How Autonomous Vehicles Perceive and Interpret Traffic Signs
![]() 01/15 2026
01/15 2026
![]() 355
355
When we're behind the wheel and aiming to navigate our journey successfully, we instinctively keep an eye out for speed limit signs, stop and yield signs, or upcoming turn instructions. Autonomous vehicles, too, require this capability to operate safely. They "observe" their surroundings through sensors like cameras and radars, with the computer system interpreting and processing this data. Among the myriad tasks, traffic sign recognition stands as a pivotal link. Only by accurately identifying diverse traffic signs can autonomous vehicles adhere to traffic rules and make sound decisions in real-world driving scenarios.
The Imperative of Traffic Sign Recognition
One of the key objectives of the perception module in an autonomous driving system is to discern various traffic signs on the road. Traffic sign recognition, commonly abbreviated as TSR, primarily captures road scene imagery via onboard forward-facing cameras. After undergoing a series of algorithmic processes, it ultimately presents traffic sign information in a comprehensible format. The recognition system must not only locate the traffic sign but also ascertain its content, subsequently transmitting this information to the vehicle control system for subsequent decision-making. This technology is paramount in autonomous driving. Incorrect recognition could lead the vehicle to operate under erroneous rules, posing safety risks.

Image source: Internet
Traffic sign recognition typically comprises two key stages: detection and classification. Detection involves pinpointing areas within the image that may contain traffic signs, while classification determines the specific content represented by the sign. This process mirrors how humans visually interpret images, but for machines, it entails intricate visual algorithms and extensive sample learning. Autonomous vehicles seamlessly integrate these two steps, also accounting for the impact of complex scenarios like lighting variations, occlusions, and motion blur on traffic sign recognition.
Perceiving the World: Starting with Camera Image Acquisition
To recognize traffic signs, autonomous vehicles must first "see" them. These vehicles are generally equipped with high-resolution cameras, along with sensors such as lidars and millimeter-wave radars, at the front. However, the primary responsibility for traffic sign recognition lies with the cameras. Cameras can perceive visual information like traffic signs, vehicles, pedestrians, and background buildings ahead of the road, akin to human eyes, providing a foundational information base for autonomous vehicles to recognize traffic signs.
The raw images captured by the camera may suffer from issues such as noise, uneven exposure, and motion blur. To enhance the accuracy of subsequent recognition, these images require preprocessing. Common preprocessing techniques include color space conversion, noise filtering, and image correction. These operations render the images more amenable to algorithmic interpretation. For instance, converting RGB (red, green, blue) images into HSV (hue, saturation, value) space can accentuate specific color ranges, facilitating the discovery of signs in various hues.
Following collection and preprocessing, the autonomous driving system must identify areas within the image that may contain traffic signs. Early methods relied on visual features like color and shape for detection. For example, a circular shape with a red border might indicate a speed limit sign, while a triangle could signify a warning sign. These features aid the autonomous driving system in swiftly distinguishing signs from the background. More advanced traffic sign recognition technologies predominantly leverage deep learning algorithms. Through neural network models, they can autonomously learn the features of numerous sign samples, enabling accurate traffic sign detection even in complex backgrounds.
How Deep Learning Facilitates Traffic Sign Recognition
Over the past decade, traditional image processing methods primarily depended on manually designed features such as edges and colors. However, for the complex and ever-changing scenarios encountered on actual roads, this approach is susceptible to interference from factors like lighting changes, occlusions, and tilts, limiting recognition accuracy. With the advent of deep learning, particularly convolutional neural network (CNN) technology, traffic sign recognition has entered a new era. Deep learning models can autonomously learn features from vast amounts of data. Compared to traditional methods, recognition techniques based on deep learning models offer higher robustness and accuracy.

Image source: Internet
The crux of deep learning lies in constructing a neural network model. This model comprises numerous layers of computing units (also known as neurons or convolutional layers), which progressively extract features from simple edges to more complex shapes and structures within the image. The neural network model is initially trained using a large-scale dataset. This dataset encompasses various traffic sign pictures along with their corresponding label information. The training process essentially enables the model to learn to map the input image to the correct sign category. Common neural network architectures include basic networks like VGG and ResNet, as well as object detection models such as the YOLO series, SSD, and Faster R-CNN, which can handle both detection and classification tasks.
