MED: A Potential Game-Changer, Emerging as the Premier Choice for "Warm and Cold" Data Storage
![]() 11/14 2025
11/14 2025
![]() 510
510
In recent years, the global market for data center storage has witnessed exponential growth, evolving along a dual trajectory characterized by "quantum leaps in magnitude and accelerated growth rates."
Since the dawn of the AI era, the trajectory of data growth has steepened dramatically. By 2024, data volumes had surged past 1.1 Zettabytes (ZB), marking a pivotal transition from Exabytes (EB) to Zettabytes, and are projected to soar to 2.4 ZB by 2028. In the AI landscape, algorithms, computing power, and data constitute the three pillars.
Historically, the industry's focus has centered on computing power and algorithms. However, with the escalating demand for large-scale model training, edge computing, and real-time inference, the significance of data has risen substantially. Data serves as the cornerstone for both training and inference processes, while storage systems underpin the physical hosting and efficient retrieval of data.
The evolution of storage technology directly influences data scalability, retrieval speed, cost-effectiveness, and the training efficiency of AI models. Storage has transcended its traditional role as a mere data repository, evolving into a critical determinant of AI performance. Consequently, storage systems have entered a new era of multi-dimensional optimization, focusing on "capacity, performance, and efficiency."
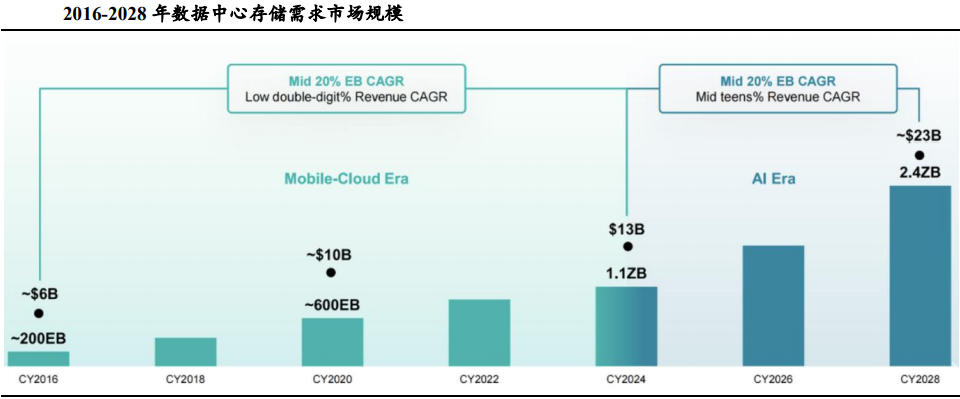
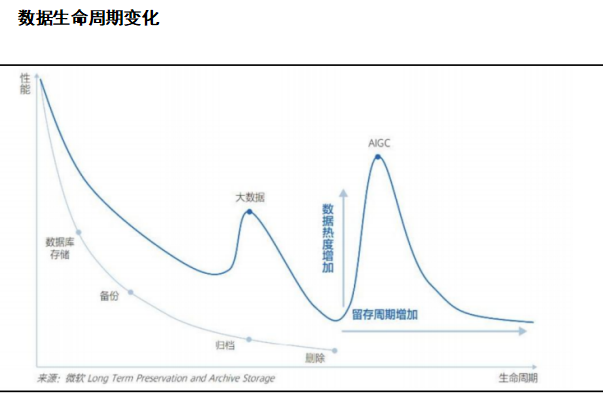
The escalating demand for data access in large-scale model training and inference, coupled with a substantial increase in data volume, has led to the reactivation of a significant portion of previously deemed "cold data." Owing to their frequent involvement in model iteration and real-time inference, this data has gradually transitioned into "warm data" and, with sustained utilization, even evolved into "hot data."
