Behind the collapse of scalpers for Huawei and Apple, a quiet change is taking place in the consumer electronics market
![]() 09/28 2024
09/28 2024
![]() 536
536
Last week, on September 20th, Apple and Huawei both released their new phones on the same day, igniting the most eye-catching head-to-head battle in the mobile phone industry this year. A large number of scalpers also arrived as scheduled, like every year, hoping to make a fortune by capitalizing on the new product launch. However, the subsequent developments caught many people off guard.
Less than a week after the new phones were released, the premium charged by scalpers fell rapidly from the initial high levels. Many tech bloggers posted videos on social media claiming that the price of Huawei's tri-fold phone had dropped from an initial markup of over 100,000 yuan to just 4,000 yuan. Meanwhile, if the Apple iPhone 16 wasn't the Pro version, scalpers found themselves stuck with unsold inventory. Some joked that it was a case of "phones not selling, save the scalpers," while others believed that the appeal of leading brands was waning, a warning sign for both Apple and Huawei.
But the real story may have nothing to do with the phones themselves. Instead, it's the rapidly rising trend of instant retail, a new channel that is shaking up the stubbornly old-fashioned scalping industry.
Platforms like Meituan, JD.com, and Ele.me have been heavily investing in instant retail in recent years, expanding their cooperation with brands and enhancing their fulfillment capabilities across the board.
As a result, we've seen the delivery times for various new electronic products shrink from days to hours, or even minutes. Since 2023, companies like Apple, Huawei, and vivo have successively launched new products on Meituan Flash Delivery, with over 75% of customers receiving their phones within 30 minutes, and the fastest delivery time even reaching 5 minutes and 36 seconds. It truly embodies the idea of "just after making a phone call, the takeout is delivered to the door."
By ordering phones through takeout apps, instant retail satisfies consumers' hard-core demands for speed, priority, and no queues. In terms of authenticity guarantees and after-sales service, scalpers simply cannot compete.
After years of persistent efforts to curb scalping, the industry's innovation has finally demonstrated its powerful impact. For instant retail, cracking down on scalping is just a small matter. The real changes go far beyond that.
1. The Third Way Beyond Stores and E-commerce
For a long time, the consumer electronics industry has relied primarily on two sales channels: online e-commerce and offline retail stores. Over the past 20 years, these channels have largely covered most consumer needs. However, as consumer behavior evolves, there are unmet needs beyond the reach of both e-commerce and physical stores that have grown to a significant level.
According to the "White Paper on Instant Retail in the Consumer Electronics Industry," based on a survey of 2,000 users, 37% and 28% of consumers, respectively, cited "complex discount mechanisms" and "inconvenient returns and exchanges" as drawbacks of express e-commerce. For offline stores, 52% and 40% of consumers, respectively, noted "high prices" and "incomplete product offerings" as issues.
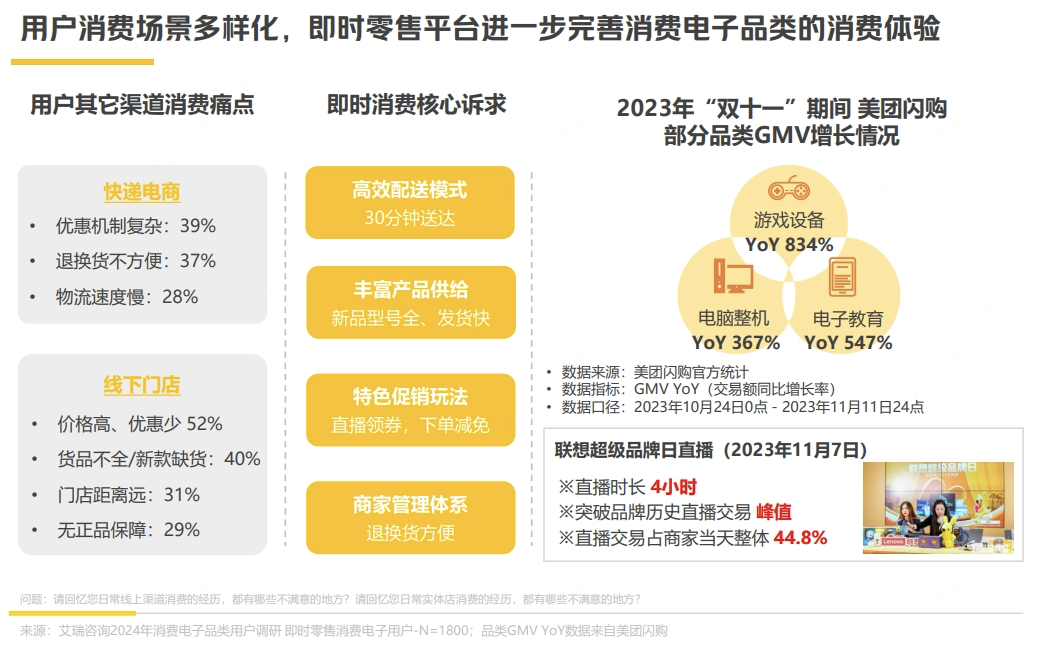
Instant retail aims to address these pain points by offering a combination of speed, variety, quality, and savings, along with advantages such as a full range of new product SKUs, fast shipping, convenient returns and exchanges, and discounts on orders.