Taking the YOLO (You Only Look Once) model as an illustration, this type of model can input the entire image into the network simultaneously. The network divides the image into grids and predicts whether each area contains a target and the target category. This approach not only swiftly detects the location of the traffic sign but also determines its type. In actual tests of YOLO v7 and YOLO v8, the recognition accuracy can exceed 99%, indicating that the YOLO model can correctly identify traffic signs in most scenarios.
Of course, enhancing the recognition accuracy of these deep learning models isn't merely a matter of providing more images for training. Instead, it necessitates a diverse array of training data. The training dataset should encompass sign images captured in various environments, such as daytime, nighttime, rain, and fog. Through diverse data training, the model's generalization ability can be bolstered, rendering it less susceptible to interference from complex road conditions. Additionally, the training data requires augmentation. For example, operations like rotating, cropping, and adjusting the brightness of the original images can enable the model to learn to recognize signs in a wider range of situations.
Detection and Classification: Determining the Sign's Identity
Within the recognition process, detection and classification are two interrelated yet distinct stages. Detection involves framing areas within the image that may contain traffic signs without concerning itself with their specific content. Classification, on the other hand, determines the type of sign the detected area represents after detection.
In the early days of autonomous driving technology, these two steps were processed separately. Feature extraction and region proposal were conducted first, followed by sending the candidate regions to the classifier to determine the category. With the proliferation of deep learning models, these two steps have been integrated into an end-to-end framework. A single model can now accomplish both the detection location and classification result tasks. The advantage of this approach is faster speed and stronger real-time performance, which is suitable for autonomous driving scenarios that demand rapid responses.
During the detection phase of traffic signs, issues like significant variations in sign size, inconsistent angles, and partial occlusions of signs frequently arise, undoubtedly increasing the detection difficulty. To address this challenge, the algorithm employs multi-scale feature extraction technology, enabling the model to capture target information on feature maps with different resolutions, thereby enhancing the detection capability of signs at varying distances.
After detecting the traffic sign, the next step is classification. Classification involves determining the specific type of traffic sign the detected target belongs to, which may encompass dozens or even hundreds of categories. During the learning process of the deep learning network, the features of each type of traffic sign are encoded into patterns within the internal vector space. When the model encounters a new test image, it calculates the matching degree between the image and these patterns and ultimately outputs a probability distribution to inform the system of the most likely category.
Combining Temporal and Contextual Information for More Reliable Judgments
Single-frame image recognition may occasionally lead to misjudgments due to factors like lighting, rain, snow, and vehicle speed. To mitigate this, the autonomous driving system also incorporates temporal and contextual information to enhance recognition stability. Simply put, it doesn't base the category of a traffic sign on a single photo but considers the results of multiple consecutive frames. If the previous few frames recognize the meaning of "speed limit 60" and the current frame yields an unstable result, causing a slight change in the recognition outcome, the system can make a comprehensive judgment based on historical information to avoid making erroneous decisions due to one or two incorrect frames.
Moreover, autonomous vehicles also integrate traffic sign recognition results with high-precision map data. High-precision maps pre-contain information about the locations and types of common traffic signs on the road. When the vehicle recognizes a particular sign, it can cross-reference it with the map data to improve accuracy, especially when the sign is occluded or damaged. Although this approach isn't strictly necessary, it can enhance overall robustness.
How Recognition Results Guide Autonomous Driving Decision-Making
After the autonomous driving system recognizes traffic signs, this information must be translated into usable instructions and transmitted to the decision-making and control modules of autonomous driving. For instance, upon recognizing the "speed limit 50" sign, the control system will adjust the currently set maximum speed to the corresponding value. When encountering the "stop and yield" sign, it will plan for the vehicle to decelerate and halt before the stop line. Upon seeing the "no left turn" sign, it will refrain from selecting a left-turn route when planning the path. The recognition results of traffic signs can directly inform the execution of these rules.
