Q2 Financial Report Highlights: Xiaomi's Automotive Business Revolutionizes Growth Dynamics
![]() 08/21 2025
08/21 2025
![]() 677
677
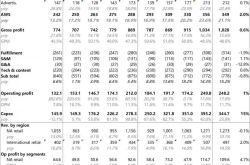
In the second quarter of 2025, Xiaomi Group surpassed market expectations with remarkable financial performance: revenues soared to RMB 116 billion, marking a 30.5% year-on-year increase, and adjusted net profit reached RMB 10.8 billion, up 75.4% from the previous year. Notably, the automotive business emerged as a standout contributor, delivering 81,300 new vehicles in a single quarter, generating RMB 20.6 billion in revenue, a 234% year-on-year surge, and accounting for 17.8% of the group's total revenue.
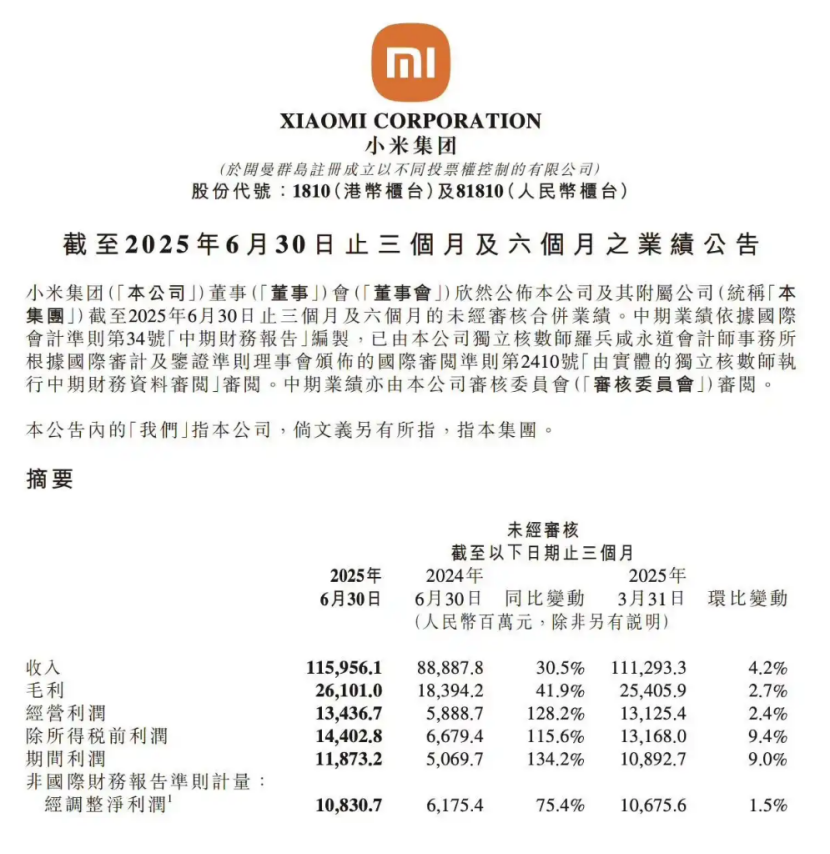
More significantly, the automotive business's gross profit margin climbed from 23.2% in Q1 to 26.4%, with operating losses narrowing from RMB 500 million to RMB 300 million. Each vehicle now generates a gross profit of RMB 67,000, positioning Xiaomi on the brink of profitability. This stellar performance not only sets a new pace for emerging auto companies but also signals Xiaomi's transformation of the competitive landscape in the new energy vehicle industry with its unique "ecosystem-based vehicle manufacturing" model.
▍Synergistic Growth from Scale and Product Strategy
The explosive growth of Xiaomi's automotive business in Q2 can be attributed to the accelerated realization of scale effects. Despite not being an industry leader in quarterly deliveries, Xiaomi's concentrated product strategy focusing on the SU7 series has enabled efficient parts procurement and cost dilution in manufacturing. For instance, as procurement volumes increase, the cost of CATL's Qilin II battery pack is 18% lower than imported battery cells, while Xiaomi's self-developed V8s motor costs only half of Bosch's similar product yet delivers 1,548 horsepower. This "transparent hardware parameters + vertical supply chain integration" model reduces the SU7's parts cost by approximately 25% compared to traditional automakers, laying the groundwork for margin improvement.

Product structure optimization also played a pivotal role. The SU7 Ultra model, which commenced deliveries in Q2, significantly raised the overall average price with its RMB 529,900 price tag and premium features. Standard-equipped carbon ceramic brake discs and lightweight carbon fiber components, traditionally reserved for ultra-luxury brands and supercars, are now accessible in the RMB 500,000 market segment, enhancing product premium while keeping costs in check. This "technology democratization" strategy allows Xiaomi to maintain an average price (inclusive of tax) of RMB 280,000 amidst intense price wars, differentiating it from cost-efficiency-focused competitors.
Capacity expansion is equally crucial. Xiaomi's Yizhuang Phase I factory in Beijing has achieved a monthly production capacity of 32,000 vehicles with double shifts, and Phase II is expected to commence production in Q3, bringing total annual capacity to over 500,000 vehicles. Notably, Xiaomi's automotive manufacturing efficiency is among the industry's best, with one SU7 rolling off the production line every 76 seconds. This efficiency advantage ensures the timely delivery of YU7 series orders (currently exceeding 200,000 backlogged orders) in the second half of the year.
