIC's "New Decade" technology conference, Li Jun, deputy dean of SAIC's Innovation Research and Development Institute, also emphasized that "a key indicator of disruptive innovation is the reduction of system costs." This concept was quickly implemented in many of SAIC's subsidiaries.
Taking SAIC Volkswagen as an example, according to the 21st Century Business Herald, its general manager Tao Hailong led the company to embark on drastic reforms within a month of taking office. SAIC Volkswagen reassessed its cost optimization potential for 2024, planning to optimize more than 2 billion yuan in structural costs that year, aiming to squeeze profits from the cost side amidst the industry's "price war."
SAIC, which has formed a systematic and modular industrial structure, does not lack the resources and strength for positive development. The key step forward into a new era lies in combining the strategic resolve of long-termism with the momentum of reform and innovation, while adhering to the overall work guideline of "making progress while ensuring stability, with the emphasis on progress."