Taking Apple as an example, nearly 7,000 Apple Authorized Resellers nationwide joined Meituan Flash Delivery to sell new phones this year. In previous years, only stores in first- and second-tier cities participated in Apple's new product pre-sales on Meituan Flash Delivery. After optimizing the model this year, the number of stores supporting the first batch of pre-sales doubled, with a focus on lower-tier cities and counties.
Furthermore, amidst the ongoing price war in e-commerce, instant retail has taken a different path. Rather than dragging merchants into the fray, it leverages incremental benefits provided by the platform to help merchants sell more effectively without engaging in price wars. In addition to live streaming promotions, interest-free installments, and other common practices, a key feature of instant retail platforms is their ability to leverage localized platform attributes to match targeted benefits with new product launches, thereby boosting sales for merchants.
For instance, Meituan Flash Delivery offered a 16-month membership to its Super membership program for customers who purchased select Apple or Huawei flagship phones this year. This membership provides benefits across various local consumption scenarios, including food delivery, group dining deals, hotel bookings, leisure activities, and daily necessities. Such targeted promotional benefits demonstrate the importance and resource tilt instant retail platforms place on consumer electronics merchants.
2. Tapping into the Increasingly Rare Incremental Market
In recent years, as China's population growth has stabilized and urbanization has matured, most industries have entered a fierce competition for market share. Consumer electronics, one of the biggest beneficiaries of population growth and urbanization, has seen many predict that further significant growth will be difficult to achieve.
However, the rise of instant retail has changed the game. We've discovered that by meeting previously overlooked needs, even established markets can generate new growth.
From 2019 to 2023, the combined online and offline sales of smartphones declined from 360 million units to 270 million units. In contrast, the number of smartphones sold through instant retail channels increased from 370,000 to 9.6 million units.
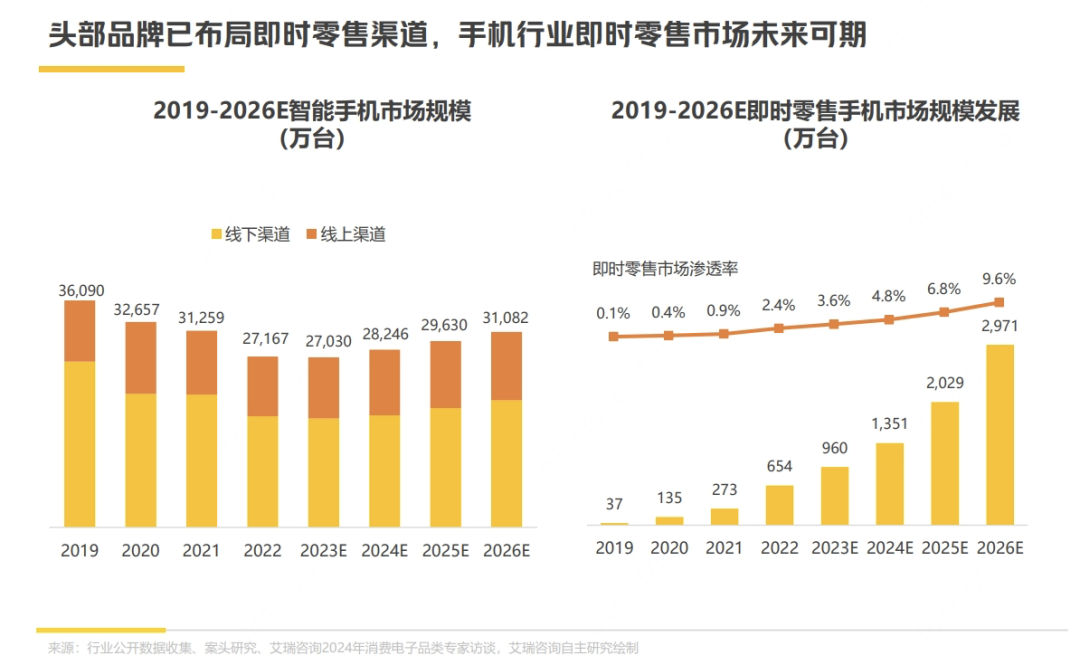
Other categories like computers, digital products, and major home appliances have followed a similar trajectory, with traditional channels stagnating while instant retail continues to grow. This suggests that many potential customers who were previously dormant due to unfulfilled needs are now being awakened by instant retail.