▍Navigating Towards Profitability
Despite its impressive achievements, Xiaomi's automotive business still grapples with the industry-wide challenge of increasing expenses with scale. In Q2, automotive business operating expenses amounted to RMB 5.9 billion, encompassing R&D, sales, management, and other expenditures, resulting in a per-vehicle cost-sharing of up to RMB 73,000. This expense structure mirrors the reality of asset-heavy industries: Since 2022, Xiaomi has invested over RMB 30 billion in automotive and other innovative ventures, with quarterly R&D investment reaching RMB 7.8 billion, a 41.2% year-on-year increase. While this intense investment fortifies technical barriers, profitability pressure will persist until sales volume reaches a critical threshold.
Market competition's complexity cannot be overlooked. Xiaomi steadfastly refuses to engage in price wars, yet the RMB 250,000-350,000 market segment it primarily targets has become fiercely contested. Competitors like BYD Han and Xpeng P7+ are capturing market share through price reductions, and Tesla has launched a facelifted Model Y. More alarmingly, competitors' counterattacks are intensifying—NIO, AITO, Li Auto, and other automakers are diverting potential Xiaomi customers through various channels, exerting pressure on Xiaomi.
The depth and breadth of ecological synergy may prove key to breaking this deadlock. Xiaomi's unique advantage lies in its vast IoT user base (Q2 IoT business revenue of RMB 38.7 billion, a 44.7% year-on-year increase) and internet service ecosystem (gross profit margin of 75.4%). For instance, users can remotely control vehicle air conditioning and schedule charging via Xiaomi mobile phones, and there are currently 32 scenarios for in-car system and Mijia smart device interconnection. This "hardware + software + services" closed loop not only enhances user stickiness but also generates differentiated profit margins—internet services contributed a gross profit of RMB 6.9 billion in a single quarter, providing stable cash flow support for the automotive business. However, transforming this ecological advantage into a direct driving force for car purchases remains to be seen.
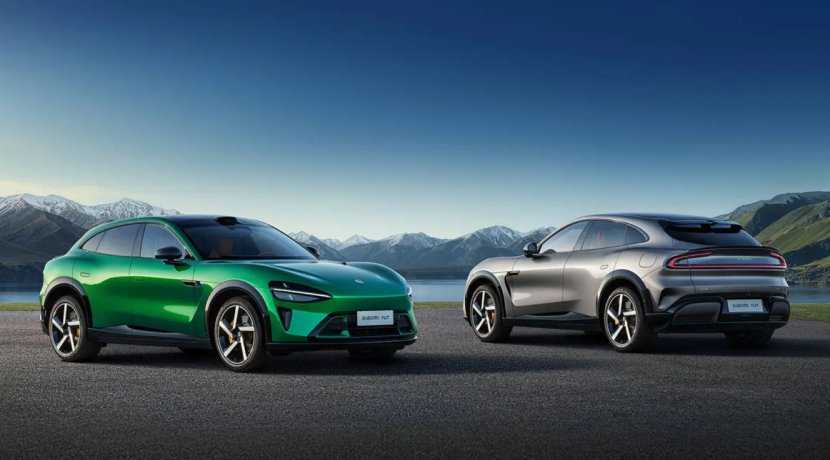

Xiaomi's automotive performance in Q2 signifies its transition from the "survival stage" to a new phase of "balancing scale and profitability." Based on financial report data, if Xiaomi stabilizes monthly automotive deliveries at 30,000 to 35,000 vehicles, with quarterly deliveries exceeding 90,000, it can achieve overall profitability by covering expenses with per-vehicle gross profit. The YU7 received 289,000 orders within an hour of its official launch and currently has over 200,000 backlogged orders, making it highly likely to achieve this target post-capacity expansion.
The YU7's success extends beyond sales, significantly altering Xiaomi's automotive user structure. It further increases the proportion of female users by 4.5% compared to the SU7, reaching 30% among initial locked-in users. Additionally, Apple users account for 52.4%, 4.4 percentage points higher than the SU7. This user structure shift not only enhances brand appeal but also opens up broader market opportunities for Xiaomi's ecological business. Some analysts predict that Xiaomi could enter the quarterly profitability stage by the end of 2025, potentially even earlier than Xpeng and NIO.
However, whether the YU7 series' deliveries in the second half of the year continue to exceed expectations and whether Phase II factory capacity ramps up smoothly will determine Xiaomi's ability to achieve its quarterly profitability goal by the end of 2025. More importantly, maintaining technology investment intensity while reducing hardware profit dependence through ecological synergy will be Xiaomi's core competitiveness, distinguishing it from traditional automakers.
From an industry perspective, Xiaomi's automotive business rise is rewriting the rules: While Tesla defines cars through software and BYD reduces costs through vertical integration, Xiaomi has chosen a third path of "ecosystem empowerment + supply chain revolution." If this model continues to succeed, it will unlock vast growth potential for Xiaomi. In late June, Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs issued research reports projecting that by 2030, Xiaomi's overall revenue could reach RMB 1 trillion, with net profit potentially reaching RMB 100 billion, valuing the company at HK$2.5 trillion (approximately US$220 billion), and the share price soaring to HK$100, directly competing with Apple and Tesla.
Typeset by Yang Shuo
Image Source: Xiaomi Group