From cloud computing to AI big models, cloud giants take a crucial step in the ecological revolution.
![]() 09/03 2024
09/03 2024
![]() 640
640
2024 is destined to be a critical juncture in the development of cloud computing. Over the past two years, the most discussed topic in the cloud computing industry has been "price cuts." Amidst slowing market growth and even some enterprises advocating "de-clouding," cloud vendors have resorted to the "price card," leading the entire industry into a state of "low-level internal competition." Nowadays, fueled by large models, intelligent transformation is intensifying across industries. Cloud computing power, as a flexible, efficient, and cost-effective way to access computing resources, is emerging as the new foundation for AI vendors. If chips are the "oil" of the intelligent era, cloud computing power is the "new energy" for AI development. The shift from old to new business models has a profound impact on cloud computing beyond mere public opinion. Perhaps the "golden age" of cloud computing is just beginning.


The next-generation cloud is becoming intelligent
IDC's report, "Focusing on Platform Capabilities to Support Intelligent Business Development," indicates that China's public cloud market will experience a CAGR of 26.9% from 2022 to 2027, with PaaS growing fastest at 30.5% and SaaS following closely at 28.7%. As cloud computing infrastructure matures, China's public cloud market is evolving from resource-driven to technology- and business-driven.
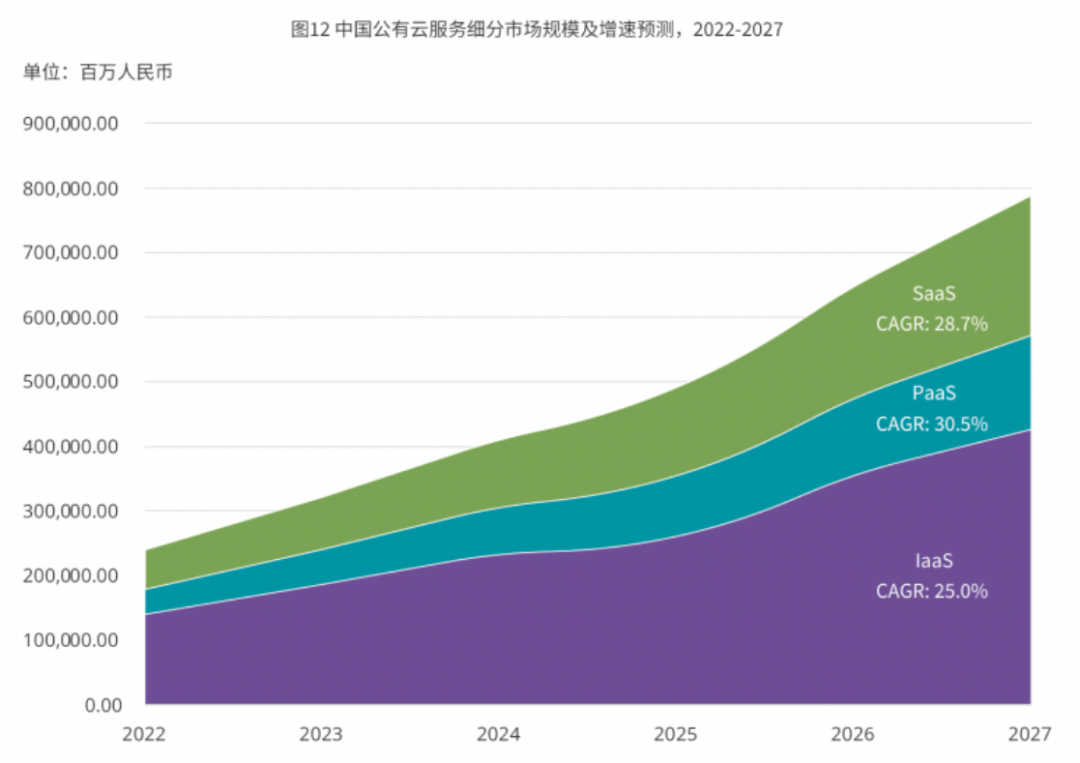
IDC's report also highlights that the rapid development of generative AI and large models is accelerating PaaS's emergence as the core capability of the next-generation intelligent cloud. As the intermediate layer, PaaS bears the pressure of IaaS's rapid expansion while supporting SaaS's platform capabilities. PaaS becomes a crucial link in helping enterprises comprehensively build and apply AI capabilities. Enterprise users' demand for cloud services primarily manifests in three aspects: acquiring AI-powered applications on the cloud, accessing AI-enhanced tools, and realizing AI-driven application innovations. IDC believes the next-generation cloud will be an "intelligent cloud" tailored to enterprises' intelligent development needs. Cloud serves as the soil for AI implementation and growth, while AI propels cloud platform advancements. Technically, enterprises need intelligent architectures and systems to accelerate AI adoption. Operationally, they leverage cloud platforms' resource management capabilities to automate workflows and enable intelligent operations. Ecologically, they rely on next-generation cloud-based intelligent tools to enhance product development efficiency and industrial collaboration, fostering intelligent innovation. After over a decade of development, cloud computing, when combined with AI, especially large models, is evolving towards greater intelligence.