The primary consumer group for instant retail is currently composed of individuals born in the 1990s and 2000s. Compared to online and offline shoppers, they tend to be younger, more educated, earn higher incomes, and pay closer attention to leading brands. This younger demographic values novelty, immediacy, and the latest experiences, making them highly sensitive to new products and delivery efficiency, with stronger purchasing power and willingness to spend.
According to the aforementioned White Paper, the average purchase price of phones through instant retail channels is 4,936 yuan, nearly 400 yuan higher than the average price through non-instant retail channels. Among these purchases, 34% are for high-end phones priced above 6,000 yuan, and the annual replacement rate is 8%, double the 4% seen in traditional channels.
Notably, many of these consumers' first experiences with instant retail began with food delivery and gradually expanded to daily necessities and, eventually, electronic products. This consumer migration pattern demonstrates how instant retail is infiltrating from essential to non-essential scenarios, evolving from an emergency-focused, low-frequency consumption model to a diverse, high-frequency one. High-potential consumption scenarios such as new product launches, promotional purchases, and gift-giving rely on the inventory of new products, discounts, and delivery speed that instant retail excels at providing.
In addition to expanding consumption scenarios, the boundaries of what consumers are willing to purchase through instant retail are also growing. Mr. Chen, a resident of Shenzhen, mentioned that his earliest electronic purchase through food delivery was a portable charger for travel emergencies. Later, he bought an iPhone 14 for its discount and direct delivery from an authorized store. Now, he even buys air conditioners through food delivery apps.
There are many consumers like Mr. Chen who have transitioned from using food delivery for emergencies to trying new things and, eventually, incorporating it into their daily lives. It is reasonable to believe that instant retail is fostering new consumer habits, much like food delivery did a decade ago. Once these habits are formed, their power becomes immense.
Over the past three years, the consumer electronics market within instant retail has grown from 11.1 billion yuan to 39.9 billion yuan, with a compound annual growth rate of 68.5%. Based on this trend, the market is projected to exceed 150.5 billion yuan by 2026. In the same year, the overall instant retail market is expected to reach 1 trillion yuan. With a trillion-yuan market on the horizon, instant retail has naturally become a crucial battleground for consumer electronics merchants.
3. Multi-brand Competition in Instant Retail
Instant retail has uncovered a significant incremental market, and it's clear that consumers ordering phones through food delivery apps is not just a passing fad but rather a sign of future consumption growth. This certainty is one of the most valuable elements in today's uncertain market.
As a result, leading mobile phone brands such as Huawei, Apple, Xiaomi, vivo, and OPPO have actively increased their cooperation with instant retail platforms like Meituan Flash Delivery, JD Express, and Ele.me over the past two years. Instant retail is gradually becoming the primary channel for new product launches across brands. In September 2023, the iPhone 15 series was first offered for pre-sale on Meituan Flash Delivery; in November 2023, vivo's iQOO 12 series debuted on the platform; and in January 2024, the OPPO Find X7 was released through Meituan Flash Delivery.

Over the past decade, China's food delivery network has expanded nationwide. In terms of both absolute numbers and coverage area, the user base accessible to instant delivery platforms far exceeds what any single brand could reach through traditional means.
Channels are an eternal topic in the business world, but their development is always constrained by costs and efficiency, especially in lower-tier markets. Opening exclusive stores poses financial pressures on brands, while relying solely on e-commerce logistics can compromise timeliness. Instant retail, however, plays a crucial role in expanding markets, attracting new customers, and addressing shortcomings for brands. By leveraging consumers' existing habits of shopping for food and daily necessities through delivery apps, instant retail can support the ecological development of various brands and operations across the entire supply chain, from digital devices to large home appliances.
As instant retail evolves, the relationship between people, products, and locations is being further restructured. Younger consumers demand differentiated experiences, while brands seek out emerging channels. Instant retail platforms are proactive in injecting new growth momentum into upstream and downstream industries.
The new era of retail has arrived, presenting both opportunities and challenges for brands and retailers alike. The next decade's sales success may hinge on seizing these opportunities. For instant retail platforms, the competition is fierce, with many seasoned players vying for market share. To survive and thrive in this intense race, full commitment and relentless innovation are essential.