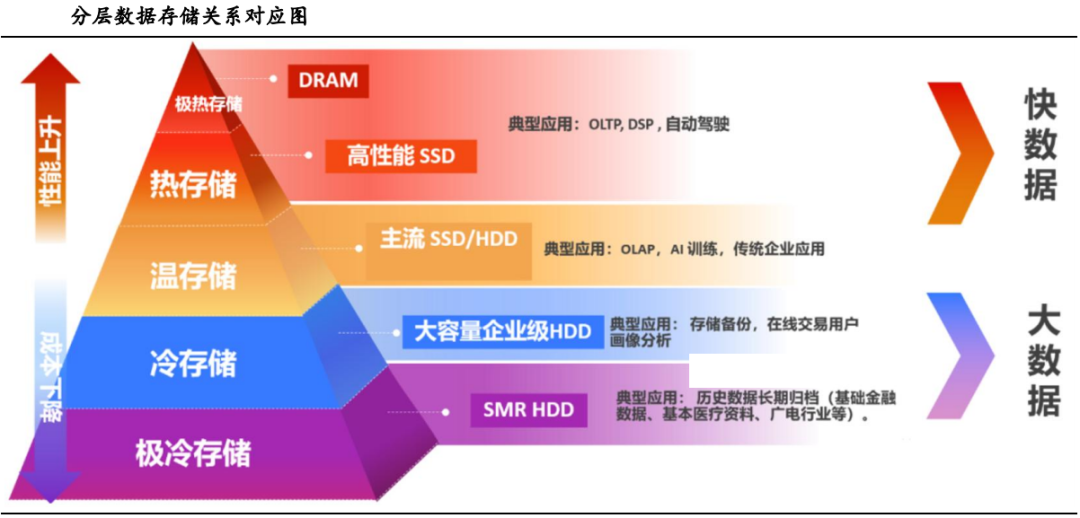
From a storage media perspective, traditional data centers classify data into three tiers: "hot," "warm," and "cold." Cold data is predominantly stored on Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and magnetic tapes; warm data is primarily housed on HDDs and Solid-State Drives (SSDs); and hot data is mainly stored on SSDs and Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DRAM). Given the trend of cold data transitioning to warm, I anticipate a surge in demand for SSDs and emerging storage media like Magnetoelectric Storage Devices (MEDs).
Currently, HDDs remain a vital component of low-frequency data storage, with sustained demand. Enterprise-grade SSDs have shifted their competitive edge from "sole performance superiority" to "Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) advantage," experiencing significant demand growth. Additionally, Huawei's MED technology aims to supplant traditional HDDs in warm and cold data storage sectors.
Therefore, I foresee SSDs and MEDs partially replacing HDDs in future warm data storage scenarios.
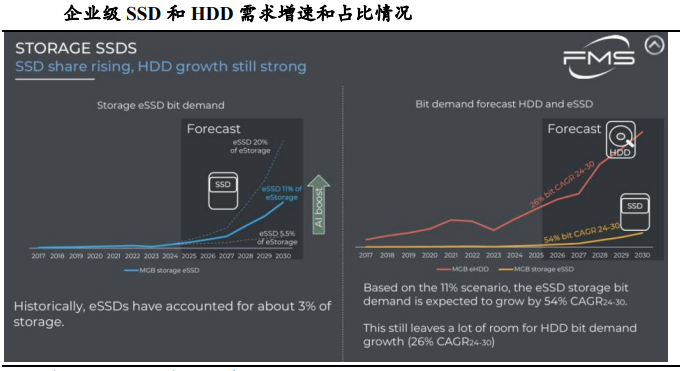
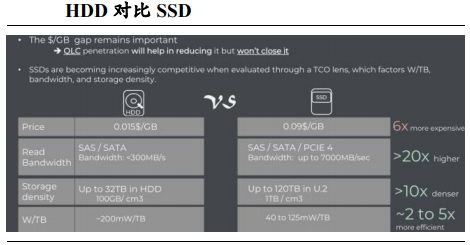
Compared to HDDs, SSDs already offer a TCO advantage and are poised to partially replace HDDs in warm storage environments. The MED technology, with its clear strategic objective, aims to replace traditional HDDs in warm and cold data storage.