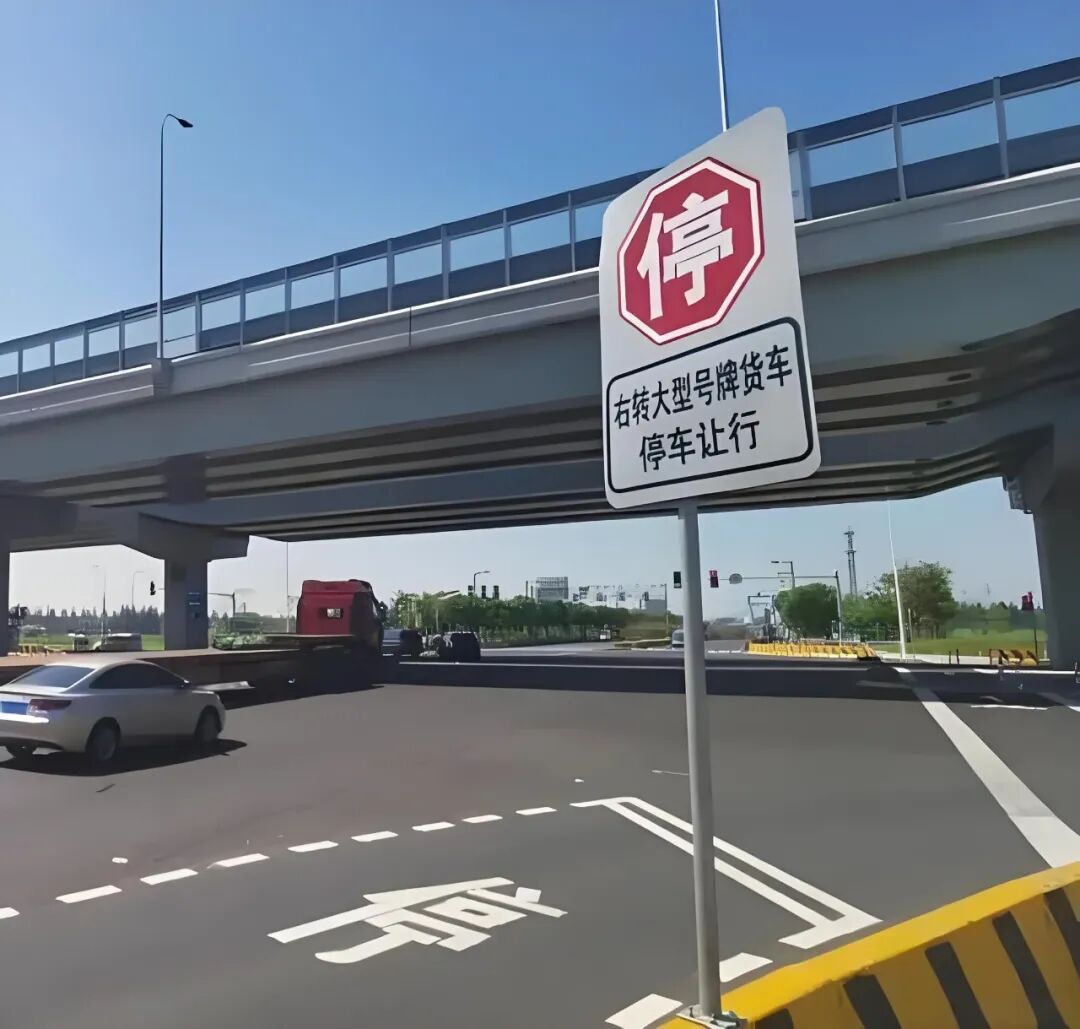

Image source: Internet
Within the entire autonomous driving system, traffic sign recognition constitutes only a portion of perception. It collaborates with other perception information, such as vehicles, pedestrians, curbs, and lane lines, to form a holistic understanding of the surrounding environment. The decision-making module comprehensively integrates the recognized information, formulates the next action in accordance with traffic rules and safety strategies, and then transmits control instructions to the vehicle's actuators. This process enables autonomous vehicles not only to "see" signs but also to drive safely based on this information.
Final Thoughts
The ability of autonomous vehicles to recognize traffic signs stems from their utilization of cameras to collect visual input, followed by preprocessing, deep learning model detection and classification, and the integration of temporal information and map data for comprehensive judgments. The recognition results are then employed to guide the vehicle in adhering to traffic rules. This process encompasses multiple links and sophisticated algorithms. Each step necessitates meticulous design and extensive debugging to maintain sufficient reliability in complex real-world road environments.
-- END --