Cloud Computing's "Second Growth Curve"
Generative AI is sweeping across industries, and "going cloud" is often the first choice for enterprises seeking to embark on the new era. Generative AI necessitates cloud computing while also fueling its growth. Microsoft, with OpenAI as its copilot, exemplifies this dynamic.
On April 25th, Microsoft released its fiscal Q3 2024 earnings report, revealing that its cloud business generated $35.1 billion in revenue, a 23% YoY increase. The Intelligent Cloud segment contributed $26.7 billion, up 21% YoY, with Azure and other cloud services revenue growing 31% and AI's contribution to Azure revenue rising to 7%, up from 6% in Q2 and 3% in Q1. Apple's AI strategy similarly showcases integration with ChatGPT, allowing users to summon Siri and leverage ChatGPT across writing tools for chatbots, image generation, and more, all processed in the cloud. This underscores AI inference's cloud-centric future, at least for the next three to five years. China's market is also prepared, as evidenced by Huawei Cloud's Ascend Cloud Service launched last September, which not only meets basic AI computing needs but also offers efficient, stable large model training environments and comprehensive toolchains, reducing end-to-end development time for 100 billion-parameter industry models from 5 months to 1. Large model vendors are also shifting towards cloud-based training and inference, with MiniMax renting cloud computing power instead of purchasing GPUs. This trend extends beyond cloud vendors and large model firms, as traditional industries adopt AI and cloud strategies.
Taking the automotive industry as an example, the anticipated penetration rate of intelligent and connected vehicles exceeds 90% in the next five years, generating petabytes of data. Given the underutilized data value in the automotive sector, AI-driven data applications are inevitable. Cloud-based autonomous driving data closed-loop platforms establish end-to-end AI foundations encompassing computing power, algorithms, and data. If resource and application cloud adoption represent cloud computing's "first growth curve," the surging demand for generative AI will usher in a "second growth curve," opening new incremental markets as underlying resource demand gradually saturates.

Cloud Giants Focus on Large Model Ecosystems
Since last year, China's cloud giants have embraced AI wholeheartedly. Despite the IaaS+PaaS market's lowest YoY growth rate in three years in H1 2023, large models have emerged as a new growth driver for cloud vendors, with AI ecosystems playing a pivotal role. Alibaba Cloud, for instance, introduced the MaaS model concept in late 2022, coinciding with ChatGPT's rise. At the 2023 Yunqi Conference, Alibaba Cloud CTO Zhou Jingren revealed that half of China's major large model companies, including Baichuan Intelligence, Zhipu AI, ZeroOne AI, Kunlun AI, vivo, and Fudan University, run on Alibaba Cloud.