Tiered Storage
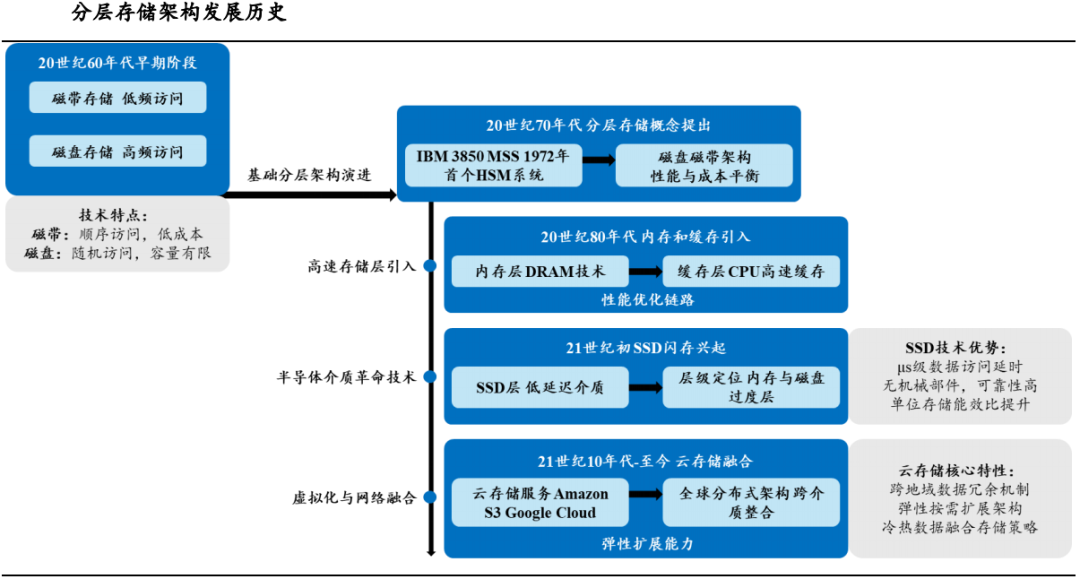
The concept of tiered storage in computer storage technology first emerged in the 1960s. At that time, storage media primarily consisted of magnetic tapes and disks with limited capacity. Due to the slow sequential access speed of magnetic tapes and the insufficient capacity of disks, system designers began to implement preliminary tiering strategies based on data usage frequency: frequently accessed data was stored on disks, while infrequently used data was archived on magnetic tapes. This laid the groundwork for the subsequent development of tiered storage.
From the 2010s to the present, hierarchical storage architectures have undergone a profound transformation, integrating seamlessly with cloud computing and distributed technologies. Cloud service providers have extended the concept of hierarchical storage to global distributed systems, offering a diverse range of storage categories from standard to archival storage.
Traditional "one-size-fits-all" storage solutions are ill-suited to the data characteristics of the AI era, whereas tiered storage precisely addresses core challenges through a "demand-matching" approach.
Faced with the explosive growth of data volumes and increasingly complex storage demands, the innovative concept of tiered storage was proposed as early as 2021. This concept advocates for classifying data into five tiers based on usage frequency and access performance requirements: extremely hot, hot, warm, cold, and extremely cold storage. Each tier is matched with appropriate storage media and solutions, aiming to finely cater to the diverse needs of enterprises in terms of data capacity, performance, TCO, and energy consumption.
Magnetoelectric Storage
In March 2024, Huawei unveiled its groundbreaking product, Magnetoelectric Storage (MED), at the Mobile World Congress in Barcelona. Huawei stated that the MED innovates on magnetic media by integrating SSDs with self-developed tape drives, effectively optimizing storage solutions for "warm and cold data."
The inherent characteristics of MED make it well-suited for low-frequency data storage scenarios, and in the future, MED is poised to replace HDDs as the optimal solution for "warm and cold data."
MED is expected to supplant traditional HDDs, revolutionizing warm and cold data storage. The fundamental principles of both HDDs and MED revolve around achieving deterministic magnetic flipping and electron spin control. The distinction lies in MED's utilization of the magnetoelectric coupling effect, endowing it with both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties. This enables MED to generate four distinct states: positive and negative magnetization and positive and negative electrode polarization, providing the conditions for four-state storage.

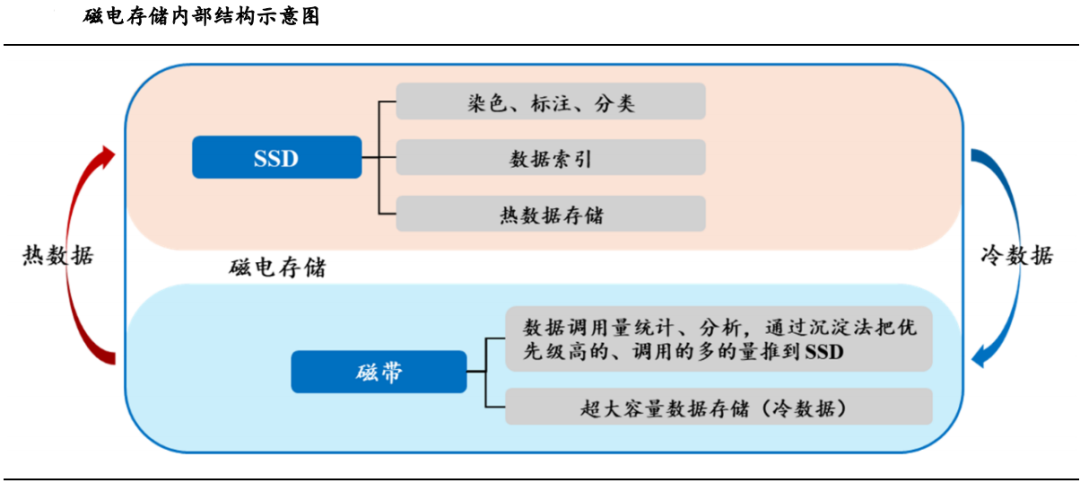
The efficiency of Huawei's MED technology is not solely attributed to its innovative hybrid hardware architecture but also to its sophisticated data management mechanism. This mechanism orchestrates data flow between SSD and tape storage media, ensuring accurate data writing, location, migration, and retrieval. Through intelligent data tiering and metadata management, the MED system achieves an optimal balance between performance and cost while maintaining data reliability.
This refined data management approach is pivotal to MED's successful replacement of traditional HDDs and simplification of storage architectures.
The introduction of Huawei's MED technology is poised to disrupt the prevailing storage architectures in data centers, offering users unprecedented advantages in terms of performance, cost, and energy efficiency.
Currently, MED technology primarily targets the archival storage market for data centers and cloud service providers, but its future development potential extends far beyond. Through continuous technological advancements, the application scope and market share of MED technology are expected to expand significantly.
I believe that MED technology presents a significant opportunity for China to achieve self-reliance and surpass international competitors in the storage industry!
Disclaimer: The individual stocks or companies mentioned in this article are solely associated with the industrial chain or relevant hot topics. The information, data, and opinions cited are recorded for personal research purposes. The mention of individual stocks or companies is for case study discussions only and does not constitute any trading recommendations.
Stick Tech (300806)
In January 2025, the company ventured into magnetic media-related businesses and secured technical patents. These patents focus on verifying the adaptability of magnetoelectric hybrid media (MED) in enterprise-level storage systems and industrial sensor applications. I believe that with the escalating demand for warm and cold data storage, such media, with their optimized "performance-cost" characteristics, will emerge as a key technological pathway for the localization and substitution of data center storage.
The rapid surge in enterprise-level data volumes has made long-term archiving, disaster recovery storage, and cold data management increasingly critical. Magnetic media, with its low cost, high durability, and low energy consumption, maintains an irreplaceable position in critical sectors such as finance, telecommunications, energy, broadcasting, and public utilities. The company's magnetic media technology is poised to become the optimal solution for meeting low-frequency data storage demands.
*Reiteration: All information mentioned in this article is sourced from announcements released by listed companies, industry associations, and publicly available research reports from licensed institutions. It is important to note that the article does not directly cite any third-party investment advice or conclusions. The purpose of this article is solely for discussion and research, and all content presented does not constitute any form of investment recommendation.