Alibaba Cloud's ModelScope, an open-source community, offers two services: direct access to Alibaba Cloud's computing power and large model training/inference platforms, and one-stop services for ecosystem partners, including model retraining and data training tailored to specific business scenarios. Tencent Cloud has also made strides, announcing a 200% YoY growth in its integrated revenue over the past two years at the Tencent Cloud Eco-Conference earlier this year. Post-large model launch, Tencent Cloud allocated 80-90% of its integrated business revenue to partners. Tencent Cloud's shift towards an "integrated" business model signals a departure from its role as a "general integrator" towards a MaaS model, facilitating vertical industry knowledge accumulation. This strategy has yielded significant resources across healthcare, finance, tourism, media, government, and education.
Vertical large models are often developed in collaboration with ecosystem partners. Tencent Cloud provides PaaS-level capabilities, while vertical industry leaders contribute data and requirements. Specialized vertical model development teams then deploy customized solutions. Huawei Cloud adopts a similar approach, partnering with software, service, consulting, and system integration partners. It supports the deployment of Pangu large models, open-source models, and third-party commercial models, offering data engineering, model development, and application development suites to help users build independent datasets and enhance base models. Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and Huawei Cloud have adopted more open and decisive MaaS-level ecosystem strategies, providing ample opportunities for ecosystem partners in terms of computing power and data. Their MaaS ecosystem models are now largely established, leveraging computing power as a foundation and focusing on large model collection, annotation, and pre-training to accelerate their own ecosystem development and support large model implementations.

The Evolution of Cloud Vendors' "Public Cloud" in the Era of Large Models
The shift from IaaS+PaaS+SaaS to IaaS+PaaS+MaaS represents cloud vendors' new profit model in the era of large models. This transition from directly offering SaaS to exploring MaaS signifies a commitment to the "integrated" ecosystem model. This model aligns with the trend of "public cloud + AI," increasingly becoming the norm. From a market demand perspective, public clouds significantly reduce AI model costs amid GPU computing power shortages. Additionally, the public cloud's AI large model model can drive cloud vendor growth. Cloud vendors generate revenue through API calls (charged per token count) and providing secondary development services to large enterprises, relying on either their own computing power accumulation or partnerships with domain experts.
Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud, and Huawei Cloud have focused on developing vertical domain large models, partnering with industry leaders to train domain-specific models based on locally deployed or public cloud models. These capabilities are then integrated into their public cloud offerings and embedded into products like Baidu Wenku, Tencent Meeting, and Alibaba DingTalk. Overseas cloud vendors offer precedents for exploring large model ecosystem models.
Microsoft Azure, rather than developing its own large model, leveraged GPT to offer services when ChatGPT gained popularity. Its products like Windows, Office, and Bing integrated AI Copilot assistants, forming a cloud-AI-software business loop. Cloud computing's growth engine is shifting from price-driven to demand- and value-driven, compelling cloud vendors to realign their market strategies, invest in core areas, and return to rational growth. Looking ahead, AI's disruption of cloud computing is just beginning. While traditional cloud services centered on functionality, future services will focus on scenarios, leveraging large model capabilities to transcend functional boundaries and solve problems contextually. Cloud computing will evolve from a resource-centric to a scenario-centric foundation for the intelligent world. A new era dawns, integrating fresh energies and unleashing new waves of innovation.
"Large Models + Robotics": Embodied Intelligence Ushers in the "Age of Intelligent Machines"
AIGC Revolutionizes Computing Power Demand; Edge Computing No Longer Marginalized
From "Computing Power Nuclear Bomb" to Generative AI: How Far is the New Era?
Large Models Drive Technological Waves; AI Security Governance Faces a "Grand Examination"
Can the Symbiotic Growth of AI and Cloud Computing Unlock the Next High-Growth Space?
[Original Report by TechCloud]
Please indicate the source as "TechCloud" and include a link to this article when reposting.